acca 考试需要带什么证件呢?
发布时间:2021-03-12
acca 考试需要带什么证件呢?
最佳答案
ACCA考试需要携带准考证和身份证才能进入考场,考生的准考证和有效身份证件二者缺一不可,请大家在考前一定注意查看并准备好,否则将无法进入考场参加考试。
ACCA迟到半小时将不允许进考场。
不允许提前交卷离开考场。
如要在ACCA考试期间上卫生间,则会有一位监考人陪同。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(e) Briefly provide five reasons to the management of Bailey’s why financial rewards could be considered to improve motivation. (5 marks)
(e) There are issues at Bailey’s as a consequence of poor pay. Although non-financial motivation has an important role to play in encouraging commitment, the fact remains that financial rewards act as a strong motivating factor, especially in what has been a low pay business. Financial rewards are all encompassing and apply to all employees at all levels, are universally applicable, able to satisfy all types of need and simple to apply and understand. At Bailey’s, financial rewards have a greater effect because they can provide recognition and prestige if pay is improved, are seen as the most important hygiene factor(especially in a business with a history of low pay and low morale) and are a measure of achievement against goals, especially if some form. of bonus or performance related pay is introduced by the new management at Bailey’s. In addition, financial rewards are a basis for satisfaction and are often used as a form. of professional or social comparison outside the organisation.
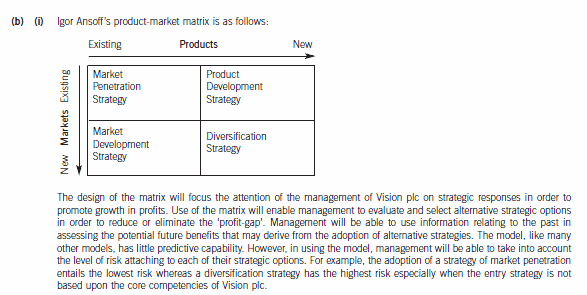
(b) (i) Explain how the use of Ansoff’s product-market matrix might assist the management of Vision plc to
reduce the profit-gap that is forecast to exist at 30 November 2009. (3 marks)
In relation to the law of contract, distinguish between and explain the effect of:
(a) a term and a mere representation; (3 marks)
(b) express and implied terms, paying particular regard to the circumstances under which terms may be implied in contracts. (7 marks)
This question requires candidates to consider the law relating to terms in contracts. It specifically requires the candidates to distinguish between terms and mere representations and then to establish the difference between express and implied terms in contracts.
(a) As the parties to a contract will be bound to perform. any promise they have contracted to undertake, it is important to distinguish between such statements that will be considered part of the contract, i.e. terms, and those other pre-contractual statements which are not considered to be part of the contract, i.e. mere representations. The reason for distinguishing between them is that there are different legal remedies available if either statement turns out to be incorrect.
A representation is a statement that induces a contract but does not become a term of the contract. In practice it is sometimes difficult to distinguish between the two, but in attempting to do so the courts will focus on when the statement was made in relation to the eventual contract, the importance of the statement in relation to the contract and whether or not the party making the statement had specialist knowledge on which the other party relied (Oscar Chess v Williams (1957) and Dick
Bentley v Arnold Smith Motors (1965)).
(b) Express terms are statements actually made by one of the parties with the intention that they become part of the contract and
thus binding and enforceable through court action if necessary. It is this intention that distinguishes the contractual term from
the mere representation, which, although it may induce the contractual agreement, does not become a term of the contract.
Failure to comply with the former gives rise to an action for breach of contract, whilst failure to comply with the latter only gives rise to an action for misrepresentation.
Such express statements may be made by word of mouth or in writing as long as they are sufficiently clear for them to be enforceable. Thus in Scammel v Ouston (1941) Ouston had ordered a van from the claimant on the understanding that the balance of the purchase price was to be paid ‘on hire purchase terms over two years’. When Scammel failed to deliver the van Ouston sued for breach of contract without success, the court holding that the supposed terms of the contract were too
uncertain to be enforceable. There was no doubt that Ouston wanted the van on hire purchase but his difficulty was that
Scammel operated a range of hire purchase terms and the precise conditions of his proposed hire purchase agreement were
never sufficiently determined.
Implied terms, however, are not actually stated or expressly included in the contract, but are introduced into the contract by implication. In other words the exact meaning and thus the terms of the contract are inferred from its context. Implied terms can be divided into three types.
Terms implied by statute
In this instance a particular piece of legislation states that certain terms have to be taken as constituting part of an agreement, even where the contractual agreement between the parties is itself silent as to that particular provision. For example, under s.5 of the Partnership Act 1890, every member of an ordinary partnership has the implied power to bind the partnership in a contract within its usual sphere of business. That particular implied power can be removed or reduced by the partnership agreement and any such removal or reduction of authority would be effective as long as the other party was aware of it. Some implied terms, however, are completely prescriptive and cannot be removed.
Terms implied by custom or usage
An agreement may be subject to terms that are customarily found in such contracts within a particular market, trade or locality. Once again this is the case even where it is not actually specified by the parties. For example, in Hutton v Warren (1836), it was held that customary usage permitted a farm tenant to claim an allowance for seed and labour on quitting his tenancy. It should be noted, however, that custom cannot override the express terms of an agreement (Les Affreteurs Reunnis SA v Walford (1919)).
Terms implied by the courts Generally, it is a matter for the parties concerned to decide the terms of a contract, but on occasion the court will presume that the parties intended to include a term which is not expressly stated. They will do so where it is necessary to give business efficacy to the contract.
Whether a term may be implied can be decided on the basis of the officious bystander test. Imagine two parties, A and B, negotiating a contract, when a third party, C, interrupts to suggest a particular provision. A and B reply that that particular term is understood. In just such a way, the court will decide that a term should be implied into a contract.
In The Moorcock (1889), the appellants, owners of a wharf, contracted with the respondents to permit them to discharge their ship at the wharf. It was apparent to both parties that when the tide was out the ship would rest on the riverbed. When the tide was out, the ship sustained damage by settling on a ridge. It was held that there was an implied warranty in the contract that the place of anchorage should be safe for the ship. As a consequence, the ship owner was entitled to damages for breach of that term.
Alternatively the courts will imply certain terms into unspecific contracts where the parties have not reduced the general agreement into specific details. Thus in contracts of employment the courts have asserted the existence of implied terms to impose duties on both employers and employees, although such implied terms can be overridden by express contractual provision to the contrary.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-04-14
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-04-01
- 2021-12-31
- 2021-05-08
- 2021-01-05
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-04-16
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-07-01
- 2021-04-15
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-07-16
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-16
- 2021-02-15
- 2021-06-09
- 2021-11-17
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-01-05
- 2021-04-16