ACCA2019-2020MA(F2)考试大纲,速看!
发布时间:2019-07-19
2019-2020年的考试大纲已经上线了,小编特地整理了MA(F2)科目的考纲变动细节情况给大家,具体内容如下。
一、科目关联(Relation Diagram)
Management Accounting(MA)《管理会计》课程中的相关知识首先与Performance Management(PM)《业绩管理》和Advanced
Performance Management(APM)《高级业绩管理》这两门科目中的知识有所关联。此外,还会涉及到一定的Strategic Business Leader(SBL)《战略商业报告》。
而在MA课程中学到的知识,将会运用到学员后续高阶课程的PM以APM科目的学习中。MA课程中的Part B最后一章节Alternative costing methods会出现在PM的Part A,Part E有关Performance management的部分会出现在PM以及APM课程里。
MA课程中为之后的PM课程以及高阶必修的SBR课程打下基础。而MA课程直接承接的是PM,二者紧密关联,MA培养学员基础的管理会计技巧和认知,PM以及APM则培养学员更高级、真实的业绩管理能力。所以对于后期选修对APM有兴趣的学员来说,MA更是极为重要的一门科目!
二、新课程框架和新考纲(New Framework and Syllabus)
整体变化是增加了一个版块,这个版块整合了关于Date analysis and
statistical techniques的内容,同时又新增了一些这个内容的其他知识点。
第一个变化
新增版块Data analysis and statistical techniques成为了Part B部分。但是其他版块内容不变,以此往后顺延。由原来的Part A-Part E
5个Part的内容;变成了现在Part A-Part F 6个Part的内容。
第二个变化
将原来考纲Part C Budgeting中的Statistical
techniques这个知识点放在了新考纲Part B Data analysis and
statistical techniques的Forecasting techniques中。
第三个变化
新增了一部分的知识点。一个是Big data and analysis,放在了Part A The nature,source and purpose ofmanagement information的Sources of data中;一个是Summarising
and analysing data,放在了Part B Date analysis and
statistical technique。
对于此次考纲的调整,可以看出对Date analysis and statistical
techniques进行了一个整合。内容基本不变,我们主要看的就是新增的知识点。
三、新增知识点1:Big data and analysis
考纲要求的是Describe the main uses of big data
andanalytics for organisations。那也就是需要大家知道和分析大数据在企业中的用途。考试依然最多是以选择题形式进行考察。
四、新增知识点2:Summarising and analysing data
考纲要求:
a)Calculate the mean,mode and median
forungrouped data and the mean for groupeddata.
b)Calculate measures of dispersion
including thevariance,standard deviation and coefficient ofvariation both
grouped and ungrouped data.
c)Calculate expected values for use in
decisionmaking.
d)Explain the properties of a
normaldistribution.
e)Interpret normal distribution graphs and
tables
那么要求大家掌握的就是对均值、中位数、离散度、标准差、变异系数、均值及期望值等的计算。对正太分布图,要了解它的性质并能够解读其中的含义。考试通常会以计算分析等形式进行考察。
关于考试:
五、MA课程考试形式和分值分布:
Section A是35道2分的填空选择,一共70分;Section
B是3道大题,每题10分,各来自Part C、D、E,也是填空选择的形式。
综合以上就是关于MA的考纲变化详情,希望能对各位小伙伴有用。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
21 Which of the following statements about contingent assets and contingent liabilities are correct?
1 A contingent asset should be disclosed by note if an inflow of economic benefits is probable.
2 A contingent liability should be disclosed by note if it is probable that a transfer of economic benefits to settle it
will be required, with no provision being made.
3 No disclosure is required for a contingent liability if it is not probable that a transfer of economic benefits to settle
it will be required.
4 No disclosure is required for either a contingent liability or a contingent asset if the likelihood of a payment or
receipt is remote.
A 1 and 4 only
B 2 and 3 only
C 2, 3 and 4
D 1, 2 and 4
(b) ‘opinion shopping’; (5 marks)
(b) ‘Opinion shopping’
Explanation of term
‘Opinion shopping’ occurs when management approach auditing firms (other than their incumbent auditors) to ask their views
on the application of accounting standards or principles to specific circumstances or transactions.
Ethical risks
The reasons for ‘opinion shopping’ may be:
■ to find alternative auditors; or
■ to get advice on a matter of contention with the incumbent auditor.
The member who is not the entity’s auditor must be alert to the possibility that their opinion – if it differs from that of the
incumbent auditor – may create undue pressure on the incumbent auditor’s judgement and so threaten the objectivity of the
audit.
Furthermore, by aligning with the interests of management when negotiating taking on an engagement, an incoming auditor
may compromise their objectivity even before the audit work commences. There is a risk that the audit fee might be seen to
be contingent upon a ‘favourable’ opinion (that is, the audit judgement coinciding with management’s preferences).
Employed professional accountants (accountants in industry) who support their company’s management in seeking second
opinions may call into question their integrity and professional behaviour.
Sufficiency of current ethical guidance
Current ethical guidance requires that when asked to provide a ‘second opinion’ a member should seek to minimise the risk
of giving inappropriate guidance, by ensuring that they have access to all relevant information.
The member should therefore:
■ ascertain why their opinion is being sought;
■ contact the auditor to provide any relevant facts;
■ with the entity’s permission, provide the auditor with a copy of their opinion.
The member’s opinion is more likely to differ if it is based on information which is different (or incomplete) as compared with
that available to the incumbent auditor. The member should therefore decline to act if permission to communicate with the
auditor is not given.
‘Opinion shopping’ might be less prevalent if company directors had no say in the appointment and remuneration of auditors.
If audit appointments were made by an independent body ‘doubtful accounting practices’ would (arguably) be less of a
negotiating factor. However, to be able to appoint auditors to multi-national/global corporations, such measures would require
the backing of regulatory bodies worldwide.
Statutory requirements in this area could also be more stringent. For example, an auditor may be required to deposit a
‘statement of circumstances’ (or a statement of ‘no circumstances’) in the event that they are removed from office or resign.
However, disclosure could be made more public if, when a change in accounting policy coincides with a change of auditors,
the financial statements and auditor’s report highlight the change and the auditors state their concurrence (or otherwise) with
the change. This could be made a statutory requirement and International Standards on Auditing (ISAs) amended to give
guidance on how auditors should report on changes.
Further, if the incoming auditor were to have a statutory right of access to the files and working papers of the outgoing auditors
they would be able to make a better and informed assessment of the desirability of the client and also appreciate the validity
(or otherwise) of any ‘statement’ issued by the outgoing auditor.
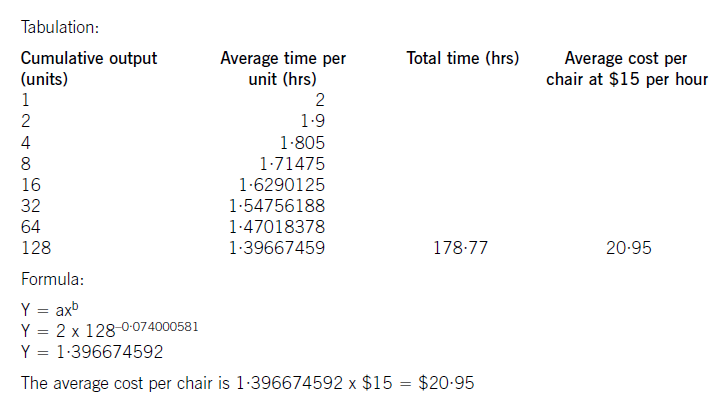
Big Cheese Chairs (BCC) manufactures and sells executive leather chairs. They are considering a new design of massaging chair to launch into the competitive market in which they operate.
They have carried out an investigation in the market and using a target costing system have targeted a competitive selling price of $120 for the chair. BCC wants a margin on selling price of 20% (ignoring any overheads).
The frame. and massage mechanism will be bought in for $51 per chair and BCC will upholster it in leather and assemble it ready for despatch.
Leather costs $10 per metre and two metres are needed for a complete chair although 20% of all leather is wasted in the upholstery process.
The upholstery and assembly process will be subject to a learning effect as the workers get used to the new design.
BCC estimates that the first chair will take two hours to prepare but this will be subject to a learning rate (LR) of 95%.
The learning improvement will stop once 128 chairs have been made and the time for the 128th chair will be the time for all subsequent chairs. The cost of labour is $15 per hour.
The learning formula is shown on the formula sheet and at the 95% learning rate the value of b is -0·074000581.
Required:
(a) Calculate the average cost for the first 128 chairs made and identify any cost gap that may be present at
that stage. (8 marks)
(b) Assuming that a cost gap for the chair exists suggest four ways in which it could be closed. (6 marks)
The production manager denies any claims that a cost gap exists and has stated that the cost of the 128th chair will be low enough to yield the required margin.
(c) Calculate the cost of the 128th chair made and state whether the target cost is being achieved on the 128th chair. (6 marks)

(W1)
The cost of the labour can be calculated using learning curve principles. The formula can be used or a tabular approach would
also give the average cost of 128 chairs. Both methods are acceptable and shown here.
(b) To reduce the cost gap various methods are possible (only four are needed for full marks)
– Re-design the chair to remove unnecessary features and hence cost
– Negotiate with the frame. supplier for a better cost. This may be easier as the volume of sales improve as suppliers often
are willing to give discounts for bulk buying. Alternatively a different frame. supplier could be found that offers a better
price. Care would be needed here to maintain the required quality
– Leather can be bought from different suppliers or at a better price also. Reducing the level of waste would save on cost.
Even a small reduction in waste rates would remove much of the cost gap that exists
– Improve the rate of learning by better training and supervision
– Employ cheaper labour by reducing the skill level expected. Care would also be needed here not to sacrifice quality or
push up waste rates.
(c) The cost of the 128th chair will be: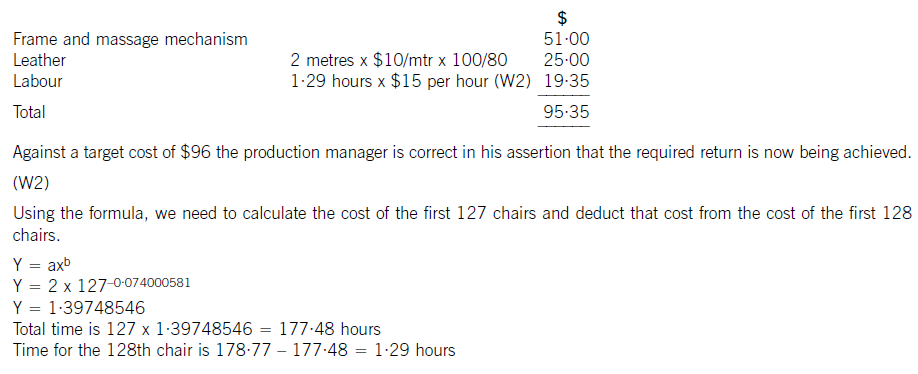
(iii) State any disadvantages to the relief in (i) that Sharon should be aware of, and identify and describe
another relief that she might use. (4 marks)
(iii) There are several disadvantages to incorporation relief as follows:
1. The requirement to transfer all business assets to the company means that it will not be possible to leave behind
certain assets, such as the property. This might lead to a double tax charge (sale of the property, then extraction
of sale proceeds) at a future date.
2. Taper relief is lost on the transfer of the business. This means that any disposal of chargeable business assets (the
shares) within two years of the incorporation will lead to a higher chargeable gain, as the full rate of business asset
taper relief will not be available.
3. The relief does not eliminate the tax charge, it merely defers the payment of tax until some future event. The
deferred gain will become taxable when Sharon sells her shares in the company.
Gift relief could be used instead of incorporation relief. The assets would be gifted to the company for no consideration,
with the base cost of the assets to the company being reduced by the deferred gain arising. Unlike incorporation relief,
gift relief applies to individual assets used in a trade and not to an entire business. This is particularly useful if the
transferor wishes to retain some assets, such as property outside the company, as not all assets have to be transferred.
Note: If the business was non-trading, incorporation relief would still be available, but gift relief would not. However,
this restriction should not apply to Sharon and gift relief remains an option in this case.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-14
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-02-20
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-03-02
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2021-05-14
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-13
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-05-20
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-05-16