想知道ACCA证书有什么用处?确定不来这里看看
发布时间:2020-05-13
好消息!好消息!关于ACCA证书有什么用处有消息啦!小伙伴们还不知道吗?今天就紧跟51题库考试学习网的脚步一起来看看吧。
ACCA是全球广受认可的专业会计师组织,是全世界有志于投身财会、金融以及管理领域的专业人才优选的资格认证。ACCA的全称是“特许公认会计师公会”,在国内也被称为“国际注册会计师”。
拥有这么高大上头衔的ACCA证书,对于我们自身发展究竟有什么作用呢?
求职ACCA证书在HR眼里是一个黄金标签,ACCA证书是求职者对财务知识掌握的证明,也是求职者学习能力和时间管理能力的证明,这些都是工作中最重要的能力,自然也是最吸引HR的东西。 升职自然也是非常容易的。
ACCA作为一张稀有且高含金量的财会类高端证书,一直以来,都被视为财务管理层岗位招聘条件之一。特别是在外企或是涉及跨国业务的本土企业,ACCA会员掌握的国际会计准则一直是企业财务报告的刚需。在四大中,毕马威的咨询版块一直将ACCA视为升经理的qualification之一,ACCA的重要性毋庸置疑。
跳槽ACCA证书是资深财务人最好的证明,一大原因在于,在拿下ACCA证书多年后可以直接变为FCCA,即资深ACCA会员。别人简历上写“5年财务管理经验”,而你,写的则是“8年ACCA会员”,一下就从众多求职者中脱颖而出了。ACCA证书在求职、升职和跳槽时均能发挥不同的价值,这也是ACCA证书倍受财务人青睐的一大原因。
ACCA证书会帮助财务人在职场中走的更稳,更远。
上文讲的就是ACCA证书有什么用处的内容啦,下面我们再来看看ACCA的其他内容。
注册资格
a.具有教育部认可的大专以上学历,既可以报名成为ACCA的正式学员。
b.教育部认可的高等院校在校生,且顺利通过第一学年的所有课程考试,既可报名成为ACCA正式学员。
c.未符合以上报名资格的申请者,但年龄在18岁以上,可以先注册为FIA,并通过FAB,FMA,FFA三门考试(该三门考试与AB、MA、FA一致)便可以转为ACCA正式学员(需要在账户中选择转换路径),并获得前三门免试,直接进入ACCA技能课程阶段的考试。
以上就是关于ACCA证书有什么用处的全部内容啦,还有没有不清楚的小伙伴呢?欢迎您咨询51题库考试学习网,我们在这里等你哦!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) (i) Discusses the principles involved in accounting for claims made under the above warranty provision.
(6 marks)
(ii) Shows the accounting treatment for the above warranty provision under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’ for the year ended 31 October 2007. (3 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and communication of advice. (2 marks)
(b) Provisions – IAS37
An entity must recognise a provision under IAS37 if, and only if:
(a) a present obligation (legal or constructive) has arisen as a result of a past event (the obligating event)
(b) it is probable (‘more likely than not’), that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle
the obligation
(c) the amount can be estimated reliably
An obligating event is an event that creates a legal or constructive obligation and, therefore, results in an enterprise having
no realistic alternative but to settle the obligation. A constructive obligation arises if past practice creates a valid expectation
on the part of a third party. If it is more likely than not that no present obligation exists, the enterprise should disclose a
contingent liability, unless the possibility of an outflow of resources is remote.
The amount recognised as a provision should be the best estimate of the expenditure required to settle the present obligation
at the balance sheet date, that is, the amount that an enterprise would rationally pay to settle the obligation at the balance
sheet date or to transfer it to a third party. This means provisions for large populations of events such as warranties, are
measured at a probability weighted expected value. In reaching its best estimate, the entity should take into account the risks
and uncertainties that surround the underlying events.
Expected cash outflows should be discounted to their present values, where the effect of the time value of money is material
using a risk adjusted rate (it should not reflect risks for which future cash flows have been adjusted). If some or all of the
expenditure required to settle a provision is expected to be reimbursed by another party, the reimbursement should be
recognised as a separate asset when, and only when, it is virtually certain that reimbursement will be received if the entity
settles the obligation. The amount recognised should not exceed the amount of the provision. In measuring a provision future
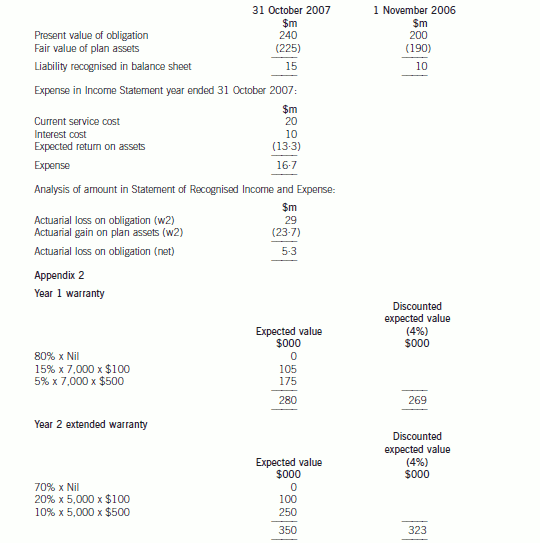
events should be considered. The provision for the warranty claim will be determined by using the expected value method.
The past event which causes the obligation is the initial sale of the product with the warranty given at that time. It would be
appropriate for the company to make a provision for the Year 1 warranty of $280,000 and Year 2 warranty of $350,000,
which represents the best estimate of the obligation (see Appendix 2). Only if the insurance company have validated the
counter claim will Macaljoy be able to recognise the asset and income. Recovery has to be virtually certain. If it is virtually
certain, then Macaljoy may be able to recognise the asset. Generally contingent assets are never recognised, but disclosed
where an inflow of economic benefits is probable.
The company could discount the provision if it was considered that the time value of money was material. The majority of
provisions will reverse in the short term (within two years) and, therefore, the effects of discounting are likely to be immaterial.
In this case, using the risk adjusted rate (IAS37), the provision would be reduced to $269,000 in Year 1 and $323,000 in
Year 2. The company will have to determine whether this is material.
Appendix 1
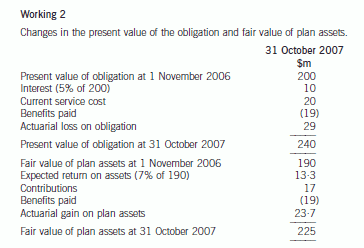
The accounting for the defined benefit plan is as follows:

(b) Prepare the balance sheet of York at 31 October 2006, using International Financial Reporting Standards,
discussing the nature of the accounting treatments selected, the adjustments made and the values placed
on the items in the balance sheet. (20 marks)

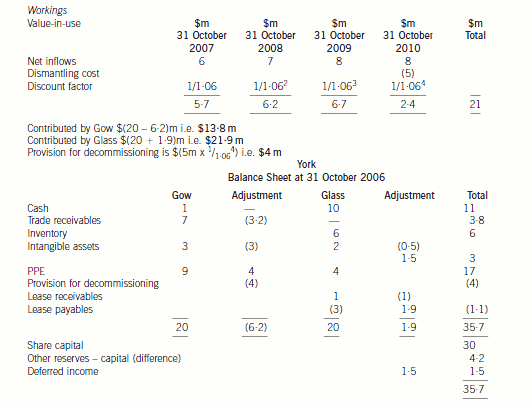
Gow’s net assets
IAS36 ‘Impairment of Assets’, sets out the events that might indicate that an asset is impaired. These circumstances include
external events such as the decline in the market value of an asset and internal events such as a reduction in the cash flows
to be generated from an asset or cash generating unit. The loss of the only customer of a cash generating unit (power station)
would be an indication of the possible impairment of the cash generating unit. Therefore, the power station will have to be
impairment tested.
The recoverable amount will have to be determined and compared to the value given to the asset on the setting up of the
joint venture. The recoverable amount is the higher of the cash generating unit’s fair value less costs to sell, and its value-inuse.
The fair value less costs to sell will be $15 million which is the offer for the purchase of the power station ($16 million)
less the costs to sell ($1 million). The value-in-use is the discounted value of the future cash flows expected to arise from the
cash generating unit. The future dismantling costs should be provided for as it has been agreed with the government that it
will be dismantled. The cost should be included in the future cash flows for the purpose of calculating value-in-use and
provided for in the financial statements and the cost added to the property, plant and equipment ($4 million ($5m/1·064)).
The value-in-use based on a discount rate of 6 per cent is $21 million (working). Therefore, the recoverable amount is
$21 million which is higher than the carrying value of the cash generating unit ($20 million) and, therefore, the value of the
cash generating unit is not impaired when compared to the present carrying value of $20 million (value before impairment
test).
Additionally IAS39, ‘Financial Instruments: recognition and measurement’, says that an entity must assess at each balance
sheet date whether a financial asset is impaired. In this case the receivable of $7 million is likely to be impaired as Race is
going into administration. The present value of the estimated future cash flows will be calculated. Normally cash receipts from
trade receivables will not be discounted but because the amounts are not likely to be received for a year then the anticipated
cash payment is 80% of ($5 million × 1/1·06), i.e. $3·8 million. Thus a provision for the impairment of the trade receivables
of $3·2 million should be made. The intangible asset of $3 million would be valueless as the contract has been terminated.
Glass’s Net Assets
The leased property continues to be accounted for as property, plant and equipment and the carrying amount will not be
adjusted. However, the remaining useful life of the property will be revised to reflect the shorter term. Thus the property will
be depreciated at $2 million per annum over the next two years. The change to the depreciation period is applied prospectively
not retrospectively. The lease liability must be assessed under IAS39 in order to determine whether it constitutes a
de-recognition of a financial liability. As the change is a modification of the lease and not an extinguishment, the lease liability
would not be derecognised. The lease liability will be adjusted for the one off payment of $1 million and re-measured to the
present value of the revised future cash flows. That is $0·6 million/1·07 + $0·6 million/(1·07 × 1·07) i.e. $1·1 million. The
adjustment to the lease liability would normally be recognised in profit or loss but in this case it will affect the net capital
contributed by Glass.
The termination cost of the contract cannot be treated as an intangible asset. It is similar to redundancy costs paid to terminate
a contract of employment. It represents compensation for the loss of future income for the agency. Therefore it must be
removed from the balance sheet of York. The recognition criteria for an intangible asset require that there should be probable
future economic benefits flowing to York and the cost can be measured reliably. The latter criterion is met but the first criterion
is not. The cost of gaining future customers is not linked to this compensation.
IAS18 ‘Revenue’ contains a concept of a ‘multiple element’ arrangement. This is a contract which contains two or more
elements which are in substance separate and are separately identifiable. In other words, the two elements can operate
independently from each other. In this case, the contract with the overseas company has two distinct elements. There is a
contract not to supply gas to any other customer in the country and there is a contract to sell gas at fair value to the overseas
company. The contract has not been fulfilled as yet and therefore the payment of $1·5 million should not be taken to profit
or loss in its entirety at the first opportunity. The non supply of gas to customers in that country occurs over the four year
period of the contract and therefore the payment should be recognised over that period. Therefore the amount should be
shown as deferred income and not as a deduction from intangible assets. The revenue on the sale of gas will be recognised
as normal according to IAS18.
There may be an issue over the value of the net assets being contributed. The net assets contributed by Glass amount to
$21·9 million whereas those contributed by Gow only total $13·8 million after taking into account any adjustments required
by IFRS. The joint venturers have equal shareholding in York but no formal written agreements, thus problems may arise ifGlass feels that the contributions to the joint venture are unequal.
5 (a) Carver Ltd was incorporated and began trading in August 2002. It is a close company with no associated
companies. It has always prepared accounts to 31 December and will continue to do so in the future.
It has been decided that Carver Ltd will sell its business as a going concern to Blade Ltd, an unconnected
company, on 31 July 2007. Its premises and goodwill will be sold for £2,135,000 and £290,000 respectively
and its machinery and equipment for £187,000. The premises, which do not constitute an industrial building,
were acquired on 1 August 2002 for £1,808,000 and the goodwill has been generated internally by the
company. The machinery and equipment cost £294,000; no one item will be sold for more than its original cost.
The tax adjusted trading profit of Carver Ltd in 2007, before taking account of both capital allowances and the
sale of the business assets, is expected to be £81,000. The balance on the plant and machinery pool for the
purposes of capital allowances as at 31 December 2006 was £231,500. Machinery costing £38,000 was
purchased on 1 March 2007. Carver Ltd is classified as a small company for the purposes of capital allowances.
On 1 August 2007, the proceeds from the sale of the business will be invested in either an office building or a
portfolio of UK quoted company shares, as follows:
Office building
The office building would be acquired for £3,100,000; the vendor is not registered for value added tax (VAT).
Carver Ltd would borrow the additional funds required from a UK bank. The building is let to a number of
commercial tenants who are not connected with Carver Ltd and will pay rent, in total, of £54,000 per calendar
quarter, in advance, commencing on 1 August 2007. The company’s expenditure for the period from 1 August
2007 to 31 December 2007 is expected to be:
£
Loan interest payable to UK bank 16,000
Building maintenance costs 7,500
Share portfolio
Shares would be purchased for the amount of the proceeds from the sale of the business with no need for further
loan finance. It is estimated that the share portfolio would generate dividends of £36,000 and capital gains, after
indexation allowance, of £10,000 in the period from 1 August 2007 to 31 December 2007.
All figures are stated exclusive of value added tax (VAT).
Required:
(i) Taking account of the proposed sale of the business on 31 July 2007, state with reasons the date(s) on
which Carver Ltd must submit its corporation tax return(s) for the year ending 31 December 2007.
(2 marks)
(a) (i) Due date for submission of corporation tax return
Carver Ltd intends to cease trading on 31 July 2007. This will bring to an end the accounting period that began on
1 January 2007. A new accounting period will commence on 1 August 2007 and end on the company’s accounting
reference date on 31 December 2007.
Carver Ltd is required to submit its corporation tax return by the later of:
– one year after the end of its accounting period; and
– one year after the end of the period of account in which the last day of the accounting period falls.
Accordingly, the company must submit its corporation tax returns for both accounting periods by 31 December 2008.
6 An important part of managing people in a professional organisation is to be able to distinguish between aggressiveness and assertiveness in an employee.
Required:
(a) Explain and give examples of aggressive behaviour. (8 marks)
6 To get the best out of people, managers need to have effective communication skills. Professional accountants as managers need to understand the difference between aggressive and assertive behaviour. Often an exchange of communication can be interpreted as a belligerent response from an employee. However, a slight difference in approach can communicate different feelings and achieve a more positive result.
(a) Aggressive behaviour is competitive and directed at defeating someone else. It is standing up for oneself at the expense of other people. It is defending one’s rights but doing so in such a way that violates the rights of other people. Aggressive behaviour ignores or dismisses the needs, wants, opinions, feelings or beliefs of others.
Characteristics of aggressive behaviour include excessive ‘I’ statements, boastfulness, and the individual’s opinions expressed as fact, threatening questions or postures from the individual, sarcasm and other throw-away remarks and a constant blaming of others.
Aggressive behaviour can be self defeating. It may cause such antagonism in the others in the organisation that they will refuse to co-operate or work with the person showing aggressive behaviour.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-03-12
- 2021-06-18
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-06
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-03-14
- 2021-06-18
- 2019-12-31
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-04-05
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-17
- 2020-01-04
- 2020-04-04
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-15
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-12-27
- 2019-12-31
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-21