江苏省考生:ACCA国际会计师报考条件中,具有高等专科以上学校毕业学历是什么意思?
发布时间:2020-01-10
既然选择了要走的路,就坚持下去,相信只要有信心,就一定能掌握自己的前途和命运。各位正在备考ACCA考试的小伙伴们,大家一定要坚持下去,攻克还有两个多月时间就要到来的ACCA考试。近期,有个小伙伴担心自己学历可能不够高,就问了51题库考试学习网一个关于报名的问题:考试条件中的高等专科学历是什么意思?是大专?高专?还是中专?51题库考试学习网就这个问题为大家答疑解惑:
想必有很多“资深”的ACCAer已经忘了报考条件是什么了吧?想必“萌新”的ACCAer还不清楚报考条件吧?不清楚自己是否符合报考条件吗?且随51题库考试学习网一起回忆一下关于报考ACCA考试的条件介绍:
报考国际注册会计师的条件有哪些?
报名国际注册会计师ACCA考试,具备以下条件之一即可:
1)凡具有教育部承认的大专以上学历,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
2)教育部认可的高等院校在校生,顺利完成大一的课程考试,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
3)未符合1、2项报名资格的16周岁以上的申请者,也可以先申请参加FIA(Foundations in Accountancy)基础财务资格考试。在完成基础商业会计(FAB)、基础管理会计(FMA)、基础财务会计(FFA)3门课程,并完成ACCA基础职业模块,可获得ACCA商业会计师资格证书(Diploma in Accounting and Business),资格证书后可豁免ACCAF1-F3三门课程的考试,直接进入技能课程的考试。
一直以来,ACCA都以培养国际性的高级会计、财务管理专家著称,其高质量的课程设计,高标准的考试要求,不仅赢得了联合国和各大国际性组织的高度评价,更为众多跨国公司和专业机构所推崇。
以上就是关于报考ACCA考试的条件介绍,由此可以看出,其实报考ACCA考试的门槛条件是比较低的了,相对于国内的注册会计师考试而言,少了工作年限。因此,让不少大学生也纷纷去报名参加考试。而至于“高等专科以上”是什么意思,可以从上面的条件得知:大专。因此,报考ACCA考试的最低学历都是大专学历,中专不行哦!
同样的路,有人敢走,有人不敢。走不走,不是路说了算,是看自己有没有那个胆。有的人摔了一跤也许一辈子再也不敢站起来走了,有目标的人,就算是摔得遍体鳞伤,依然勇往直前。人和人其实也没什么太多的差异,只在思维一念之间,学会换位思考,成就自己人生。坚持信念,找对平台,跟对人,懂得感恩,诚信为人,坚持不懈,梦想终会成真。无论是初次备考ACCA还是多次备考ACCA的同学,51题库考试学习网相信你定会赢!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) State the specific inquiries you should make of Robson Construction Co’s management relevant to its
accounting for construction contracts. (6 marks)
(c) Specific inquiries – accounting for construction contracts
Tutorial note: This answer is illustrative of the types of inquiry that should be made. Other relevant answer points will be
awarded similar credit. For each full mark to be earned an inquiry should address the specifics of Robson (e.g. that its
accounting policies are ‘generally less prudent’). The identification of asset overstatement/liability understatement may
reduce the purchase price offered by Prescott.
■ Are any constructions being undertaken without signed contracts?
Tutorial note: Any expenditure on constructions without contracts (e.g. of a speculative nature, perhaps to keep the
workforce employed) must be accounted for under IAS ‘Inventories’; revenue cannot be recognised nor profit taken.
■ Is full provision made for future losses foreseen on loss-making contracts?
Tutorial note: The information in the brief is that ‘provisions are made’. The level of provision is not indicated and
could be less than full.
■ Which contracts started during the year are likely to be/have been identified as loss-making (for which no provision has
yet been made)?
Tutorial note: Profits and losses are only determined by contract at each financial year end.
■ What are management’s assumptions and judgments on the likely future outcome on the Sarwar contract (and other
actual and contingent liabilities)?
Tutorial note: Robson would be imprudent if it underestimates the probability of an unfavourable outcome (or
overestimates the likelihood of successful recourse).
■ What claims history has Robson experienced? (What proportion of contracts have been subject to claims? What
proportion of claims brought have been successful? How have they been settled? Under insurance? Out-of-court
settlement?) How effective are the penalty clauses? (Is Robson having to pay penalties for overrunning on contracts?)
■ What are the actual useful lives of assets used in construction? What level of losses are made on disposal?
Tutorial note: If such assets are depreciated over useful lives that are estimated to be too long, depreciation costs
incurred to date (and estimated depreciation to be included in costs to completion) will be understated. This will result
in too much profit/too little loss being calculated on contracts.
■ What is the cause of losses on contracts? For example, if due to theft of building supplies Robson’s management is not
exercising sufficient control over the company’s assets.
(iii) The extent to which Amy will be subject to income tax in the UK on her earnings in respect of duties
performed for Cutlass Inc and the travel costs paid for by that company. (5 marks)
Appropriateness of format and presentation of the report and the effectiveness with which its advice is
communicated. (2 marks)
Note:
You should assume that the income tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and the corporation tax
rates and allowances for the financial year 2006 apply throughout this questio
(iii) Amy’s UK income tax position
Amy will remain UK resident and ordinarily resident as she is not leaving the UK permanently or for a complete tax year
under a full time contract of employment. Accordingly, she will continue to be subject to UK tax on her worldwide income
including her earnings in respect of the duties she performs for Cutlass Inc. The earnings from these duties will also be
taxable in Sharpenia as the income arises in that country.
The double tax treaty between the UK and Sharpenia will either exempt the employment income in one of the two
countries or give double tax relief for the tax paid in Sharpenia. The double tax relief will be the lower of the UK tax and
the Sharpenian tax on the income from Cutlass Inc.
Amy will not be subject to UK income tax on the expenses borne by Cutlass Inc in respect of her flights to and from
Sharpenia provided her journeys are wholly and exclusively for the purposes of performing her duties in Sharpenia.
The amounts paid by Cutlass Inc in respect of Amy’s family travelling to Sharpenia will be subject to UK income tax as
Amy will not be absent from the UK for a continuous period of at least 60 days.
(ii) Construct the argument against Professor West’s opinion, and in favour of Professor Leroi’s opinion that
a principles-based approach would be preferable in developing countries. Your answer should consider
the particular situations of developing countries. (10 marks)
(ii) Principles-based approach
Advantages of a principles-based approach
The rigour with which governance systems are applied can be varied according to size, situation, stage of development
of business, etc. Organisations (in legal terms) have a choice to the extent to which they wish to comply, although they
will usually have to ‘comply or explain’. Explanations are more accepted by shareholders and stock markets for smaller
companies.
Obeying the spirit of the law is better than ‘box ticking’ (‘sort of business you are’ rather than ‘obeying rules’). Being
aware of overall responsibilities is more important than going through a compliance exercise merely to demonstrate
conformance.
Avoids the ‘regulation overload’ of rules based (and associated increased business costs). The costs of compliance have
been a cause of considerable concern in the United States.
Self-regulation (e.g. by Financial Services Authority in the UK) rather than legal control has proven itself to underpin
investor confidence in several jurisdictions and the mechanisms are self-tightening (quicker and cheaper than legislation)
if initial public offering (IPO) volumes fall or capital flows elsewhere.
Context of developing countries
Developing countries’ economies tend to be dominated by small and medium sized organisations (SMEs). It would be
very costly and probably futile, to attempt to burden small businesses with regulatory requirements comparable to larger
concerns.
Having the flexibility to ‘comply or explain’ allows for those seeking foreign equity to increase compliance whilst those
with different priorities can delay full compliance. In low-liquidity stock markets (such as those in some developing
countries) where share prices are not seen as strategically important for businesses, adopting a more flexible approach
might be a better use of management talent rather than ‘jumping through hoops’ to comply with legally-binding
constraints.
The state needs to have an enforcement mechanism in place to deal with non-compliance and this itself represents a
cost to taxpayers and the corporate sector. Developing countries may not have the full infrastructure in place to enable
compliance (auditors, pool of NEDs, professional accountants, internal auditors, etc) and a principles-based approach
goes some way to recognise this.
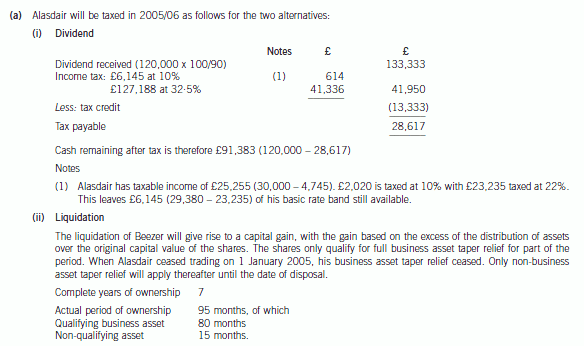
6 Alasdair, aged 42, is single. He is considering investing in property, as he has heard that this represents a good
investment. In order to raise the funds to buy the property, he wants to extract cash from his personal company, Beezer
Limited, whose year end is 31 December.
Beezer Limited was formed on 1 May 1998 with £1,000 of capital issued as 1,000 £1 ordinary shares, and traded
until 1 January 2005 when Alasdair sold the trade and related assets. The company’s only asset is cash of
£120,000. Alasdair wants to extract this cash from the company with the minimum amount of tax payable. He is
considering either, paying himself a dividend of £120,000, on 31 March 2006, after which the company would have
no assets and be wound up or, leaving the cash in the company and then liquidating the company. Costs of liquidation
of £5,000 would then be incurred.
Since Beezer Limited ceased trading, Alasdair has been taken on as a partner at a marketing firm, Gallus & Co. He
estimates his profit share for the year of assessment 2005/06 will be £30,000. He has not made any capital disposals
in the current tax year.
Alasdair wishes to reinvest the cash extracted from Beezer Limited in property but is not sure whether he should invest
directly in residential or commercial property, or do so via some form. of collective investment. He is aware that Gallus
& Co are looking to rent a new warehouse which could be bought for £200,000. Alasdair thinks that he may be able
to buy the warehouse himself and lease it to his firm, but only if he can borrow the additional money to buy the
property.
Alasdair has a 25% shareholding in another company, Glaikit Limited, whose year end is 31 March. The remaining
shares in this company are held by his friend, Gill. Alasdair is considering borrowing £15,000 from Glaikit Limited
on 1 January 2006. He does not intend to pay any interest on the loan, which is likely to be written off some time
in 2007. Alasdair does not have any connection with Glaikit Limited other than his shareholding.
Required:
(a) Advise Alasdair whether or not a dividend payment will result in a higher after-tax cash sum than the
liquidation of Beezer Limited. Assume that either the dividend would be paid on 31 March 2006 or the
liquidation would take place on 31 March 2006. (9 marks)
Assume that Beezer Limited has always paid corporation tax at or above the small companies rate of 19%
and that the tax rates and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this part.

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-04
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-06
- 2019-01-17
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-10