ACCA考试难度大揭秘
发布时间:2022-02-06
ACCA考试的难度是以英国大学学位考试的难度为准,考试主要分为三个部分:主要是F阶段以及P阶段和核心科目SBL以及SBR的难度划分,每个部分的难度不同,下面就带大家一起来看看吧。
第一部分(AB-FA)、每门考试只是测试本门课程所包含的知识,着重于为后两个部分中实务性的课程所要运用的理论和技能打下基础。第二部分(LW-FM)的难度分别相当于学士学位高年级课程的考试,考试除了本门课程的内容之外,还会考到第一部分的一些知识,着重培养考生的分析能力,第三部分p阶段的考试相当于硕士学位最后阶段的考试,考试要求考生综合运用学到的知识、技能和决断力。不仅会考到以前的课程内容,还会考到其他相关科目的内容。
ACCA考试难度:F阶段
F阶段主要包括:F1 会计师与企业 Accountant in Business (AB) 、F2 管理会计 Management Accounting (MA) 、F3 财务会计 Financial Accounting (FA) 、F4 公司法与商法 Corporate and Business Law (CL) 、F5 业绩管理 Performance Management (PM) 、F6 税务 Taxation (TX) 、F7 财务报告 Financial Reporting (FR) 、F8 审计与认证业务 Audit and Assurance (AA) F9 财务管理 Financial Management (FM) ,如果你取得会计专业学士学位,是可以免试F1-F5的,CICPA全科通过可以免试F1-F4以及F6。所以你一共可以免试F1-F6前六门。
ACCA考试难度:P阶段
P1 专业会计师 Professional Accountant (PA) 、P2 公司报告 Corporate Reporting (CR) 、P3 商务分析 Business Analysis (BA) 、P4 高级财务管理 Advanced Financial Management (AFM) 、P5 高级业绩管理 Advanced Performance Management (APM) 、P6 高级税务 Advanced Taxation (ATX) 、P7 高级审计与认证业务 Advanced Audit and Assurance (AAA),P阶段的课程更深入更专业而且很多都要靠自己去分析领悟,根据实际情况具体分析,要有非常专业的判断分析能力,所以在考P阶段的课程时你得多花点时间,ACCA从F4开始的考试都是全主观题,根据答的要点得分,很多都是要靠自己分析理解得出。
ACCA考试难度:SBR&SBL
acca sbL和abr这两门是有一定难度的,比F阶段的科目难度都上了一个台阶,需要大家更加用心耐心的去对待。
以上就是今天51题库考试学习网为大家带来的ACCA考试相关的内容。相信大家只要用心备考,一直坚持下去,都能够取得一个好的成绩!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
2 Graeme, aged 57, is married to Catherine, aged 58. They work as medical consultants, and both are higher rate
taxpayers. Barry, their son, is aged 32. Graeme, Catherine and Barry are all UK resident, ordinarily resident and
domiciled. Graeme has come to you for some tax advice.
Graeme has invested in shares for some time, in particular shares in Thistle Dubh Limited. He informs you of the
following transactions in Thistle Dubh Limited shares:
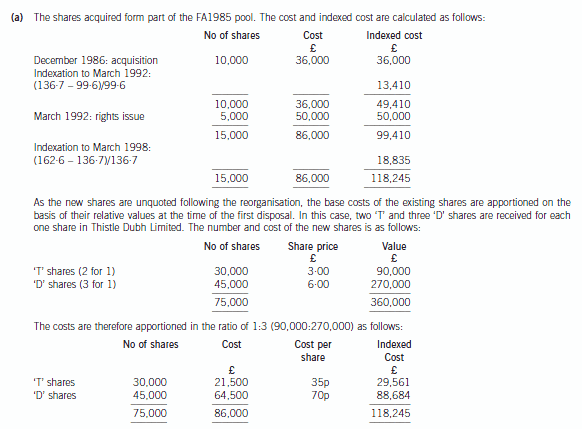
(i) In December 1986, on the death of his grandmother, he inherited 10,000 £1 ordinary shares in Thistle Dubh
Limited, an unquoted UK trading company providing food supplies for sporting events. The probate value of the
shares was 360p per share.
(ii) In March 1992, he took up a rights issue, buying one share for every two held. The price paid for the rights
shares was £10 per share.
(iii) In October 1999, the company underwent a reorganisation, and the ordinary shares were split into two new
classes of ordinary share – ‘T’ shares and ‘D’ shares, each with differing rights. Graeme received two ‘T’ and three
‘D’ shares for each original Thistle Dubh Limited share held. The market values for the ‘T’ shares and the ‘D’
shares on the date of reorganisation were 135p and 405p per share respectively.
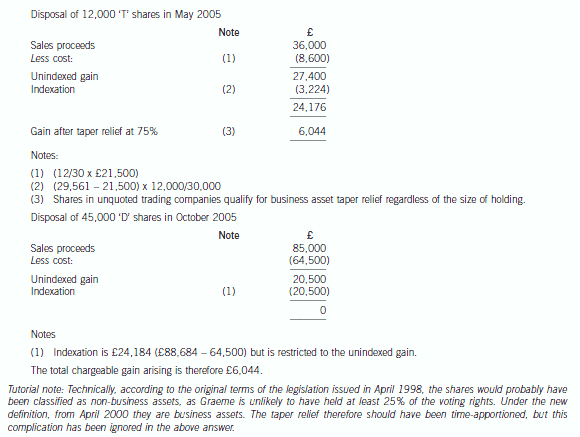
(iv) On 1 May 2005, Graeme sold 12,000 ‘T’ shares. The market values for the ‘T’ shares and the ‘D’ shares on that
day were 300p and 600p per share respectively.
(v) In October 2005, Graeme sold all of his ‘D’ shares for £85,000.
(vi) The current market value of ‘T’ shares is 384p per share. The shares remain unquoted.
Graeme and Catherine have owned a holiday cottage in a remote part of the UK for many years. In recent years, they
have used the property infrequently, as they have taken their holidays abroad and the cottage has been let out as
furnished holiday accommodation.
Graeme and Catherine are now considering selling the UK country cottage and purchasing a holiday villa abroad.
Initially they plan to let this villa out on a furnished basis, but following their anticipated retirement, would expect to
occupy the property for a significant part of the year themselves, possibly moving to live in the villa permanently.
Required:
(a) Calculate the total chargeable gains arising on Graeme’s disposals of ‘T’ and ‘D’ ordinary shares in May and
October 2005 respectively. (7 marks)
(b) Calculate the amount of input tax that will be recovered by Vostok Ltd in respect of the new premises in the
year ending 31 March 2009 and explain, using illustrative calculations, how any additional recoverable input
tax will be calculated in future years. (5 marks)
(b) Recoverable input tax in respect of new premises
Vostok Ltd will recover £47,880 (£446,500 x 7/47 x 72%) in the year ending 31 March 2009.
The capital goods scheme will apply to the purchase of the building because it is to cost more than £250,000. Under the
scheme, the total amount of input tax recovered reflects the use of the building over the period of ownership, up to a maximum
of ten years, rather than merely the year of purchase.
Further input tax will be recovered in future years as the percentage of exempt supplies falls. (If the percentage of exempt
supplies were to rise, Vostok Ltd would have to repay input tax to HMRC.)
The additional recoverable input tax will be computed by reference to the percentage of taxable supplies in each year including
the year of sale. For example, if the percentage of taxable supplies in a particular subsequent year were to be 80%, the
additional recoverable input tax would be computed as follows.
£446,500 x 7/47 x 1/10 x (80% – 72%) = £532.
Further input tax will be recovered in the year of sale as if Vostok Ltd’s supplies in the remaining years of the ten-year period
are fully vatable. For example, if the building is sold in year seven, the additional recoverable amount for the remaining three
years will be calculated as follows.
£446,500 x 7/47 x 1/10 x (100% – 72%) x 3 = £5,586.
4 (a) The purpose of ISA 250 Consideration of Laws and Regulations in an Audit of Financial Statements is to
establish standards and provide guidance on the auditor’s responsibility to consider laws and regulations in an
audit of financial statements.
Explain the auditor’s responsibilities for reporting non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention
during the conduct of an audit. (5 marks)
4 CLEEVES CO
(a) Reporting non-compliance
Non-compliance refers to acts of omission or commission by the entity being audited, either intentional or unintentional, that
are contrary to the prevailing laws or regulations.
To management
Regarding non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention the auditor should, as soon as practicable, either:
■ communicate with those charged with governance; or
■ obtain audit evidence that they are appropriately informed.
However, the auditor need not do so for matters that are clearly inconsequential or trivial and may reach agreement1 in
advance on the nature of such matters to be communicated.
If in the auditor’s judgment the non-compliance is believed to be intentional and material, the auditor should communicate
the finding without delay.
If the auditor suspects that members of senior management are involved in non-compliance, the auditor should report the
matter to the next higher level of authority at the entity, if it exists (e.g. an audit committee or a supervisory board). Where
no higher authority exists, or if the auditor believes that the report may not be acted upon or is unsure as to the person to
whom to report, the auditor would consider seeking legal advice.
To the users of the auditor’s report on the financial statements
If the auditor concludes that the non-compliance has a material effect on the financial statements, and has not been properly
reflected in the financial statements, the auditor expresses a qualified (i.e. ‘except for disagreement’) or an adverse opinion.
If the auditor is precluded by the entity from obtaining sufficient appropriate audit evidence to evaluate whether or not noncompliance
that may be material to the financial statements has (or is likely to have) occurred, the auditor should express a
qualified opinion or a disclaimer of opinion on the financial statements on the basis of a limitation on the scope of the audit.
Tutorial note: For example, if management denies the auditor access to information from which he would be able to assess
whether or not illegal dumping had taken place (and, if so, the extent of it).
If the auditor is unable to determine whether non-compliance has occurred because of limitations imposed by circumstances
rather than by the entity, the auditor should consider the effect on the auditor’s report.
Tutorial note: For example, if new legal requirements have been announced as effective but the detailed regulations are not
yet published.
To regulatory and enforcement authorities
The auditor’s duty of confidentiality ordinarily precludes reporting non-compliance to a third party. However, in certain
circumstances, that duty of confidentiality is overridden by statute, law or by courts of law (e.g. in some countries the auditor
is required to report non-compliance by financial institutions to the supervisory authorities). The auditor may need to seek
legal advice in such circumstances, giving due consideration to the auditor’s responsibility to the public interest.
Assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2004 apply throughout.
(b) Explain the corporation tax (CT) and value added tax (VAT) issues that Irroy should be aware of, if she
proceeds with her proposal for the Irish subsidiary, Green Limited. Your answer should clearly identify those
factors which will determine whether or not Green Limited is considered UK resident or Irish resident and
the tax implications of each alternative situation.
You need not repeat points that are common to each situation. (16 marks)
(b) There are several matters that Irroy will need to be aware of in relation to value added tax and corporation tax. These are set
out below.
Residence of subsidiary
Irroy will want to ensure that the subsidiary is treated as being resident in the Republic of Ireland. It will then pay corporation
tax on its profits at lower rates than in the UK. The country of incorporation usually claims taxing rights, but this is not by
itself sufficient. Irroy needs to be aware that a company can be treated as UK resident by virtue of the location of its central
management and control. This is usually defined as being where the board of directors meets to make strategic decisions. As
a result, Irroy needs to ensure that board meetings are conducted outside the UK.
If Green Limited is treated as being UK resident, it will be taxed in the UK on its worldwide income, including that arising in
the Republic of Ireland. However, as it will be conducting trading activities in the Republic of Ireland, Green Limited will also
be treated as being Irish resident as its activities in that country are likely to constitute a permanent establishment. Thus it
may also suffer tax in the Republic of Ireland as a consequence, although double tax relief will be available (see later).
A permanent establishment is broadly defined as a fixed place of business through which a business is wholly or partly carried
on. Examples of a permanent establishment include an office, factory or workshop, although certain activities (such as storage
or ancillary activities) can be excluded from the definition.
If Green Limited is treated as being an Irish resident company, any dividends paid to Aqua Limited will be taxed under
Schedule D Case V in the UK. Despite being non resident, Green Limited will still count as an associate of the existing UK
companies, and may affect the rates of tax paid by Aqua Limited and Aria Limited in the UK. However, as a non UK resident
company, Green Limited will not be able to claim losses from the UK companies by way of group relief.
Double tax relief
If Green Limited is treated as UK resident, corporation tax at UK rates will be payable on all profits earned. However, income
arising in the Republic of Ireland is likely to have been taxed in that country also by virtue of having a permanent
establishment located there. As the same profits have been taxed twice, double tax relief is available, either by reference to
the tax treaty between the UK and the Republic of Ireland, or on a unilateral basis, where the UK will give relief for the foreign
tax suffered.
If Green Limited is treated as an Irish resident company, it will pay tax in the Republic of Ireland, based on its worldwide
taxable profits. However, any repatriation of profits to the UK by dividend will be taxed on a receipts basis in the UK. Again,
double tax relief will be available as set out above.
Double tax relief is available against two types of tax. For payments made by Green Limited to Aqua Limited on which
withholding tax has been levied, credit will be given for the tax withheld. In addition, relief is available for the underlying tax
where a dividend is received from a foreign company in which Aqua Limited owns at least 10% of the voting power. The
underlying tax is the tax attributable to the relevant profits from which the dividend was paid.
Double tax relief is given at the lower rate of the UK tax and the foreign tax (withholding and underlying taxes) suffered.
Transfer pricing
Where groups have subsidiaries in other countries, they may be tempted to divert profits to subsidiaries which pay tax at lower
rates. This can be achieved by artificially changing the prices charged (known as the transfer price) between the group
companies. While they can do this commercially through common control, anti avoidance legislation seeks to correct this by
ensuring that for taxation purposes, profits on such intra-group transactions are calculated as if the transactions were carried
out on an arms length basis. Since 1 April 2004, this legislation can also be applied to transactions between UK group
companies.
If Green Limited is treated as a UK resident company, the group’s status as a small or medium sized enterprise means that
transfer pricing issues will not apply to transactions between Green Limited and the other UK group companies.
If Green Limited is an Irish resident company, transfer pricing issues will not apply to transactions between Green Ltd and the
UK resident companies because of the group’s status as a small or medium-sized enterprise and the existence of a double
tax treaty, based on the OECD model, between the UK and the Republic of Ireland.
Controlled foreign companies
Tax legislation exists to stop a UK company accumulating profits in a foreign subsidiary which is subject to a low tax rate.
Such a subsidiary is referred to as a controlled foreign company (CFC), and exists where:
(1) the company is resident outside the UK, and
(2) is controlled by a UK resident entity or persons, and
(3) pays a ‘lower level of tax’ in its country of residence.
A lower level of tax is taken to be less than 75% of the tax that would have been payable had the company been UK resident.
If Green Limited is an Irish resident company, it will be paying corporation tax at 12·5% so would appear to be caught by
the above rules and is therefore likely to be treated as a CFC.
Where a company is treated as a CFC, its profits are apportioned to UK resident companies entitled to at least 25% of its
profits. For Aqua Limited, which would own 100% of the shares in Green Limited, any profits made by Green Limited would
be apportioned to Aqua Limited as a deemed distribution. Aqua Limited would be required to self-assess this apportionment
on its tax return and pay UK tax on the deemed distribution (with credit being given for the Irish tax suffered).
There are some exemptions which if applicable the CFC legislation does not apply and no apportionments of profits will be
made. These include where chargeable profits of the CFC do not exceed £50,000 in an accounting period, or where the CFC
follows an acceptable distribution policy (distributing at least 90% of its chargeable profits within 18 months of the relevant
period).
Value added tax (VAT)
Green Limited will be making taxable supplies in the Republic of Ireland and thus (subject to exceeding the Irish registration
limit) liable to register for VAT there. If Green Limited is registered for VAT in the Republic of Ireland, then supplies of goods
made from the UK will be zero rated. VAT on the goods will be levied in the Republic of Ireland at a rate of 21%. Aqua Limited
will need to have proof of supply in order to apply the zero rate, and will have to issue an invoice showing Green Limited’s
Irish VAT registration number as well as its own. In the absence of such evidence/registration, Aqua Limited will have to treat
its transactions with Green Limited as domestic sales and levy VAT at the UK standard rate of 17·5%.
In addition to making its normal VAT returns, Aqua Limited will also be required to complete an EU Sales List (ESL) statement
each quarter. This provides details of the sales made to customers in the return period – in this case, Green Limited. Penalties
can be applied for inaccuracies or non-compliance.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-04
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-05
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-18
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-06
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-01-10