ACCA考试F3考试模拟试题(2020-08-13)
发布时间:2020-08-13
备考2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴赶紧来围观,51题库考试学习网为大家准备了ACCA考试F3考试模拟试题,以供小伙伴们备考练习。
1.You are given the following information:
Receivables at 1 January
20X3
$10,000
Receivables at 31 December
20X3
$9,000
Total receipts during 20X3 (including cash
sales of $5 ,000) $85,000
What are sales on credit during 20X3?
A $81 ,000
B $86,000
C $79,000
D $84,000
答案:C
2. A business
sells $100 worth of goods to a customer, the customer pays $50 in cash
immediately and will pay the remaining $50 in 30 days\' time.
What is the double entry to record the
purchase in the customer\'s accounting records?
A Debit cash $50, credit payables $50,
credit purchases $50
B Debit payables $50, debit cash $50,
credit purchases $100
C Debit purchases $100, credit payables
$50, credit cash $50
D Debit purchases $100, credit cash $100
答案:C
3. Mew Ling has
the following transactions:
1 Receipt of cash from R Singh in respect
of an invoice for goods sold three weeks ago
2 Receipt of cash from S Kalu for cash
sales
What are the ledger entries required to
record the above transactions?
A Dr Cash
Cr Sales
B Dr Cash
Cr Sales
Cr Trade Receivables
C Dr Sales
Cr Cash
D Dr Trade Receivables
Dr Sales
Cr Cash
答案:B
4. How is the
total of the sales day book recorded in the nominal ledger?
Debit
Credit
A
Receivables
Receivables
Ledger
Control Account
B Receivables
Receivables
Control
Account
Ledger
C
Sales Receivables
Control Account
D
Receivables
Sales
Control Account
答案:D
5. Are the
following statements about debit entries true or false?
1 A debit entry in the cash book will
increase an overdraft in the accounts.
2 A debit entry in the cash book will
increase a bank balance in the accounts.
A Both true
B Both false
C 1 true and 2 false
D 1 false and 2 true
答案:D
以上是本次51题库考试学习网分享给大家的ACCA考试试题,备考的小伙伴抓紧时间练习一下吧。欲了解更多关于ACCA考试的试题,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
A new internal auditor, Daisy Rosepetal, has recently joined Bluebell Co. She has been asked by management to
establish and to monitor a variety of social and environmental Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Daisy has no
experience in this area, and has asked you for some advice. It has been agreed with Bluebell Co’s audit committee
that you are to provide guidance to Daisy to help her in this part of her role, and that this does not impair the
objectivity of the audit.
(c) Recommend EIGHT KPIs which could be used to monitor Bluebell Co’s social and environmental
performance, and outline the nature of evidence that should be available to provide assurance on the
accuracy of the KPIs recommended. Your answer should be in the form. of briefing notes to be used at a
meeting with Daisy Rosepetal. (10 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks.


2 Which of the following are correct?
1. The balance sheet value of inventory should be as close as possible to net realisable value.
2. The valuation of finished goods inventory must include production overheads.
3. Production overheads included in valuing inventory should be calculated by reference to the company’s normal
level of production during the period.
4. In assessing net realisable value, inventory items must be considered separately, or in groups of similar items,
not by taking the inventory value as a whole.
A 1 and 2 only
B 3 and 4 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2, 3 and 4
Explain the grounds upon which a person may be disqualified under the Company Directors Disqualification Act 1986.(10 marks)
The Company Directors Disqualification Act (CDDA) 1986 was introduced to control individuals who persistently abused the various privileges that accompany incorporation, most particularly the privilege of limited liability. The Act applies to more than just directors and the court may make an order preventing any person (without leave of the court) from being:
(i) a director of a company;
(ii) a liquidator or administrator of a company;
(iii) a receiver or manager of a company’s property; or
(iv) in any way, whether directly or indirectly, concerned with or taking part in the promotion, formation or management of a company.
The CDDA 1986 identifies three distinct categories of conduct, which may, and in some circumstances must, lead the court to disqualify certain persons from being involved in the management of companies.
(a) General misconduct in connection with companies
This first category involves the following:
(i) A conviction for an indictable offence in connection with the promotion, formation, management or liquidation of a company or with the receivership or management of a company’s property (s.2 of the CDDA 1986). The maximum period for disqualification under s.2 is five years where the order is made by a court of summary jurisdiction, and 15 years in any other case.
(ii) Persistent breaches of companies legislation in relation to provisions which require any return, account or other document to be filed with, or notice of any matter to be given to, the registrar (s.3 of the CDDA 1986). Section 3 provides that a person is conclusively proved to be persistently in default where it is shown that, in the five years ending with the date of the application, he has been adjudged guilty of three or more defaults (s.3(2) of the CDDA 1986). This is without prejudice to proof of persistent default in any other manner. The maximum period of disqualification under this section is five years.
(iii) Fraud in connection with winding up (s.4 of the CDDA 1986). A court may make a disqualification order if, in the course of the winding up of a company, it appears that a person:
(1) has been guilty of an offence for which he is liable under s.993 of the CA 2006, that is, that he has knowingly been a party to the carrying on of the business of the company either with the intention of defrauding the company’s creditors or any other person or for any other fraudulent purpose; or
(2) has otherwise been guilty, while an officer or liquidator of the company or receiver or manager of the property of the company, of any fraud in relation to the company or of any breach of his duty as such officer, liquidator, receiver or manager (s.4(1)(b) of the CDDA 1986).
The maximum period of disqualification under this category is 15 years.(b) Disqualification for unfitness
The second category covers:
(i) disqualification of directors of companies which have become insolvent, who are found by the court to be unfit to be directors (s.6 of the CDDA 1986). Under s. 6, the minimum period of disqualification is two years, up to a maximum of 15 years;
(ii) disqualification after investigation of a company under Pt XIV of the CA 1985 (it should be noted that this part of the previous Act still sets out the procedures for company investigations) (s.8 of the CDDA 1986). Once again, the maximum period of disqualification is 15 years.
Schedule 1 to the CDDA 1986 sets out certain particulars to which the court is to have regard in deciding whether a person’s conduct as a director makes them unfit to be concerned in the management of a company. In addition, the courts have given indications as to what sort of behaviour will render a person liable to be considered unfit to act as a company director. Thus, in Re Lo-Line Electric Motors Ltd (1988), it was stated that:
‘Ordinary commercial misjudgment is in itself not sufficient to justify disqualification. In the normal case, the conduct complained of must display a lack of commercial probity, although . . . in an extreme case of gross negligence or total incompetence, disqualification could be appropriate.’
(c) Other cases for disqualification
This third category relates to:
(i) participation in fraudulent or wrongful trading under s.213 of the Insolvency Act (IA)1986 (s.10 of the CDDA 1986);
(ii) undischarged bankrupts acting as directors (s.11 of the CDDA 1986); and
(iii) failure to pay under a county court administration order (s.12 of the CDDA 1986).
For the purposes of most of the CDDA 1986, the court has discretion to make a disqualification order. Where, however, a person has been found to be an unfit director of an insolvent company, the court has a duty to make a disqualification order (s.6 of the CDDA 1986). Anyone who acts in contravention of a disqualification order is liable:
(i) to imprisonment for up to two years and/or a fine, on conviction on indictment; or
(ii) to imprisonment for up to six months and/or a fine not exceeding the statutory maximum, on conviction summarily (s.13 of the CDDA 1986).
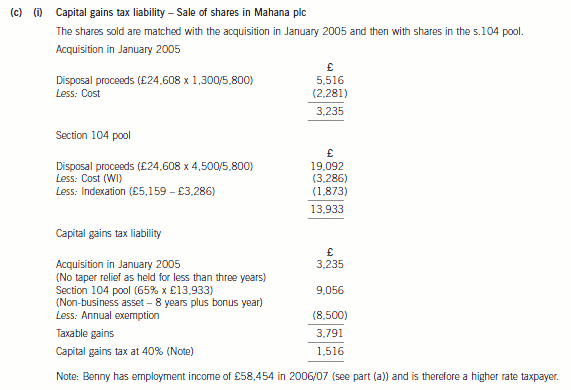
(c) (i) Calculate Benny’s capital gains tax liability for 2006/07. (6 marks)
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-08-13
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-08-13
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-05
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08