江西省大学生在校期间备考ACCA有什么优势?
发布时间:2020-01-10
很多小伙伴都会纠结,大学期间既要完成学业,又要考研,还要准备毕业论文,这么多的事还要准备ACCA??那不是得不偿失吗?其实,学习ACCA的相关知识对我们的大学生活可谓百利而无一害的,并且相比较于你工作几年之后再来备考ACCA,在校期间备考51题库考试学习网认为更为妥帖一些,为什么这样说呢?且随51题库考试学习网一起了解一下,在校备考ACCA有何优势所在:
(一)高薪岗位:ACCA本科毕业生非常容易进入四大国际注册会计师事务所!如果在大学期间考过ACCA证书,证明你的确是一个十分有能力的人,让企业更加的认可你,你也会得到各式各样的工作机会和接触更多层面的人。
(二)三重保障:本校学历+国外文凭+ACCA证书,学员通过ACCA前两个阶段的考试后,在国内即可申请英国牛津布鲁克斯大学的应用会计理学士学位,如果你有意愿继续深造,还可以申请攻读伦敦大学专业会计硕士学位。
(三)技能教育:ACCA的课程就是根据现时商务社会对财会人员的实际要求进行开发、设计的,特别注意培养学员的分析能力和在复杂条件下的决策、判断能力。系统的、高质量的培训给予学员真才实学,学员学成后能适应各种环境,并逐步成为具有全面管理素质的高级财务管理专家。
(四)学习时间:相比较在职人员而言在校大学生有充足的时间来学习,没有工作上的琐事打扰,并且还有一个更加优良的学习氛围(校园),且因为大学生生活不像社会,有许许多多的诱惑和安逸考验着ACCAer们。
(五)学习能力:大学期间,正处于青春年少时刻,学习能力和精力是处于人生的旺期,相比较于在职人员,学习能力和效率高的不是一点半点。
学习和考试时间该怎样分配?
一、大一同学的ACCA规划:
NOW:提升自我财务英语水平
大一下学期:学习F1F2F3
大二上学期:学习F4F5F6
大二下学期:学习F7F8F9
大三上学期:申请牛津布鲁克斯学士学位及高级商业会计证书,并继续学习ACCA最后5门课程,或凭借ACCA成绩实习就业。
二、大二同学的ACCA规划:
NOW:提升自我财务英语水平
大二上学期:学习F1F2F3
大二下学期:学习F4F5F6
大三上学期:学习F7F8F9
大三下学期:申请牛津布鲁克斯学士学位及高级商业会计证书,并继续学习ACCA最后5门课程,或凭借ACCA成绩实习就业。
最后,51题库考试学习网想对大家说:“物不经锻炼,终难成器;人不得切琢,终不成人。”各位ACCAer们,加油~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Briefly discuss TWO factors which could reduce the rate of return earned by the investment as per the
results in part (a). (4 marks)
(ii) Two factors which might reduce the return earned by the investment are as follows:
(i) Poor product quality
The very nature of the product requires that it is of the highest quality i.e. the cakes are made for human
consumption. Bad publicity via a ‘product recall’ could potentially have a catastrophic effect on the total sales to
Superstores plc over the eighteen month period.
(ii) The popularity of the Mighty Ben character
There is always the risk that the popularity of the character upon which the product is based will diminish with a
resultant impact on sales volumes achieved. In this regard it would be advisable to attempt to negotiate with
Superstores plc in order to minimise potential future losses.
(iii) Explain the potential corporation tax (CT) implications of Tay Limited transferring work to Trent Limited,
and suggest how these can be minimised or eliminated. (3 marks)
(iii) Trading losses may not be carried forward where, within a period of three years there is both a change in the ownership
of a company and a major change in the nature or conduct of its trade. The transfer of work from Tay Limited to Trent
Limited is likely to constitute a major change in the nature or conduct of the latter’s trade. As a consequence, any tax
losses at the date of acquisition will be forfeited. Assuming losses were incurred uniformly in 2005, the tax losses at the
date of acquisition were £380,000 (300,000 + 2/3 x 120,000)). This is worth £114,000 assuming a corporation tax
rate of 30%.
Thus, Tay Limited should not consider transferring any trade to Trent Limited until after the third anniversary of the date
of the change of ownership i.e. not before 1 September 2008. As the trades are similar, there should be little problem
in transferring work from that date onwards.
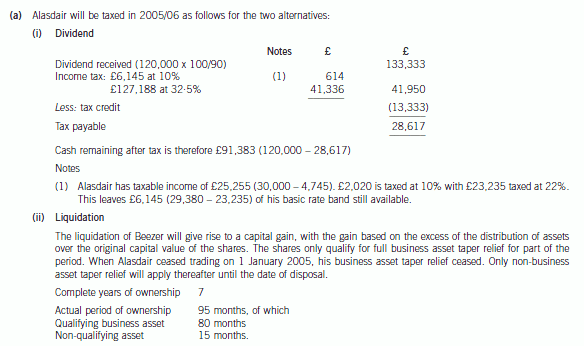
6 Alasdair, aged 42, is single. He is considering investing in property, as he has heard that this represents a good
investment. In order to raise the funds to buy the property, he wants to extract cash from his personal company, Beezer
Limited, whose year end is 31 December.
Beezer Limited was formed on 1 May 1998 with £1,000 of capital issued as 1,000 £1 ordinary shares, and traded
until 1 January 2005 when Alasdair sold the trade and related assets. The company’s only asset is cash of
£120,000. Alasdair wants to extract this cash from the company with the minimum amount of tax payable. He is
considering either, paying himself a dividend of £120,000, on 31 March 2006, after which the company would have
no assets and be wound up or, leaving the cash in the company and then liquidating the company. Costs of liquidation
of £5,000 would then be incurred.
Since Beezer Limited ceased trading, Alasdair has been taken on as a partner at a marketing firm, Gallus & Co. He
estimates his profit share for the year of assessment 2005/06 will be £30,000. He has not made any capital disposals
in the current tax year.
Alasdair wishes to reinvest the cash extracted from Beezer Limited in property but is not sure whether he should invest
directly in residential or commercial property, or do so via some form. of collective investment. He is aware that Gallus
& Co are looking to rent a new warehouse which could be bought for £200,000. Alasdair thinks that he may be able
to buy the warehouse himself and lease it to his firm, but only if he can borrow the additional money to buy the
property.
Alasdair has a 25% shareholding in another company, Glaikit Limited, whose year end is 31 March. The remaining
shares in this company are held by his friend, Gill. Alasdair is considering borrowing £15,000 from Glaikit Limited
on 1 January 2006. He does not intend to pay any interest on the loan, which is likely to be written off some time
in 2007. Alasdair does not have any connection with Glaikit Limited other than his shareholding.
Required:
(a) Advise Alasdair whether or not a dividend payment will result in a higher after-tax cash sum than the
liquidation of Beezer Limited. Assume that either the dividend would be paid on 31 March 2006 or the
liquidation would take place on 31 March 2006. (9 marks)
Assume that Beezer Limited has always paid corporation tax at or above the small companies rate of 19%
and that the tax rates and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this part.

5 Financial statements have seen an increasing move towards the use of fair values in accounting. Advocates of ‘fair
value accounting’ believe that fair value is the most relevant measure for financial reporting whilst others believe that
historical cost provides a more useful measure.
Issues have been raised over the reliability and measurement of fair values, and over the nature of the current level
of disclosure in financial statements in this area.
Required:
(a) Discuss the problems associated with the reliability and measurement of fair values and the nature of any
additional disclosures which may be required if fair value accounting is to be used exclusively in corporate
reporting. (13 marks)
(a) Reliability and Measurement
Fair value can be defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability. The fair value can
be thought of as an ‘exit price’. A fair value measurement assumes that the transaction to sell the asset or transfer the liability
occurs in the principal market for the asset or liability or, in the absence of a principal market, the most advantageous market
for the asset or liability which is the market in which the reporting entity would sell the asset or transfer the liability with the
price that maximises the amount that would be received or minimises the amount that would be paid. IAS39 ‘Financial
Instruments: Recognition and Measurement’ requires an entity to use the most advantageous active market in measuring the
fair value of a financial asset or liability when multiple markets exist whereas IAS41 ‘Agriculture’ requires an entity to use the
most relevant market. Thus there can be different approaches for estimating exit prices. Additionally valuation techniques and
current replacement cost could be used.
A hierarchy of fair value measurements would have to be developed in order to convey information about the nature of the
information used in creating the fair values. For example quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets would provide better
quality information than quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets which would provide better quality
information than prices which reflect the reporting entity’s own thinking about the assumptions that market participants would
use in pricing the asset or liability. Enron made extensive use of what it called ‘mark-to-market’ accounting which was based
on valuation techniques and estimates. IFRSs currently do not have a single hierarchy that applies to all fair value measures.
Instead individual standards indicate preferences for certain inputs and measures of fair value over others, but this guidance
is not consistent among all IFRSs.
Some companies, in order to effectively manage their businesses, have already developed models for determining fair values.
Businesses manage their operations by managing risks. A risk management process often requires measurement of fair values
of contracts, financial instruments, and risk positions.
If markets were liquid and transparent for all assets and liabilities, fair value accounting clearly would give reliable information
which is useful in the decision making process. However, because many assets and liabilities do not have an active market,
the inputs and methods for estimating their fair value are more subjective and, therefore, the valuations are less reliable. Fair
value estimates can vary greatly, depending on the valuation inputs and methodology used. Where management uses
significant judgment in selecting market inputs when market prices are not available, reliability will continue to be an issue.
Management can use significant judgment in the valuation process. Management bias, whether intentional or unintentional,
may result in inappropriate fair value measurements and consequently misstatements of earnings and equity capital. Without
reliable fair value estimates, the potential for misstatements in financial statements prepared using fair value measurements
will be even greater.
Consideration must be given to revenue recognition issues in a fair value system. It must be ensured that unearned revenue
is not recognised early as it recently was by certain high-tech companies.
As the variety and complexity of financial instruments increases, so does the need for independent verification of fair value
estimates. However, verification of valuations that are not based on observable market prices is very challenging. Users of
financial statements will need to place greater emphasis on understanding how assets and liabilities are measured and how
reliable these valuations are when making decisions based on them.
Disclosure
Fair values reflect point estimates and do not result in transparent financial statements. Additional disclosures are necessary
to bring meaning to these fair value estimates. These disclosures might include key drivers affecting valuations, fair-valuerange
estimates, and confidence levels. Another important disclosure consideration relates to changes in fair value amounts.
For example, changes in fair values on securities can arise from movements in interest rates, foreign-currency rates, and credit
quality, as well as purchases and sales from the portfolio. For users to understand fair value estimates, they must be given
adequate disclosures about what factors caused the changes in fair value. It could be argued that the costs involved in
determining fair values may exceed the benefits derived therefrom. When considering how fair value information should be
presented in the financial statements, it is important to consider what type of financial information investors want. There are
indications that some investors desire both fair value information and historical cost information. One of the issues affecting
the credibility of fair value disclosures currently is that a number of companies include ‘health warnings’ with their disclosures
indicating that the information is not used by management. This language may contribute to users believing that the fair value
disclosures lack credibility.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-01-15
- 2020-04-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-02-15
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-26