2020年宁夏7月ACCA考试成绩查询时间
发布时间:2020-08-12
宁夏2020年7月ACCA考试成绩查询时间,大家想知道吗?下面51题库考试学习网就带领大家一起来了解看看宁夏ACCA考试成绩查询相关内容,感兴趣的小伙伴赶紧来围观吧。
根据官网消息,2020年7月ACCA考试成绩预计将于8月1日公布。
2020ACCA成绩查询方式与流程
ACCA成绩查询方式
1.电子邮件(e-mail)---您可在MYACCA内选择通过e-mail接收考试成绩。
2.短信通知---ACCA可采用短信通知考试成绩,但由于跨国服务较为复杂,可能不能接收短信。
3.网站查看考试成绩—在ACCA官网注册过的所有学生都能登录官网查看自己的成绩。
官网成绩查询的步骤:
1、登录
点击myACCA,输入学员账ID和密码,
2、点击exam entry,
查看自己的考试报名结果。
3、下载
确认好考试报名的信息后,一定要确认自己的身份信息,考试科目以及考试地点。点击“Download”j进行准考证的下载。
ACCA成绩查询结果显示:
到ACCA全球官方网站http://www.accaglobal.com/;点击Myacca登陆,点左面框架里的“EXAMS”进入页面,中间有一段:
EXAM STATUS REPORT Your status report
provides details of the ACCA exams you have already passed and those you have
still to complete
EXAM STATUS REPORT Your status report
provides details of the ACCA exams you have already passed and those you have
still to complete
View your status report————这个是超级链接,点进去就是你全部的考试分数记录了。
2020年ACCA成绩合格标准:
ACCA考试是百分制,50分为及格线。这意味着考生需要单科考试分数至少需要达到50分才算通过了考试。
成绩有效期:
ACCA 应用课程(F阶段)成绩有效期为无限期,战略课程(P阶段)成绩有效期为7年
ACCA考试期限跟CPA一样实行轮废制,即需要在一定的时间里面考完规定的科目,否则成绩将会无效。
时间计算:
根据以前的规则,学员必须在首次报名注册后10年内通过所有考试,否则将注销其学员资格。而后ACCA对时限做出了重要调整即:F段成绩永久有效,P段要在7年内考完。根据新规则,专业阶段考试的时限将为7年。因此,国际财会基础资格(Foundations in Accountancy,简称FIA)的考试以及ACCA资格考试的基础阶段F1-F9考试将不再有通过时限。
“7年政策”意味着从你通过P阶段的第一门科目开始,7年内需完成P阶段所要求的所有ACCA考试科目。否则,从第8年开始,你第1年所考过的P阶段科目成绩将会被视为过期作废,须重新考试。
另外,需要说明的是——此政策实行滚动式废除,也就是说不会在第8年时把你之前7年所有考过的P阶段科目成绩都废除,只会废除你第1年考过的P阶段科目成绩,第9年会废除你前2年所通过的P阶段科目成绩,以此类推。
以上是关于宁夏2020年7月ACCA考试成绩查询相关内容,小伙伴们都了解了吗?如果大家对于ACCA考试还有别的问题,可以多多关注51题库考试学习网,我们将继续为大家答疑解惑!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
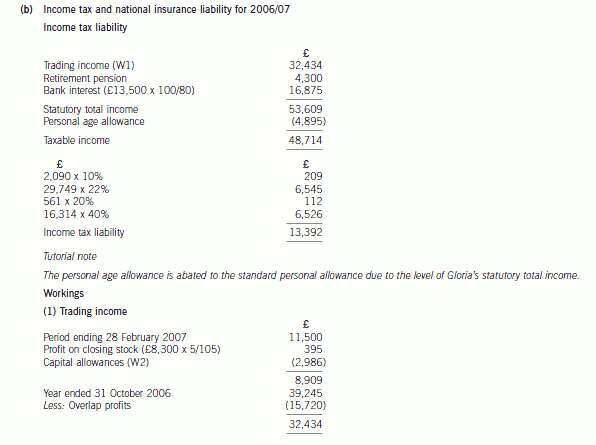
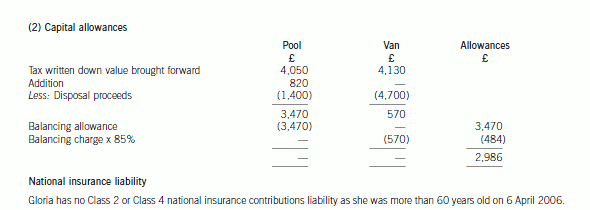
(b) Compute Gloria’s total income tax and national insurance liability for 2006/07. (7 marks)
(ii) Assuming that Donald operates through a company, advise Donald on the corporation tax (CT) that
would be payable for the year ended 31 March 2007 if he pays himself a gross salary of £31,000, plus
a net dividend of £10,000, instead of a gross salary of £42,648. (4 marks)

(b) Comment on the need for ethical guidance for accountants on money laundering. (4 marks)
(b) Need for ethical guidance
■ Accountants (firms and individuals) working in a country that criminalises money laundering are required to comply with
anti-money laundering legislation and failure to do so can lead to severe penalties. Guidance is needed because:
– legal requirements are onerous;
– money laundering is widely defined; and
– accountants may otherwise be used, unwittingly, to launder criminal funds.
■ Accountants need ethical guidance on matters where there is conflict between legal responsibilities and professional
responsibilities. In particular, professional accountants are bound by a duty of confidentiality to their clients. Guidance
is needed to explain:
– how statutory provisions give protection against criminal action for members in respect of their confidentiality
requirements;
– when client confidentiality over-ride provisions are available.
■ Further guidance is needed to explain the interaction between accountants’ responsibilities to report money laundering
offences and other reporting responsibilities, for example:
– reporting to regulators;
– auditor’s reports on financial statements (ISA 700);
– reports to those charged with governance (ISA 260);
– reporting misconduct by members of the same body.
■ Professional accountants are required to communicate with each other when there is a change in professional
appointment (i.e. ‘professional etiquette’). Additional ethical guidance is needed on how to respond to a ‘clearance’ letter
where a report of suspicion has been made (or is being contemplated) in respect of the client in question.
Tutorial note: Although the term ‘professional clearance’ is widely used, remember that there is no ‘clearance’ that the
incumbent accountant can give or withhold.
■ Ethical guidance is needed to make accountants working in countries that do not criminalise money laundering aware
of how anti-money laundering legislation may nevertheless affect them. Such accountants may commit an offence if,
for example, they conduct limited assignments or have meetings in a country having anti-money laundering legislation
(e.g. UK, Ireland, Singapore, Australia and the United States).
4 Graham Smith is Operations Director of Catering Food Services (CFS) a £1·5 billion UK based distributor of foods to
professional catering organisations. It has 30 trading units spread across the country from which it can supply a
complete range of fresh, chilled and frozen food products. Its customers range from major fast food chains, catering
services for the armed forces down to individual restaurants and cafes. Wholesale food distribution is very much a
price driven service, in which it is very difficult to differentiate CFS’s service from its competitors.
Graham is very aware of the Government’s growing interest in promoting good corporate environmental practices and
encouraging companies to achieve the international quality standard for environmentally responsible operations. CFS
operates a fleet of 1,000 lorries and each lorry produces the equivalent of its own weight in pollutants over the course
of a year without the installation of expensive pollution control systems. Graham is also aware that his larger
customers are looking to their distributors to become more environmentally responsible and the ‘greening’ of their
supply chain is becoming a real issue. Unfortunately his concern with developing a company-wide environmental
management strategy is not shared by his fellow managers responsible for the key distribution functions including
purchasing, logistics, warehousing and transportation. They argued that time spent on corporate responsibility issues
was time wasted and simply added to costs.
Graham has decided to propose the appointment of a project manager to develop and implement a company
environmental strategy including the achievement of the international quality standard. The person appointed must
have the necessary project management skills to see the project through to successful conclusion.
You have been appointed project manager for CFS’s ‘environmentally aware’ project.
Required:
(a) What are the key project management skills that are necessary in achieving company-wide commitment in
CFS to achieve the desired environmental strategy? (15 marks)
(a) Simply defined, a project is ‘activity that has a start, a middle and an end and consumes resources’ – it is therefore a discrete
activity aimed at achieving a specific objective or range of objectives. Graham is intent on using the ‘environmentally aware’
project to achieve a specific objective – the attainment of the international environmental standard. He is, however, aware
that there are a number of internal stakeholders inside the company who question the significance of such a project.
Externally, he can point to significant stakeholders, including customers and government who are looking for CFS to become
more environmentally aware. The project is likely to have strategic and not simply operational or administrative significance
and the person appointed into the role of project manager, ideally, should have both the traditional skills associated with
project management plus those of strategic management. Grundy and Brown list the traditional project management
techniques as:

Clearly, the project manager must have the technical project management skills, being able to manage the project through its
life cycle, which involves defining the project in terms of project objectives and scope as defined by time, cost and quality.
Planning the project in terms of breaking the overall project down into separate activities, estimating the resources required
and linking activities to resources in terms of time and priorities. Implementing the plan, including reviewing the progress in
meeting time and cost objectives and taking corrective action where and when necessary. Finally, reviewing the outcomes of
the project in terms of what was delivered to the customer and the extent to which client expectations were met.
The strategic nature of the project means that the project manager must have significant leadership skills, not only of the
project team, who are likely to come from different functions and parts of the company, but also influential stakeholders inside
and outside the company. This implies they should have good ‘political’ and communication skills as the project is of strategic
significance to the company. The ability to show how this particular project fits with the overall strategy of the firm is
important. The project is an important part in the achievement of the company strategy and in CFS’s case may help it
differentiate itself from its competitors. However, the project manager must recognise that there will be resistance from existing
managers reluctant to see resources committed to projects outside of the traditional value chain of the company. Certainly,
the project manager for the ‘environmentally aware’ project will themselves need to be aware of the external environmental
pressures prompting the firm to set itself specific environmental objectives and be able to link into supportive networks and
alliances. Finally, Grundy and Brown argue that the project manager will be the key to reviewing and learning from the project,
assessing whether defined objectives were achieved, the effectiveness or otherwise of the implementation process and how
key stakeholders were managed. The danger is that projects are seen as ‘one-off’ rather than contributing to the knowledge
and learning of the organisation. There may be a significant ‘learning curve’ that the firm has to go down and look tocontinuously improve its project management process.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-09-05
- 2019-01-05
- 2019-01-05
- 2021-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-05
- 2021-04-07
- 2021-04-08
- 2021-01-07
- 2021-01-06
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-01-07
- 2021-01-06
- 2021-01-06
- 2020-08-12
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-04-11
- 2021-04-07
- 2019-03-20
- 2019-03-20
- 2020-09-05
- 2019-01-05
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-09-05
- 2020-01-01