在西藏,ACCA考试通过了你不这样做你还是不能拿到证书
发布时间:2020-01-08
近些年,随着各式各样的考试风靡全国以来,ACCA证书也是从众多资格证书里脱颖而出,逐渐映入大众的眼帘。了解它的人称之为“金饭碗”,那么有些通过所以ACCA考试全部科目的小伙伴就来咨询51题库考试学习网,成绩通过之后,证书是怎么样领取呢?是等待官方邮寄过来?还是自己去申请领证呢?这些疑问51题库考试学习网会为大家逐一解决,请大家耐心地往下看哟~
首先要恭喜你成为了ACCA准会员了,当你通过14门ACCA考试的那一科开始,你就成为准会员了。但是需要注意的是从准会员并不是会员,想从准会员到ACCA会员,这些事情你必须要做:
1.ACCA每年2月份和8月份会分别公布12月份和6月份的考试成绩。每一个通过ACCA全部考试的学员随后会收到ACCA英国总部邮寄的《ACCA会员或准会员申请手册》(一般收到时间是3月初和9月初)。每人必须根据自身的情况,如是否满足ACCA相关工作经验要求,向ACCA英国申请成为会员或准会员。
2.ACCA总部收到学员申请后,不论是申请会员和准会员,都会给学员颁发ACCA准会员证书,以确认学员成功通过所有考试。
3.对于申请会员的学员,要求如实填写会员申请手册,并总结平时记录的STR(Student Training Record)中的主要工作经历和取得的工作能力,填入申请手册(在递交会员申请表时,可以暂时不提交STR,但是,一旦ACCA英国总部通知需要提交STR,以便了解更详细的信息完成评估,学员需要再补交STR)。ACCA英国总部会对学员所填的工作记录进行评估和并与其监督人联系进行核查,确认无误后,则批准其成为ACCA会员,一般这个过程需要两个月的时间。
4.如果学员在规定的时间内没有收到以上申请手册,可以直接登陆ACCA全球官网下载。
5.对于暂时未满足工作经验的准会员,可以在条件满足的任何时间向ACCA递交ACCA会员申请表。
完成了以上所有步骤之后,你就算是成功申请ACCA会员了,只需要等待官方发送证书即可。
都说,阳光总在风雨后,当你拿到通过自己努力获得的证书时,那份喜悦肯定是独一无二的,那一刻你也明白了自己的努力是值得的;所以,为了那一天的到来,各位ACCAer们加油复习,早日完成目标~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Volcan, a long-established limited liability company. Volcan operates
a national supermarket chain of 23 stores, five of which are in the capital city, Urvina. All the stores are managed in
the same way with purchases being made through Volcan’s central buying department and product pricing, marketing,
advertising and human resources policies being decided centrally. The draft financial statements for the year ended
31 March 2005 show revenue of $303 million (2004 – $282 million), profit before taxation of $9·5 million (2004
– $7·3 million) and total assets of $178 million (2004 – $173 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) On 1 May 2005, Volcan announced its intention to downsize one of the stores in Urvina from a supermarket to
a ‘City Metro’ in response to a significant decline in the demand for supermarket-style. shopping in the capital.
The store will be closed throughout June, re-opening on 1 July 2005. Goodwill of $5·5 million was recognised
three years ago when this store, together with two others, was bought from a national competitor. It is Volcan’s
policy to write off goodwill over five years. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Volcan for the year ended
31 March 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 VOLCAN
(a) Store impairment
(i) Matters
■ Materiality
? The cost of goodwill represents 3·1% of total assets and is therefore material.
? However, after three years the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) represents only 1·2% of total assets –
and is therefore immaterial in the context of the balance sheet.
? The annual amortisation charge ($1·1m) represents 11·6% profit before tax (PBT) and is therefore also
material (to the income statement).
? The impact of writing off the whole of the carrying amount would be material to PBT (23%).
Tutorial note: The temporary closure of the supermarket does not constitute a discontinued operation under IFRS 5
‘Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’.
■ Under IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ Volcan should no longer be writing goodwill off over five years but
subjecting it to an annual impairment test.
■ The announcement is after the balance sheet date and is therefore a non-adjusting event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the
Balance Sheet Date’) insofar as no provision for restructuring (for example) can be made.
■ However, the event provides evidence of a possible impairment of the cash-generating unit which is this store and,
in particular, the value of goodwill assigned to it.
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) can be allocated on a reasonable and consistent basis to this and the
other two stores (purchased at the same time) Volcan’s management should have applied an impairment test to
the goodwill of the downsized store (this is likely to show impairment).
■ If more than 22% of goodwill is attributable to the City Metro store – then its write-off would be material to PBT
(22% × $2·2m ÷ $9·5m = 5%).
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill cannot be so allocated; the impairment test should be applied to the
cash-generating unit that is the three stores (this may not necessarily show impairment).
■ Management should have considered whether the other four stores in Urvina (and elsewhere) are similarly
impaired.
■ Going concern is unlikely to be an issue unless all the supermarkets are located in cities facing a downward trend
in demand.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for stating the rules for recognition of an impairment loss for a cash-generating
unit. However, as it is expected that the majority of candidates will not deal with this matter, the rules of IAS 36 are
not reproduced here.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Board minutes approving the store’s ‘facelift’ and documenting the need to address the fall in demand for it as a
supermarket.
■ Recomputation of the carrying amount of goodwill (2/5 × $5·5m = $2·2m).
■ A schedule identifying all the assets that relate to the store under review and the carrying amounts thereof agreed
to the underlying accounting records (e.g. non-current asset register).
■ Recalculation of value in use and/or fair value less costs to sell of the cash-generating unit (i.e. the store that is to
become the City Metro, or the three stores bought together) as at 31 March 2005.
Tutorial note: If just one of these amounts exceeds carrying amount there will be no impairment loss. Also, as
there is a plan NOT to sell the store it is most likely that value in use should be used.
■ Agreement of cash flow projections (e.g. to approved budgets/forecast revenues and costs for a maximum of five
years, unless a longer period can be justified).
■ Written management representation relating to the assumptions used in the preparation of financial budgets.
■ Agreement that the pre-tax discount rate used reflects current market assessments of the time value of money (and
the risks specific to the store) and is reasonable. For example, by comparison with Volcan’s weighted average cost
of capital.
■ Inspection of the store (if this month it should be closed for refurbishment).
■ Revenue budgets and cash flow projections for:
– the two stores purchased at the same time;
– the other stores in Urvina; and
– the stores elsewhere.
Also actual after-date sales by store compared with budget.
(b) Anne is experiencing some tension due to the conflict between her duties and responsibilities as an employee of
Fillmore Pierce and as a qualified professional accountant.
Required:
(i) Compare and contrast her duties and responsibilities in the two roles of employee and professional
accountant. (6 marks)
(b) (i) Contrasting roles
Joint professional and organisational roles are common to most professionals (medical professionals, for example).
Although the roles are rarely in conflict, in most cases it is assumed that any professional’s primary duty is to the public
interest rather than the organisation.
Organisational role
As a member of the staff of Fillmore Pierce, Anne is a part of the hierarchy of an organisation and answerable to her
seniors. This means that under normal circumstances, she should comply with the requirements of her seniors. As an
employee, Anne is ultimately accountable to the principals of the organisation (the partners in an audit firm or the
shareholders in a company), and, she is subject to the cultural norms and reasonable expectations of work-group
membership. It is expected that her behaviour at work will conform. to the social and cultural norms of the organisation
and that she will be efficient and hard working in her job.
Professional role
As an accountant, Anne is obliged to maintain the high professional and ethical standards of her profession. If her
profession is underpinned by an ethical or professional code, she will need to comply with that in full. She needs to
manage herself and co-ordinate her activities so as to meet professional standards. In this, she needs to ensure that she
informs herself in current developments in her field and undertakes continuing professional development as required by
her professional accounting body. She is and will remain accountable to her professional body in terms of continued
registration and professional behaviour. In many cases, this accountability will be more important than an accountability
to a given employer as it is the membership of the professional body that validates Anne’s professional skills.
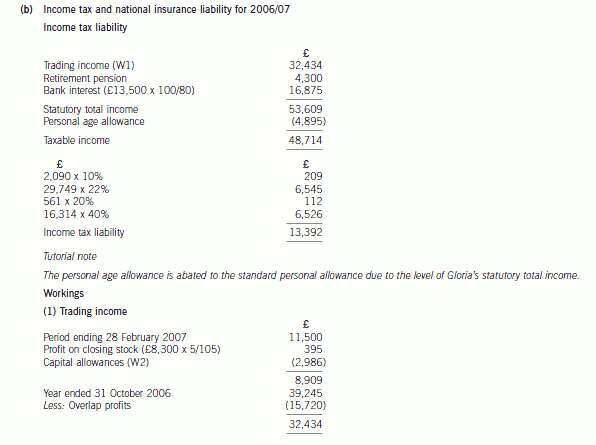
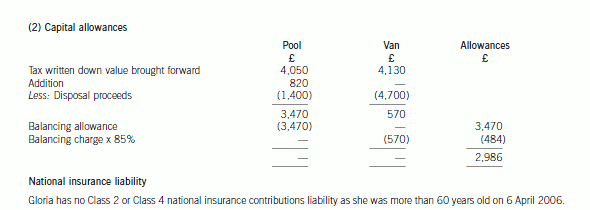
(b) Compute Gloria’s total income tax and national insurance liability for 2006/07. (7 marks)
(b) ‘opinion shopping’; (5 marks)
(b) ‘Opinion shopping’
Explanation of term
‘Opinion shopping’ occurs when management approach auditing firms (other than their incumbent auditors) to ask their views
on the application of accounting standards or principles to specific circumstances or transactions.
Ethical risks
The reasons for ‘opinion shopping’ may be:
■ to find alternative auditors; or
■ to get advice on a matter of contention with the incumbent auditor.
The member who is not the entity’s auditor must be alert to the possibility that their opinion – if it differs from that of the
incumbent auditor – may create undue pressure on the incumbent auditor’s judgement and so threaten the objectivity of the
audit.
Furthermore, by aligning with the interests of management when negotiating taking on an engagement, an incoming auditor
may compromise their objectivity even before the audit work commences. There is a risk that the audit fee might be seen to
be contingent upon a ‘favourable’ opinion (that is, the audit judgement coinciding with management’s preferences).
Employed professional accountants (accountants in industry) who support their company’s management in seeking second
opinions may call into question their integrity and professional behaviour.
Sufficiency of current ethical guidance
Current ethical guidance requires that when asked to provide a ‘second opinion’ a member should seek to minimise the risk
of giving inappropriate guidance, by ensuring that they have access to all relevant information.
The member should therefore:
■ ascertain why their opinion is being sought;
■ contact the auditor to provide any relevant facts;
■ with the entity’s permission, provide the auditor with a copy of their opinion.
The member’s opinion is more likely to differ if it is based on information which is different (or incomplete) as compared with
that available to the incumbent auditor. The member should therefore decline to act if permission to communicate with the
auditor is not given.
‘Opinion shopping’ might be less prevalent if company directors had no say in the appointment and remuneration of auditors.
If audit appointments were made by an independent body ‘doubtful accounting practices’ would (arguably) be less of a
negotiating factor. However, to be able to appoint auditors to multi-national/global corporations, such measures would require
the backing of regulatory bodies worldwide.
Statutory requirements in this area could also be more stringent. For example, an auditor may be required to deposit a
‘statement of circumstances’ (or a statement of ‘no circumstances’) in the event that they are removed from office or resign.
However, disclosure could be made more public if, when a change in accounting policy coincides with a change of auditors,
the financial statements and auditor’s report highlight the change and the auditors state their concurrence (or otherwise) with
the change. This could be made a statutory requirement and International Standards on Auditing (ISAs) amended to give
guidance on how auditors should report on changes.
Further, if the incoming auditor were to have a statutory right of access to the files and working papers of the outgoing auditors
they would be able to make a better and informed assessment of the desirability of the client and also appreciate the validity
(or otherwise) of any ‘statement’ issued by the outgoing auditor.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-09-04
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-02-29
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-02-29
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-04-09
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20