你知道ACCA考试中的免试政策是什么吗?
发布时间:2020-01-04
ACCA在中国设立的免试政策,主要针对于获得财会证书的在职人士和相关专业的大学生们,但是按照学院的不同类别,有不同情况。可大致分为四大类,具体如下:
一、ACCA对中国教育部认可的全日制大学在读生设置的免试政策
1.会计学或金融学:可以注册为ACCA正式学员,无免试;
2.会计学或金融学:免试3门课程;
3.会计学或金融学:免试5门课程;
4.其他专业:可以注册但无免试。
二、ACCA对中国教育部认可高校毕业生设置的免试政策
1.会计学:免试5门课程;
2.会计学:免试3门课程;
3.金融专业:免试5门课程;
4.法律专业:免试1门课程;
5.商务及管理专业:免试1门课程;
6.非相关专业:无免试。
三、注册会计师考生
1.2009年CICPA“6+1”新制度实行之前获得CICPA全科通过的人员:免试5门课程;
2.2009年CICPA“6+1”新制度实行之后获得CICPA全科通过的人员:免试9们课程;
3.如果在学习ACCA基础阶段科目的过程中获得了CICPA全科合格证,可以自行决定是否申请追加免试。
四、其他
CMA全科通过并取得证书:免试F1-F3;
USCPA全科通过:免试F1-F6、F8、F9;
ACCA免考政策相关注意事项:
获得大学学历的非在校人员,只要年满21周岁即可通过成人途径注册成为ACCA学员,但不能申请任何科目的免考。•学员只有顺利通过整学年的课程才能够申请免试。针对在校生的部分课程免试政策只适用于大学本科的在读学生,而不适用于硕士学位或大专学历的在读学生。获得硕士学位和大专文凭的学生的免试课程只能按所学课程的相关性由ACCA免试评估部门进行逐门评估而定。在中国,会计学学士学位是指会计学士、会计学学士、会计与金融学士或经济学学士。取得与会计学相关领域专业的学位都按“其他专业”对待,例如财务会计、工业会计、外贸会计、会计电算化、铁路会计等。
好了,看了上面的内容,相信大家对ACCA免试政策有了一定的了解。如果还想了解更多信息,欢迎来51题库考试学习网留言。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) (i) Discusses the principles involved in accounting for claims made under the above warranty provision.
(6 marks)
(ii) Shows the accounting treatment for the above warranty provision under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’ for the year ended 31 October 2007. (3 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and communication of advice. (2 marks)
(b) Provisions – IAS37
An entity must recognise a provision under IAS37 if, and only if:
(a) a present obligation (legal or constructive) has arisen as a result of a past event (the obligating event)
(b) it is probable (‘more likely than not’), that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle
the obligation
(c) the amount can be estimated reliably
An obligating event is an event that creates a legal or constructive obligation and, therefore, results in an enterprise having
no realistic alternative but to settle the obligation. A constructive obligation arises if past practice creates a valid expectation
on the part of a third party. If it is more likely than not that no present obligation exists, the enterprise should disclose a
contingent liability, unless the possibility of an outflow of resources is remote.
The amount recognised as a provision should be the best estimate of the expenditure required to settle the present obligation
at the balance sheet date, that is, the amount that an enterprise would rationally pay to settle the obligation at the balance
sheet date or to transfer it to a third party. This means provisions for large populations of events such as warranties, are
measured at a probability weighted expected value. In reaching its best estimate, the entity should take into account the risks
and uncertainties that surround the underlying events.
Expected cash outflows should be discounted to their present values, where the effect of the time value of money is material
using a risk adjusted rate (it should not reflect risks for which future cash flows have been adjusted). If some or all of the
expenditure required to settle a provision is expected to be reimbursed by another party, the reimbursement should be
recognised as a separate asset when, and only when, it is virtually certain that reimbursement will be received if the entity
settles the obligation. The amount recognised should not exceed the amount of the provision. In measuring a provision future
events should be considered. The provision for the warranty claim will be determined by using the expected value method.
The past event which causes the obligation is the initial sale of the product with the warranty given at that time. It would be
appropriate for the company to make a provision for the Year 1 warranty of $280,000 and Year 2 warranty of $350,000,
which represents the best estimate of the obligation (see Appendix 2). Only if the insurance company have validated the
counter claim will Macaljoy be able to recognise the asset and income. Recovery has to be virtually certain. If it is virtually
certain, then Macaljoy may be able to recognise the asset. Generally contingent assets are never recognised, but disclosed
where an inflow of economic benefits is probable.
The company could discount the provision if it was considered that the time value of money was material. The majority of
provisions will reverse in the short term (within two years) and, therefore, the effects of discounting are likely to be immaterial.
In this case, using the risk adjusted rate (IAS37), the provision would be reduced to $269,000 in Year 1 and $323,000 in
Year 2. The company will have to determine whether this is material.
Appendix 1
The accounting for the defined benefit plan is as follows:
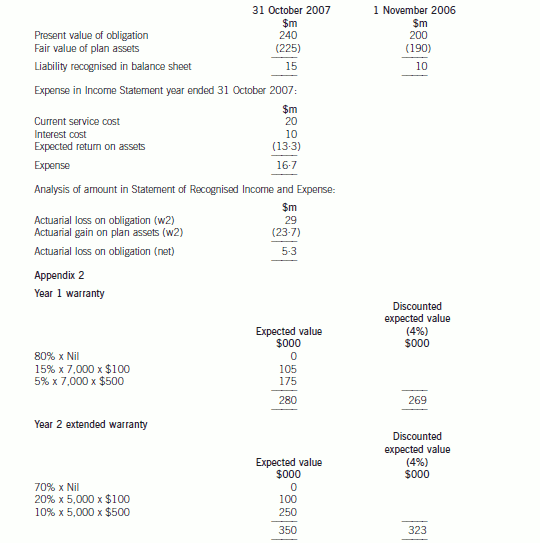

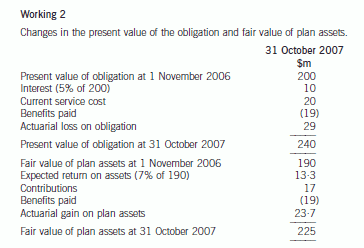
6 Assume today’s date is 16 April 2005.
Henry, aged 48, is the managing director of Happy Home Ltd, an unquoted UK company specialising in interior
design. He is wealthy in his own right and is married to Helen, who is 45 years old. They have two children – Stephen,
who is 19, and Sally who is 17.
As part of his salary, Henry was given 3,000 shares in Happy Home Ltd with an option to acquire a further 10,000
shares. The options were granted on 15 July 2003, shortly after the company started trading, and were not part of
an approved share option scheme. The free shares were given to Henry on the same day.
The exercise price of the share options was set at the then market value of £1·00 per share. The options are not
capable of being exercised after 10 years from the date of grant. The company has been successful, and the current
value of the shares is now £14·00 per share. Another shareholder has offered to buy the shares at their market value,
so Henry exercised his share options on 14 April 2005 and will sell the shares next week, on 20 April 2005.
With the company growing in size, Henry wishes to recruit high quality staff, but the company lacks the funds to pay
them in cash. Henry believes that giving new employees the chance to buy shares in the company would help recruit
staff, as they could share in the growth in value of Happy Home Ltd. Henry has heard that there is a particular share
scheme that is suitable for small, fast growing companies. He would like to obtain further information on how such
a scheme would work.
Henry has accumulated substantial assets over the years. The family house is owned jointly with Helen, and is worth
£650,000. Henry has a £250,000 mortgage on the house. In addition, Henry has liquid assets worth £340,000
and Helen has shares in quoted companies currently worth £125,000. Henry has no forms of insurance, and believes
he should make sure that his wealth and family are protected. He is keen to find out what options he should be
considering.
Required:
(a) (i) State how the gift of the 3,000 shares in Happy Home Ltd was taxed. (1 mark)
(a) (i) Gift of shares
Shares, which are given free or sold at less than market value, are charged to income tax on the difference between the
market value and the amount paid (if any) for the shares. Henry was given 3,000 shares with a market value of £1 at
the time of gift, so he was assessed to income tax on £3,000, in the tax year 2003/04.
(ii) Calculate her income tax (IT) and national insurance (NIC) payable for the year of assessment 2006/07.
(4 marks)
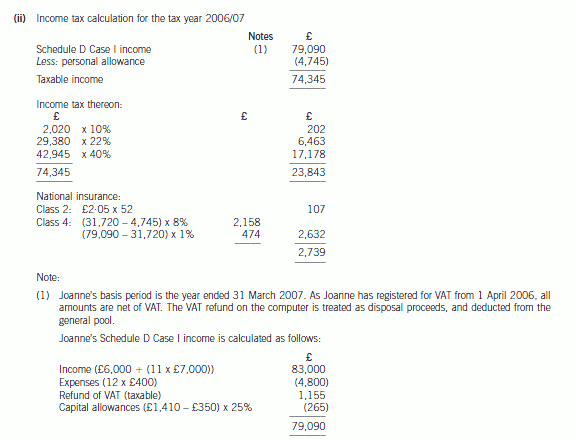
(ii) The property of the former administrative centre of Tyre is owned by the company. Tyre had decided in the year
that the property was surplus to requirements and demolished the building on 10 June 2006. After demolition,
the company will have to carry out remedial environmental work, which is a legal requirement resulting from the
demolition. It was intended that the land would be sold after the remedial work had been carried out. However,
land prices are currently increasing in value and, therefore, the company has decided that it will not sell the land
immediately. Tyres uses the ‘cost model’ in IAS16 ‘Property, plant and equipment’ and has owned the property
for many years. (7 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors of Tyre on how to treat the above items in the financial statements for the year ended
31 May 2006.
(The mark allocation is shown against each of the above items)
(ii) Former administrative building
The land and buildings of the former administrative centre are accounted for as separate elements. The demolition of the
building is an indicator of the impairment of the property under IAS36. The building will not generate any future cash flows
and its recoverable amount is zero. Therefore, the carrying value of the building will be written down to zero and the loss
charged to profit or loss in the year to 31 May 2006 when the decision to demolish the building was made. The land value
will be in excess of its carrying amount as the company uses the cost model and land prices are rising. Thus no impairment
charge is recognised in respect of the land.
The demolition costs will be expensed when incurred and a provision for environmental costs recognised when an obligation
arises, i.e. in the financial year to 31 May 2007. It may be that some of these costs could be recognised as site preparation
costs and be capitalised under IAS16.
The land will not meet the criteria set out in IFRS5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’ as a noncurrent
asset which is held for sale. IFRS5 says that a non-current asset should be classified as ‘held for sale’ if its carrying
amount will be recovered principally through a sale transaction rather than through continuing use. However, the non-current
asset must be available for immediate sale and must be actively marketed at its current fair value (amongst other criteria) and
these criteria have not been met in this case.
When the building has been demolished and the site prepared, the land could be considered to be an investment property
and accounted for under IAS40 ‘Investment Property’ where the fair value model allows gains (or losses) to be recognised inprofit or loss for the period.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-02-01
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-07
- 2020-01-13
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-15
- 2020-05-24
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-28