小伙伴们看过来,ACCA与CPA哪个更好?
发布时间:2020-03-25
ACCA和CPA都是金融财会类热门证书,我们报考哪个更好呢?51题库考试学习网带领大家一起来了解一下。
一、证书介绍
ACCA,中文名称为特许公认会计师,被誉为国际财经领域通行证的国际注册会计师资格。在国际领域上,ACCA可有着十分高的认可度以及含金量,有着国际财会界通行证的美誉。
CPA是国内唯一具有签字权的最高级的注册会计师资格,是国内热度非常火热的考试,而且其证书含金量也非常高,对于持有CPA证书并注册成为注册会计师协会执业会员的人士,还具备唯一签字权的资质。
二、考试内容
关于两者的考试内容,ACCA考试所涉及到的科目课程内容相比起CPA来说会比较多。ACCA考试涉及的一共有15门的课程,主要分为了3个阶段,基础课程,技能课程,战略核心课程及选修课。CPA考试,主要分为了专业阶段考试和综合阶段考试两个部分,其中,专业阶段考试科目:《会计》、《审计》、《财务成本管理》、《经济法》、《税法》、《战略与风险管理》。综合阶段考试科目:职业能力综合测试。
三、就业方向
ACCA方面,对于持有ACCA证书的会员,除了会计师事务所外,还可以选择从事一些事业单位中的财务、相关金融机构、税务等工作。相对于CPA来说,ACCA就业的范围会更广一些,除了国内,通过ACCA考试的学员也可以选择到国外担任相关企业的财务人员,要知道,取得ACCA证书的人士,在全球范围都获得企业的一致认可。CPA方面,会计师事务所是大家热门的首选,其次像政府机关、大中型企业都是CPA持证人士可以选择担任的工作职务。
从证书、考试内容、就业方向三点给大家做了个介绍,那么,我们选哪个更好呢?关于这个问题,各位还是按照自己的实际情况和需求作出选择,ACCA和CPA都是含金量比较高的会计证书,ACCA对比CPA来说会比较偏向于国际化领域,对于想在一些跨国企业、外企、合资企业工作的人士,不妨可以考虑报考ACCA。另外,CPA相较于ACCA,报考的门槛较高,一般只有本科以上的毕业生才可以报考CPA。如果你并不是本科学历,或者刚刚就读大学,那么,ACCA就是你唯一可以选择的证书了。
好了,以上就是51题库考试学习网介绍的内容,如果还想了解更多信息,欢迎来51题库考试学习网留言咨询。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
14 Alpha buys goods from Beta. At 30 June 2005 Beta’s account in Alpha’s records showed $5,700 owing to Beta.
Beta submitted a statement to Alpha as at the same date showing a balance due of $5,200.
Which of the following could account fully for the difference?
A Alpha has sent a cheque to Beta for $500 which has not yet been received by Beta.
B The credit side of Beta’s account in Alpha’s records has been undercast by $500.
C An invoice for $250 from Beta has been treated in Alpha’s records as if it had been a credit note.
D Beta has issued a credit note for $500 to Alpha which Alpha has not yet received.
(d) Evaluate the circumstances in which a government can act as an aid to business performance. (5 marks)
(d) Governments may act as an aid to business performance in the following ways:
– A government can increase aggregate demand for goods and services by increased government spending and/or by
reducing taxation so that firms (and individuals) have more after tax income available to spend.
– Government policy may encourage firms to locate to particular areas. This is particularly the case where there is high
unemployment in such areas.
– Government policy via the use of quotas and import tariffs might make it more difficult for overseas firms to compete in
domestic markets.
– A government can regulate monopolies in particular with regard to the prices they charge and the quality of their goods
and services.
– Government policy can regulate the activities of those firms which do not act in the best interests of the environment.
(Alternative relevant discussion would be acceptable)
4 Graham Smith is Operations Director of Catering Food Services (CFS) a £1·5 billion UK based distributor of foods to
professional catering organisations. It has 30 trading units spread across the country from which it can supply a
complete range of fresh, chilled and frozen food products. Its customers range from major fast food chains, catering
services for the armed forces down to individual restaurants and cafes. Wholesale food distribution is very much a
price driven service, in which it is very difficult to differentiate CFS’s service from its competitors.
Graham is very aware of the Government’s growing interest in promoting good corporate environmental practices and
encouraging companies to achieve the international quality standard for environmentally responsible operations. CFS
operates a fleet of 1,000 lorries and each lorry produces the equivalent of its own weight in pollutants over the course
of a year without the installation of expensive pollution control systems. Graham is also aware that his larger
customers are looking to their distributors to become more environmentally responsible and the ‘greening’ of their
supply chain is becoming a real issue. Unfortunately his concern with developing a company-wide environmental
management strategy is not shared by his fellow managers responsible for the key distribution functions including
purchasing, logistics, warehousing and transportation. They argued that time spent on corporate responsibility issues
was time wasted and simply added to costs.
Graham has decided to propose the appointment of a project manager to develop and implement a company
environmental strategy including the achievement of the international quality standard. The person appointed must
have the necessary project management skills to see the project through to successful conclusion.
You have been appointed project manager for CFS’s ‘environmentally aware’ project.
Required:
(a) What are the key project management skills that are necessary in achieving company-wide commitment in
CFS to achieve the desired environmental strategy? (15 marks)
(a) Simply defined, a project is ‘activity that has a start, a middle and an end and consumes resources’ – it is therefore a discrete
activity aimed at achieving a specific objective or range of objectives. Graham is intent on using the ‘environmentally aware’
project to achieve a specific objective – the attainment of the international environmental standard. He is, however, aware
that there are a number of internal stakeholders inside the company who question the significance of such a project.
Externally, he can point to significant stakeholders, including customers and government who are looking for CFS to become
more environmentally aware. The project is likely to have strategic and not simply operational or administrative significance
and the person appointed into the role of project manager, ideally, should have both the traditional skills associated with
project management plus those of strategic management. Grundy and Brown list the traditional project management
techniques as:

Clearly, the project manager must have the technical project management skills, being able to manage the project through its
life cycle, which involves defining the project in terms of project objectives and scope as defined by time, cost and quality.
Planning the project in terms of breaking the overall project down into separate activities, estimating the resources required
and linking activities to resources in terms of time and priorities. Implementing the plan, including reviewing the progress in
meeting time and cost objectives and taking corrective action where and when necessary. Finally, reviewing the outcomes of
the project in terms of what was delivered to the customer and the extent to which client expectations were met.
The strategic nature of the project means that the project manager must have significant leadership skills, not only of the
project team, who are likely to come from different functions and parts of the company, but also influential stakeholders inside
and outside the company. This implies they should have good ‘political’ and communication skills as the project is of strategic
significance to the company. The ability to show how this particular project fits with the overall strategy of the firm is
important. The project is an important part in the achievement of the company strategy and in CFS’s case may help it
differentiate itself from its competitors. However, the project manager must recognise that there will be resistance from existing
managers reluctant to see resources committed to projects outside of the traditional value chain of the company. Certainly,
the project manager for the ‘environmentally aware’ project will themselves need to be aware of the external environmental
pressures prompting the firm to set itself specific environmental objectives and be able to link into supportive networks and
alliances. Finally, Grundy and Brown argue that the project manager will be the key to reviewing and learning from the project,
assessing whether defined objectives were achieved, the effectiveness or otherwise of the implementation process and how
key stakeholders were managed. The danger is that projects are seen as ‘one-off’ rather than contributing to the knowledge
and learning of the organisation. There may be a significant ‘learning curve’ that the firm has to go down and look tocontinuously improve its project management process.
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
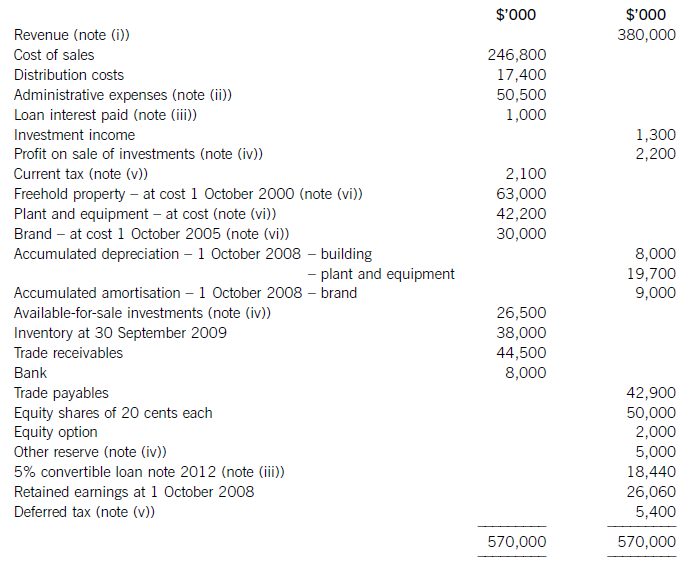
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-09
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-03-31
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-21
- 2020-02-12