宁夏考生:ACCA国际会计师报考条件中,具有高等专科以上学校毕业学历是什么意思?
发布时间:2020-01-10
既然选择了要走的路,就坚持下去,相信只要有信心,就一定能掌握自己的前途和命运。各位正在备考ACCA考试的小伙伴们,大家一定要坚持下去,攻克还有两个多月时间就要到来的ACCA考试。近期,有个小伙伴担心自己学历可能不够高,就问了51题库考试学习网一个关于报名的问题:考试条件中的高等专科学历是什么意思?是大专?高专?还是中专?51题库考试学习网就这个问题为大家答疑解惑:
想必有很多“资深”的ACCAer已经忘了报考条件是什么了吧?想必“萌新”的ACCAer还不清楚报考条件吧?不清楚自己是否符合报考条件吗?且随51题库考试学习网一起回忆一下关于报考ACCA考试的条件介绍:
报考国际注册会计师的条件有哪些?
报名国际注册会计师ACCA考试,具备以下条件之一即可:
1)凡具有教育部承认的大专以上学历,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
2)教育部认可的高等院校在校生,顺利完成大一的课程考试,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
3)未符合1、2项报名资格的16周岁以上的申请者,也可以先申请参加FIA(Foundations in Accountancy)基础财务资格考试。在完成基础商业会计(FAB)、基础管理会计(FMA)、基础财务会计(FFA)3门课程,并完成ACCA基础职业模块,可获得ACCA商业会计师资格证书(Diploma in Accounting and Business),资格证书后可豁免ACCAF1-F3三门课程的考试,直接进入技能课程的考试。
一直以来,ACCA都以培养国际性的高级会计、财务管理专家著称,其高质量的课程设计,高标准的考试要求,不仅赢得了联合国和各大国际性组织的高度评价,更为众多跨国公司和专业机构所推崇。
以上就是关于报考ACCA考试的条件介绍,由此可以看出,其实报考ACCA考试的门槛条件是比较低的了,相对于国内的注册会计师考试而言,少了工作年限。因此,让不少大学生也纷纷去报名参加考试。而至于“高等专科以上”是什么意思,可以从上面的条件得知:大专。因此,报考ACCA考试的最低学历都是大专学历,中专不行哦!
同样的路,有人敢走,有人不敢。走不走,不是路说了算,是看自己有没有那个胆。有的人摔了一跤也许一辈子再也不敢站起来走了,有目标的人,就算是摔得遍体鳞伤,依然勇往直前。人和人其实也没什么太多的差异,只在思维一念之间,学会换位思考,成就自己人生。坚持信念,找对平台,跟对人,懂得感恩,诚信为人,坚持不懈,梦想终会成真。无论是初次备考ACCA还是多次备考ACCA的同学,51题库考试学习网相信你定会赢!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Calculate the chargeable gain arising as a consequence of Jan accepting Jumper’s offer. (4 marks)
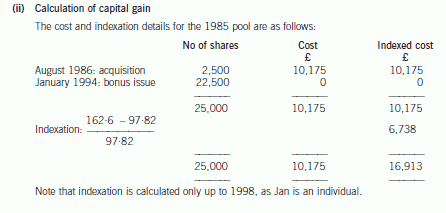

(d) Corporate annual reports contain both mandatory and voluntary disclosures.
Required:
(i) Distinguish, using examples, between mandatory and voluntary disclosures in the annual reports of
public listed companies. (6 marks)
(d) (i) Mandatory and voluntary disclosures
Mandatory disclosures
These are components of the annual report mandated by law, regulation or accounting standard.
Examples include (in most jurisdictions) statement of comprehensive income (income or profit and loss statement),
statement of financial position (balance sheet), cash flow statement, statement of changes in equity, operating segmental
information, auditors’ report, corporate governance disclosure such as remuneration report and some items in the
directors’ report (e.g. summary of operating position). In the UK, the business review is compulsory.
Voluntary disclosures
These are components of the annual report not mandated in law or regulation but disclosed nevertheless. They are
typically mainly narrative rather than numerical in nature.
Examples include (in most jurisdictions) risk information, operating review, social and environmental information, and
the chief executive’s review.
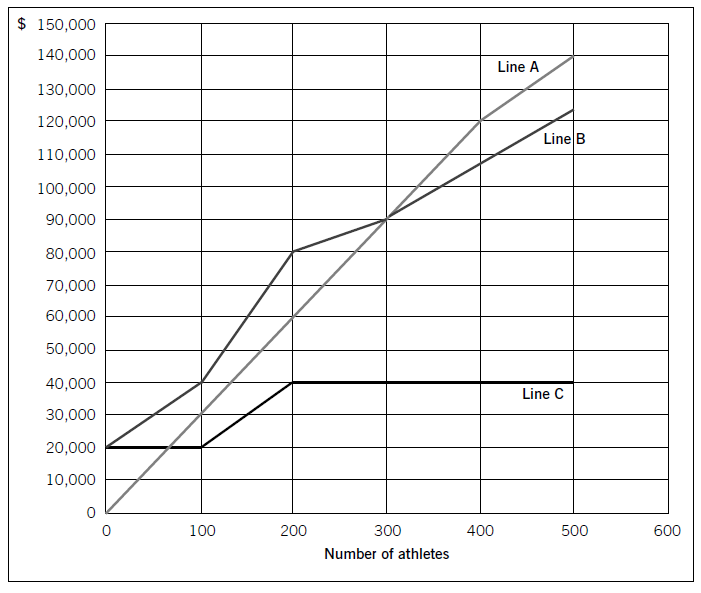
Swim Co offers training courses to athletes and has prepared the following breakeven chart:
Required:
(a) State the breakeven sales revenue for Swim Co and estimate, to the nearest $10,000, the company’s profit if 500 athletes attend a training course. (2 marks)
(b) Using the chart above, explain the cost and revenue structure of the company. (8 marks)
(a)ThebreakevensalesrevenueforSwimCois$90,000.Thecompany’sprofit,tothenearest$10,000,if500athletesattendthecourseis$20,000($140,000–$120,000).(Fromthegraph,itisclearthatthepreciseamountwillbenearer$17,000,i.e.$140,000–approximately$123,000.)(b)CoststructureFromthechart,itisclearthatLineCrepresentsfixedcosts,LineBrepresentstotalcostsandLineArepresentstotalrevenue.LineCshowsthatinitially,fixedcostsare$20,000evenifnoathletesattendthecourse.Thisleveloffixedcostsremainsthesameif100athletesattendbutoncethenumberofattendeesincreasesabovethislevel,fixedcostsincreaseto$40,000.LineBrepresentstotalcosts.If100athletesattend,totalcostsare$40,000($400perathlete).Since$20,000ofthisrelatestofixedcosts,thevariablecostperathletemustbe$200.Whenfixedcostsstepupbeyondthispointatthelevelof200athletes,totalcostsobviouslyincreaseaswellandLineBconsequentlygetsmuchsteeper.However,sincetherearenow200athletestoabsorbthefixedcosts,thecostperathleteremainsthesameat$400perathlete($80,000/200),eventhoughfixedcostshavedoubled.If300athletesattendthecourse,totalcostperathletebecomes$300each($90,000/300).Sincefixedcostsaccountfor$40,000ofthistotalcost,variablecoststotal$50,000,i.e.$166·67perathlete.So,economiesofscaleariseatthislevel,asdemonstratedbythefactthatLineBbecomesflatter.At400athletes,thegradientofthetotalcostslineisunchangedfrom300athleteswhichindicatesthatthevariablecostshaveremainedthesame.Thereisnofurtherchangeat500athletes;fixedandvariablecostsremainsteady.RevenuestructureAsregardstherevenuestructure,itcanbeseenfromLineAthatfor100–400athletesthepriceremainsthesameat$300perathlete.However,if500athletesattend,thepricehasbeenreducedasthetotalrevenuelinebecomesflatter.$140,000/500meansthatthepricehasgonedownto$280perathlete.Thiswasobviouslynecessarytoincreasethenumberofattendeesandatthispoint,profitismaximised.1
3 Local neighbourhood shops are finding it increasingly difficult to compete with supermarkets. However, three years
ago, the Perfect Shopper franchise group was launched that allowed these neighbourhood shops to join the group
and achieve cost savings on tinned and packaged goods, particularly groceries. Perfect Shopper purchases branded
goods in bulk from established food suppliers and stores them in large purpose-built warehouses, each designed to
serve a geographical region. When Perfect Shopper was established it decided that deliveries to these warehouses
should be made by the food suppliers or by haulage contractors working on behalf of these suppliers. Perfect Shopper
places orders with these suppliers and the supplier arranges the delivery to the warehouse. These arrangements are
still in place. Perfect Shopper has no branded goods of its own.
Facilities are available in each warehouse to re-package goods into smaller units, more suitable for the requirements
of the neighbourhood shop. These smaller units, typically containing 50–100 tins or packs, are usually small trays,
sealed with strong transparent polythene. Perfect Shopper delivers these to its neighbourhood shops using specialist
haulage contractors local to the regional warehouse. Perfect Shopper has negotiated significant discounts with
suppliers, part of which it passes on to its franchisees. A recent survey in a national grocery magazine showed that
franchisees saved an average of 10% on the prices they would have paid if they had purchased the products directly
from the manufacturer or from an intermediary – such as cash and carry wholesalers.
As well as offering savings due to bulk buying, Perfect Shopper also provides, as part of its franchise:
(i) Personalised promotional material. This usually covers specific promotions and is distributed locally, either using
specialist leaflet distributors or loosely inserted into local free papers or magazines.
(ii) Specialised signage for the shops to suggest the image of a national chain. The signs include the Perfect Shopper
slogan ‘the nation’s local’.
(iii) Specialist in-store display units for certain goods, again branded with the Perfect Shopper logo.
Perfect Shopper does not provide all of the goods required by a neighbourhood shop. Consequently, it is not an
exclusive franchise. Franchisees agree to purchase specific products through Perfect Shopper, but other goods, such
as vegetables, fruit, stationery and newspapers they source from elsewhere. Deliveries are made every two weeks to
franchisees using a standing order for products agreed between the franchisee and their Perfect Shopper sales
representative at a meeting they hold every three months. Variations to this order can be made by telephone, but only
if the order is increased. Downward variations are not allowed. Franchisees cannot reduce their standing order
requirements until the next meeting with their representative.
Perfect Shopper was initially very successful, but its success has been questioned by a recent independent report that
showed increasing discontent amongst franchisees. The following issues were documented.
(i) The need to continually review prices to compete with supermarkets
(ii) Low brand recognition of Perfect Shopper
(iii) Inflexible ordering and delivery system based around forecasts and restricted ability to vary orders (see above)
As a result of this survey, Perfect Shopper has decided to review its business model. Part of this review is to reexamine
the supply chain, to see if there are opportunities for addressing some of its problems.
Required:
(a) Describe the primary activities of the value chain of Perfect Shopper. (5 marks)
(a) Inbound logistics: Handling and storing bulk orders delivered by suppliers and stored on large pallets in regional warehouses.
All inbound logistics currently undertaken by the food suppliers or by contractors appointed by these suppliers.
Operations: Splitting bulk pallets into smaller packages, packing, sealing and storing these packages.
Outbound logistics: Delivery to neighbourhood shops using locally contracted distribution companies.
Marketing & Sales: Specially commissioned signs and personalised sales literature. Promotions and special offers.
Service: Specialist in-store display units for certain goods, three monthly meeting between franchisee and representative.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-23
- 2019-01-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-03
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-08-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-09-03
- 2021-05-02
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-17
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-28