2020年海南ACCA考试准考证打印时间考前两周
发布时间:2020-08-14
2020年海南ACCA考试准考证打印时间大家知道吗?下面51题库考试学习网就带领大家一起来了解了解海南ACCA考试准考证打印相关内容,感兴趣的小伙伴赶紧来围观吧。
ACCA考试准考证打印步骤:
(1)ACCA考试学员需登陆www.accaglobal.com
(2)点击MYACCA后登入您的学员号和密码进入
(3)点击左侧栏里EXAM ENTRY&RESULTS进入
(4)点击EXAM ATTENDANCE DOCKET生成页面打印即可
请仔细阅读准考证上EXAMINATION REGULATIONS和EXAMINATION
GUIDELINES,务必严格遵守。ACCA考试学员请仔细核对的考试地点,仔细看准考证上的地址,以免走错考场。
考生特别注意:
在考前两周,可以登陆MYACCA里打印准考证(准考证是学员考试必带的证明,请重视;打印准考证数量须和考试科数相同)。因邮寄的准考证收到时间较晚,建议提前打印好准考证,仔细核对报考科目和考试地点有无错误。
考试注意事项:
1.考前必带证件:身份证、准考证。
考试科目必须与准考证一致,考试中心编号必须与准考证一致,不可以在准考证上乱涂乱写。考场中的每一个桌子上都标有编号,必须确认自己的桌子编号与准考证上的编号相同,如果参加了多科考试,必须注意每一科考试的考场桌子编号的变化,如果没有坐在正确编号的桌子上考试,那么答题册将被宣告无效。
2.考试必备文具:黑色圆珠笔、小尺、铅笔、橡皮、计算器(单功能)、手表等(笔试)。
3.请考试学员尽量提前半小时到场(开考后一个小时后不允许进入考场)。
4.进入考场请仔细听考官所讲的考试规则,以免在考试中出现问题。在监考官宣布考试开始前,请勿打开试卷。请确认所发试卷是否正确。每位学员将会收到:试卷、答题本、机读卡、坐标纸(若有画图题),若有任何问题,请举手示意监考官。
5.规定ACCA考试学员进入考场后,必须把通讯设备及所携带的资料、书包等一并放置在监考官指定的位置并按照准考证上标明的考场及座位号就座。请注意不能携带手机到座位上,即使已经关机也不行。
6.考试正式开始前,必须用黑色圆珠笔填写答题册前面的具体信息:
学员ID和名字
桌子编号
考场编号
考试科目编号和版本
在考试结束前,必须在答题册封皮及答题页上方辨明已答题目的题号。
考生必须确认考试中所有答题册中的详细信息都填写完毕,考试结束后都不会再有多余时间填写以上信息。
以上是关于2020年海南ACCA考试准考证打印相关内容,小伙伴们都清楚了吗?如果想要了解更多关于ACCA 的资讯,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Discuss the usefulness of the managerial grid in assessing the attributes of managers. (5 marks)
Part (c):
This all assumes that leadership styles can be categorised into the two dimensions and that the results can be plotted on the grid.
The position of team management is accepted as the best form. of leadership. This may not be practical or indeed advisable. In
many industries, concern for the task may be more important than concern for people, and vice versa. It will always depend on
the individual situation; behaving in a way which is alien to one’s attitudes will be seen as inconsistent and confusing.
However, if the grid has relevance to leadership skills, it can provide the basis for training and for management development. One
way in which it could be useful is (for example) to support a 9,1 leader with a 1,9 subordinate.
The managerial grid also links in to the motivational ideas of Douglas Macgregor. Theory X assumes that the average person has
an inherent dislike of work. The approach is likely to be task driven, and thus managers will have a high score on the x axis.
Theory Y is based on the idea that the goals of the individual and the organisation can be integrated. In this case, the approach
is likely to be concerned with the individual and thus managers will have a high score on the y axis.
3 At a recent international meeting of business leaders, Seamus O’Brien said that multi-jurisdictional attempts to
regulate corporate governance were futile because of differences in national culture. He drew particular attention to
the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and International Corporate Governance
Network (ICGN) codes, saying that they were, ‘silly attempts to harmonise practice’. He said that in some countries,
for example, there were ‘family reasons’ for making the chairman and chief executive the same person. In other
countries, he said, the separation of these roles seemed to work. Another delegate, Alliya Yongvanich, said that the
roles of chief executive and chairman should always be separated because of what she called ‘accountability to
shareholders’.
One delegate, Vincent Viola, said that the right approach was to allow each country to set up its own corporate
governance provisions. He said that it was suitable for some countries to produce and abide by their own ‘very
structured’ corporate governance provisions, but in some other parts of the world, the local culture was to allow what
he called, ‘local interpretation of the rules’. He said that some cultures valued highly structured governance systems
while others do not care as much.
Required:
(a) Explain the roles of the chairman in corporate governance. (5 marks)
(a) Roles of the chairman in corporate governance
The chairman is the leader of the board of directors in a private or public company although other organisations are often run
on similar governance lines. In this role, he or she is responsible for ensuring the board’s effectiveness as a unit, in the service
of the shareholders. This means agreeing and, if necessary, setting the board’s agenda and ensuring that board meetings
take place on a regular basis.
The chairman represents the company to investors and other outside stakeholders/constituents. He or she is often the
‘public face’ of the organisation, especially if the organisation must account for itself in a public manner. Linked to this,
the chairman’s roles include communication with shareholders. This occurs in a statutory sense in the annual report
(where, in many jurisdictions, the chairman must write to shareholders each year in the form. of a chairman’s statement)
and at annual and extraordinary general meetings.
Internally, the chairman ensures that directors receive relevant information in advance of board meetings so that all
discussions and decisions are made by directors fully apprised of the situation under discussion. Finally, his or her role
extends to co-ordinating the contributions of non-executive directors (NEDs) and facilitating good relationships between
executive and non-executive directors.
(ii) the recent financial performance of Merton plc from a shareholder perspective. Clearly identify any
issues that you consider should be brought to the attention of the ordinary shareholders. (15 marks)
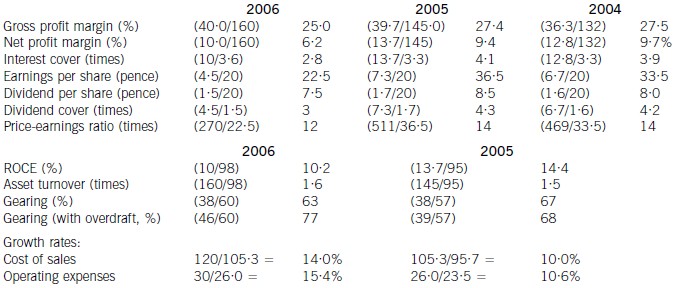
(ii) Discussion of financial performance
It is clear that 2006 has been a difficult year for Merton plc. There are very few areas of interest to shareholders where
anything positive can be found to say.
Profitability
Return on capital employed has declined from 14·4% in 2005, which compared favourably with the sector average of
12%, to 10·2% in 2006. Since asset turnover has improved from 1·5 to 1·6 in the same period, the cause of the decline
is falling profitability. Gross profit margin has fallen each year from 27·5% in 2004 to 25% in 2006, equal to the sector
average, despite an overall increase in turnover during the period of 10% per year. Merton plc has been unable to keep
cost of sales increases (14% in 2006 and 10% in 2005) below the increases in turnover. Net profit margin has declined
over the same period from 9·7% to 6·2%, compared to the sector average of 8%, because of substantial increases in
operating expenses (15·4% in 2006 and 10·6% in 2005). There is a pressing need here for Merton plc to bring cost
of sales and operating costs under control in order to improve profitability.
Gearing and financial risk
Gearing as measured by debt/equity has fallen from 67% (2005) to 63% (2006) because of an increase in
shareholders’ funds through retained profits. Over the same period the overdraft has increased from £1m to £8m and
cash balances have fallen from £16m to £1m. This is a net movement of £22m. If the overdraft is included, gearing
has increased to 77% rather than falling to 63%.
None of these gearing levels compare favourably with the average gearing for the sector of 50%. If we consider the large
increase in the overdraft, financial risk has clearly increased during the period. This is also evidenced by the decline in
interest cover from 4·1 (2005) to 2·8 (2006) as operating profit has fallen and interest paid has increased. In each year
interest cover has been below the sector average of eight and the current level of 2·8 is dangerously low.
Share price
As the return required by equity investors increases with increasing financial risk, continued increases in the overdraft
will exert downward pressure on the company’s share price and further reductions may be expected.
Investor ratios
Earnings per share, dividend per share and dividend cover have all declined from 2005 to 2006. The cut in the dividend
per share from 8·5 pence per share to 7·5 pence per share is especially worrying. Although in its announcement the
company claimed that dividend growth and share price growth was expected, it could have chosen to maintain the
dividend, if it felt that the current poor performance was only temporary. By cutting the dividend it could be signalling
that it expects the poor performance to continue. Shareholders have no guarantee as to the level of future dividends.
This view could be shared by the market, which might explain why the price-earnings ratio has fallen from 14 times to
12 times.
Financing strategy
Merton plc has experienced an increase in fixed assets over the last period of £10m and an increase in stocks and
debtors of £21m. These increases have been financed by a decline in cash (£15m), an increase in the overdraft (£7m)
and an increase in trade credit (£6m). The company is following an aggressive strategy of financing long-term
investment from short-term sources. This is very risky, since if the overdraft needed to be repaid, the company would
have great difficulty in raising the funds required.
A further financing issue relates to redemption of the existing debentures. The 10% debentures are due to be redeemed
in two years’ time and Merton plc will need to find £13m in order to do this. It does not appear that this sum can be
raised internally. While it is possible that refinancing with debt paying a lower rate of interest may be possible, the low
level of interest cover may cause concern to potential providers of debt finance, resulting in a higher rate of interest. The
Finance Director of Merton plc needs to consider the redemption problem now, as thought is currently being given to
raising a substantial amount of new equity finance. This financing choice may not be available again in the near future,
forcing the company to look to debt finance as a way of effecting redemption.
Overtrading
The evidence produced by the financial analysis above is that Merton plc is showing some symptoms of overtrading
(undercapitalisation). The board are suggesting a rights issue as a way of financing an expansion of business, but it is
possible that a rights issue will be needed to deal with the overtrading problem. This is a further financing issue requiring
consideration in addition to the redemption of debentures mentioned earlier.
Conclusion
Ordinary shareholders need to be aware of the following issues.
1. Profitability has fallen over the last year due to poor cost control
2. A substantial increase in the overdraft over the last year has caused gearing to increase
3. It is possible that the share price will continue to fall
4. The dividend cut may warn of continuing poor performance in the future
5. A total of £13m of debentures need redeeming in two year’s time
6. A large amount of new finance is needed for working capital and debenture redemption
Appendix: Analysis of key ratios and financial information
(b) On 31 May 2007, Leigh purchased property, plant and equipment for $4 million. The supplier has agreed to
accept payment for the property, plant and equipment either in cash or in shares. The supplier can either choose
1·5 million shares of the company to be issued in six months time or to receive a cash payment in three months
time equivalent to the market value of 1·3 million shares. It is estimated that the share price will be $3·50 in
three months time and $4 in six months time.
Additionally, at 31 May 2007, one of the directors recently appointed to the board has been granted the right to
choose either 50,000 shares of Leigh or receive a cash payment equal to the current value of 40,000 shares at
the settlement date. This right has been granted because of the performance of the director during the year and
is unconditional at 31 May 2007. The settlement date is 1 July 2008 and the company estimates the fair value
of the share alternative is $2·50 per share at 31 May 2007. The share price of Leigh at 31 May 2007 is $3 per
share, and if the director chooses the share alternative, they must be kept for a period of four years. (9 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
(b) Transactions that allow choice of settlement are accounted for as cash-settled to the extent that the entity has incurred a
liability (IFRS2 para 34). The share based transaction is treated as the issuance of a compound financial instrument. IFRS2
applies similar measurement principles to determine the value of the constituent parts of a compound instrument as that
required by IAS32 ‘Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation’. The purchase of the property, plant and equipment
(PPE) and the grant to the director, both fall under this section of IFRS2 as the supplier and the director have a choice of
settlement. The fair value of the goods can be measured directly as regards the purchase of the PPE and therefore this fact
determines that the transaction is treated in a certain way. In the case of the director, the fair value of the service rendered
will be determined by the fair value of the equity instruments given and IFRS2 says that this type of share based transaction
should be dealt with in a certain way. Under IFRS2, if the fair value of the goods or services received can be measured directly
and easily then the equity element is determined by taking the fair value of the goods or services less the fair value of the
debt element of this instrument. The debt element is essentially the cash payment that will occur. If the fair value of the goods
or services is measured by reference to the fair value of the equity instruments given then the whole of the compound
instrument should be fair valued. The equity element becomes the difference between the fair value of the equity instruments
granted less the fair value of the debt component. It should take into account the fact that the counterparty must forfeit its
right to receive cash in order to receive the equity instrument.
When Leigh received the property, plant and equipment it should have recorded a liability of $4 million and an increase in
equity of $0·55 million being the difference between the value of the property, plant and equipment and the fair value of theliability. The fair value of the liability is the cash payment of $3·50 x 1·3 million shares, i.e. $4·55 million.
The accounting entry would be:

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-09-04
- 2021-01-14
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-06-27
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-12-24
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-05-22
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-09-04
- 2021-01-14
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-01-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-12-24
- 2020-01-09