从2019年ACCA大纲来看,2020年考试教材可能会变动多少?
发布时间:2020-03-11
目前,2020年的ACCA考试教材尚未发布。但是一些准备参加上半年ACCA考试的小伙伴,已经在查询教材相关的信息了。比如,2020年ACCA教材内容可能会变动多少。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来ACCA考试教材的相关信息,以供参考。
通常而言,每年的ACCA教材一般7,8月份出。目前,2020年ACCA教材尚未发布。不过,根据历年情况,在大纲不换的情况下,每年的教材内容变化不大,所以2020年教材与去年变化不大。虽然考试教材基本不变,但是ACCA考试教材的配套练习册是半年换一次,2,3月和7,8月,与考试同步。配套练习册每次的变化就是加入上一次考试的试题,并且删除一些以前的试题,总的收录试题数差不多。因此,2020年ACCA教材配套练习册的内容也不会出现明显的增减。虽然ACCA教材内容变动比较少,但是这些变动往往都集中在几个科目中。
首先,教材中法律类的基本上不变的,比如F4,即使用2、3年前的教材问题都不大。不过F6的税率每年会变化(只要用最新税率去计算即可)。这就需要小伙伴们关注每年的税率变化情况。审计类,管理会计类,绩效管理类,管理学类以及财务管理类基本上每年内容是不会变化的,比如F1,F2,F5,F8,F9,P1,P4,P5等,学员在备考这些科目时都能使用以前的教材。另外,ACCA学员在购买教材时需要特别关注的应该就是会计类了,F3,F7和P2,如果准则变了,相应的会计处理也会变化,因此小伙伴们在备考这几科时尽量买新版教材。这几科也是ACCA考试教材中内容容易发生变化的科目。
值得注意的是,2019年ACCA考试教材发生了重大变化,ACCA官方在 2018年就把P1和P3取消了,改为一个新科目SBL,P2改为一个新科目SBR。那么对应的教材练习册都会发生相应的变化。也就是说,2020年的教材基本不会发生变化,但是教材练习册是会发生变化的。
以上就是关于ACCA考试教材的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:目前距离2020年第二考试季的ACCA考试所剩时间不多,小伙伴们要注意安排复习哦。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) How might the marketing mix vary between the three channels Helen is considering using? (8 marks)
(b) The analysis of each of the market entry strategies has begun the process of identifying how the marketing mix of product,
price, place and promotion will vary significantly between the three outlets.
Product – here the nature of the product in terms of recipes and product range can be varied reasonably easily to meet the
demands of the outlet.
Price – again this will vary in significance between the three outlets with the greatest pressure coming from the supermarkets
and catering wholesalers. Margins may come under pressure with the supermarkets looking for a contribution to sales
promotions.
Promotion – here the issue of brand development is a crucial factor. Using her own brand, Helen can develop the product
range and extend the outlets she sells through.

(ii) Explain the organisational factors that determine the need for internal audit in public listed companies.
(5 marks)
(ii) Factors affecting the need for internal audit and controls
(Based partly on Turnbull guidance)
The nature of operations within the organisation arising from its sector, strategic positioning and main activities.
The scale and size of operations including factors such as the number of employees. It is generally assumed that larger
and more complex organisations have a greater need for internal controls and audit than smaller ones owing to the
number of activities occurring that give rise to potential problems.
Cost/benefit considerations. Management must weigh the benefits of instituting internal control and audit systems
against the costs of doing so. This is likely to be an issue for medium-sized companies or companies experiencing
growth.
Internal or external changes affecting activities, structures or risks. Changes arising from new products or internal
activities can change the need for internal audit and so can external changes such as PESTEL factors.
Problems with existing systems, products and/or procedures including any increase in unexplained events. Repeated or
persistent problems can signify the need for internal control and audit.
The need to comply with external requirements from relevant stock market regulations or laws. This appears to be a
relevant factor at Gluck & Goodman.
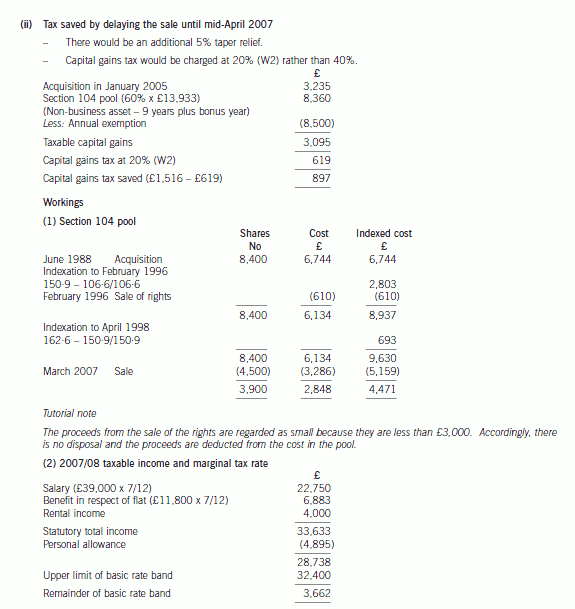
(ii) Advise Benny of the amount of tax he could save by delaying the sale of the shares by 30 days. For the
purposes of this part, you may assume that the benefit in respect of the furnished flat is £11,800 per
year. (3 marks)
Explain the grounds upon which a person may be disqualified under the Company Directors Disqualification Act 1986.(10 marks)
The Company Directors Disqualification Act (CDDA) 1986 was introduced to control individuals who persistently abused the various privileges that accompany incorporation, most particularly the privilege of limited liability. The Act applies to more than just directors and the court may make an order preventing any person (without leave of the court) from being:
(i) a director of a company;
(ii) a liquidator or administrator of a company;
(iii) a receiver or manager of a company’s property; or
(iv) in any way, whether directly or indirectly, concerned with or taking part in the promotion, formation or management of a company.
The CDDA 1986 identifies three distinct categories of conduct, which may, and in some circumstances must, lead the court to disqualify certain persons from being involved in the management of companies.
(a) General misconduct in connection with companies
This first category involves the following:
(i) A conviction for an indictable offence in connection with the promotion, formation, management or liquidation of a company or with the receivership or management of a company’s property (s.2 of the CDDA 1986). The maximum period for disqualification under s.2 is five years where the order is made by a court of summary jurisdiction, and 15 years in any other case.
(ii) Persistent breaches of companies legislation in relation to provisions which require any return, account or other document to be filed with, or notice of any matter to be given to, the registrar (s.3 of the CDDA 1986). Section 3 provides that a person is conclusively proved to be persistently in default where it is shown that, in the five years ending with the date of the application, he has been adjudged guilty of three or more defaults (s.3(2) of the CDDA 1986). This is without prejudice to proof of persistent default in any other manner. The maximum period of disqualification under this section is five years.
(iii) Fraud in connection with winding up (s.4 of the CDDA 1986). A court may make a disqualification order if, in the course of the winding up of a company, it appears that a person:
(1) has been guilty of an offence for which he is liable under s.993 of the CA 2006, that is, that he has knowingly been a party to the carrying on of the business of the company either with the intention of defrauding the company’s creditors or any other person or for any other fraudulent purpose; or
(2) has otherwise been guilty, while an officer or liquidator of the company or receiver or manager of the property of the company, of any fraud in relation to the company or of any breach of his duty as such officer, liquidator, receiver or manager (s.4(1)(b) of the CDDA 1986).
The maximum period of disqualification under this category is 15 years.(b) Disqualification for unfitness
The second category covers:
(i) disqualification of directors of companies which have become insolvent, who are found by the court to be unfit to be directors (s.6 of the CDDA 1986). Under s. 6, the minimum period of disqualification is two years, up to a maximum of 15 years;
(ii) disqualification after investigation of a company under Pt XIV of the CA 1985 (it should be noted that this part of the previous Act still sets out the procedures for company investigations) (s.8 of the CDDA 1986). Once again, the maximum period of disqualification is 15 years.
Schedule 1 to the CDDA 1986 sets out certain particulars to which the court is to have regard in deciding whether a person’s conduct as a director makes them unfit to be concerned in the management of a company. In addition, the courts have given indications as to what sort of behaviour will render a person liable to be considered unfit to act as a company director. Thus, in Re Lo-Line Electric Motors Ltd (1988), it was stated that:
‘Ordinary commercial misjudgment is in itself not sufficient to justify disqualification. In the normal case, the conduct complained of must display a lack of commercial probity, although . . . in an extreme case of gross negligence or total incompetence, disqualification could be appropriate.’
(c) Other cases for disqualification
This third category relates to:
(i) participation in fraudulent or wrongful trading under s.213 of the Insolvency Act (IA)1986 (s.10 of the CDDA 1986);
(ii) undischarged bankrupts acting as directors (s.11 of the CDDA 1986); and
(iii) failure to pay under a county court administration order (s.12 of the CDDA 1986).
For the purposes of most of the CDDA 1986, the court has discretion to make a disqualification order. Where, however, a person has been found to be an unfit director of an insolvent company, the court has a duty to make a disqualification order (s.6 of the CDDA 1986). Anyone who acts in contravention of a disqualification order is liable:
(i) to imprisonment for up to two years and/or a fine, on conviction on indictment; or
(ii) to imprisonment for up to six months and/or a fine not exceeding the statutory maximum, on conviction summarily (s.13 of the CDDA 1986).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-03-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-01
- 2019-03-08
- 2020-03-12
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-05-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-12
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20