上海市考生注意:在ACCA考试中提前交卷后果怎么样?不堪设想……
发布时间:2020-01-09
近期,有不少第一次备考ACCA考试的小伙伴来咨询51题库考试学习网,问:考试能不能提前交卷呢?在这里告诉大家,根据考试的相关规定是不允许的。什么?还有些小伙伴不知道考试时应当注意些什么?没关系,现在了解还来得及,51题库考试学习网这就将相关注意事项告诉大家:
ACCA考试之前注意事项:
1.考生必须准时到场考试,一旦迟到,考试时间不会延长。因此,再次强调考生必须时刻关注考试时间,以防迟到。
2.三小时答题时间及15分钟的读题时间以准考证时间为准。阅读过程中,考生可以浏览试题册,但是不能打开并书写答题册。如果违法相关规定,有可能会取消考试资格
3.需要注意的还有,考试开始一小时后,考生不允许再进入考场。
4.直到考试结束,考生才允许离开考场。
5.如果考生要求短时间离开考场,必须有监考人员陪同。
6.不得私自携带手机等电子工具,考生必须将书包和公文包放置监考人员规定处。
7.对于笔考的科目,考生只能用黑色圆珠笔作答。
8.考生必须确认自己参加的考试的代号与准考证上的考试科目代号一致。
ACCA考试时的注意事项有哪些?
1.在新版的考生答题册上(candidate answer booklet)的第一页仔细填涂以下项目
1)考试的科目和版本(注:如P2,应填INT;F4填写ENG;F6填写UK等)
2)考场代码(包括Hall code)考场名字和座位号
3)以上信息均在你个人的准考证(Exam Attendance Docket)上有显示;
2.在新的一页上开始每答一道新题,要在这页上部填涂题号;
3.所有答题均使用黑色圆珠笔作答,(铅笔,黑色签字笔,荧光笔等不允许);
4.答错可划掉错误的答案,不允许使用涂改液;51题库考试学习网建议考生在不确定答案的时候最好不要填写,卷面也是影响得分的一大因素
5.不能将答案写在答题纸边缘及答题本两页的中间位置,否则将视为无效作答;
学生如需要,可索要第二本答题本,第二本答题本上同样必须填写完整个人信息。
当然,对于笔考,机考的确是有些差别的。这主要体现在:
1、大题部分需要通过计算机进行解答,相较于笔试,计算机打字能力和某些公式的熟练度会间接地影响考试结果;
2、考试时间有所不同。目前,应用技能课程的机考时间均为3个小时,而战略课程的笔试一般为3小时15分钟,SBL为4个小时。因此,考试在考试之前需要提前了解是机考还是笔考,以免出现战略层面上的失误。
以上ACCA考试的注意事项大家要提高警觉哦,遇到了上文提到以外突发事故及时向监考老师提出来,听从监考老师的安排即可,不要因为突发事件而影响了自己的考试心态从而影响到成绩。调整好心态,重新积极考试!~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(d) Estimate by how much the bid might be increased without the shareholders of Paxis suffering a fall in their expected wealth, and discuss whether or not the directors of Paxis should proceed with the bid. (5 marks)
(d) The current bid values the shares of Wragger at £19·07 million, compared to the current market value of £15·36 million, a premium of £3·71 million. The expected synergy is £15,570,000. If these data are accurate the bid could be substantially increased without the shareholders of Paxis suffering a fall in their expected wealth. In theory, the bid could be increased by an additional £11,860,000, or 148 pence for each existing Wragger share.
There might also be strategic reasons for undertaking the bid, and the acquisition of Wragger might lead to future options that are not valued by the above analysis.
The proposed acquisition is expected to result in substantial synergy, and to create wealth for the shareholders of both companies. The directors are recommended to proceed with the bid.
(ii) Describe the evidence you would seek to support the assertion that development costs are technically
feasible. (3 marks)
(ii) Evidence supporting the assertion that development costs are technically feasible would include the following:
– Review the results of scientific tests performed on the products, for example, the results of animal or human testing
of the products.
– Discuss any detrimental results of these tests, e.g. harmful side effects, with the scientists working on the project
to determine what corrective action is being taken.
– Enquire whether any licences necessary for continued development and/or commercial production have been
granted by the appropriate regulatory body.
– Compare expected to actual development costs incurred per product being developed. Where actual costs are in
excess of expected costs investigate whether the extra costs have been incurred in order to make good any problems
identified in the development process.
– Review board minutes for relevant discussion of the product development taking place during the year.
1 Stuart is a self-employed business consultant aged 58. He is married to Rebecca, aged 55. They have one child,
Sam, who is aged 24 and single.
In November 2005 Stuart sold a house in Plymouth for £422,100. Stuart had inherited the house on the death of
his mother on 1 May 1994 when it had a probate value of £185,000. The subsequent pattern of occupation was as
follows:
1 May 1994 to 28 February 1995 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca as main residence
1 March 1995 to 31 December 1998 unoccupied
1 January 1999 to 31 March 2001 let out (unfurnished)
1 April 2001 to 30 November 2001 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca
1 December 2001 to 30 November 2005 used occasionally as second home
Both Stuart and Rebecca had lived in London from March 1995 onwards. On 1 March 2001 Stuart and Rebecca
bought a house in London in their joint names. On 1 January 2002 they elected for their London house to be their
principal private residence with effect from that date, up until that point the Plymouth property had been their principal
private residence.
No other capital disposals were made by Stuart in the tax year 2005/06. He has £29,500 of capital losses brought
forward from previous years.
Stuart intends to invest the gross sale proceeds from the sale of the Plymouth house, and is considering two
investment options, both of which he believes will provide equal risk and returns. These are as follows:
(1) acquiring shares in Omikron plc; or
(2) acquiring further shares in Omega plc.
Notes:
1. Omikron plc is a listed UK trading company, with 50,250,000 shares in issue. Its shares currently trade at 42p
per share.
2. Stuart and Rebecca helped start up the company, which was then Omega Ltd. The company was formed on
1 June 1990, when they each bought 24,000 shares for £1 per share. The company became listed on 1 May
1997. On this date their holding was subdivided, with each of them receiving 100 shares in Omega plc for each
share held in Omega Ltd. The issued share capital of Omega plc is currently 10,000,000 shares. The share price
is quoted at 208p – 216p with marked bargains at 207p, 211p, and 215p.
Stuart and Rebecca’s assets (following the sale of the Plymouth house but before any investment of the proceeds) are
as follows:
Assets Stuart Rebecca
£ £
Family house in London 450,000 450,000
Cash from property sale 422,100 –
Cash deposits 165,000 165,000
Portfolio of quoted investments – 250,000
Shares in Omega plc see above see above
Life insurance policy note 1 note 1
Note:
1. The life insurance policy will pay out a sum of £200,000 on the death of the first spouse to die.
Stuart has recently been diagnosed with a serious illness. He is expected to live for another two or three years only.
He is concerned about the possible inheritance tax that will arise on his death. Both he and Rebecca have wills whose
terms transfer all assets to the surviving spouse. Rebecca is in good health.
Neither Stuart nor Rebecca has made any previous chargeable lifetime transfers for the purposes of inheritance tax.
Required:
(a) Calculate the taxable capital gain on the sale of the Plymouth house in November 2005 (9 marks)
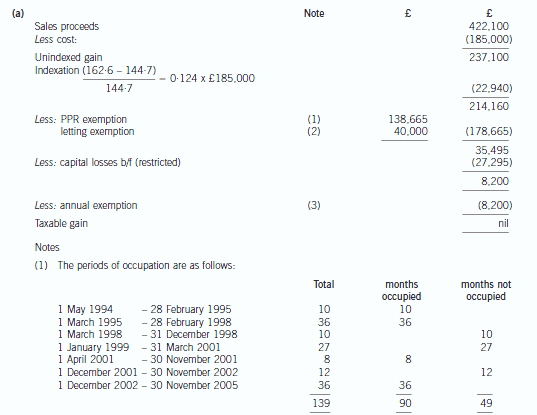
Note that the last 36 months count as deemed occupation, as the house was Stuart’s principal private residence (PPR)
at some point during his period of ownership.
The first 36 months of the period from 1 March 1995 to 31 March 2001 qualifies as a deemed occupation period as
Stuart and Rebecca returned to occupy the property on 1 April 2001. The remainder of the period will be treated as a
period of absence, although letting relief is available for part of the period (see below).
The exempt element of the gain is the proportion during which the property was occupied, real or deemed. This is
£138,665 (90/139 x £214,160).
(2) The chargeable gain is restricted for the period that the property was let out. This is restricted to the lowest of the
following:
(i) the gain attributable to the letting period (27/139 x 214,160) = £41,599
(ii) £40,000
(iii) the total exempt PPR gain = £138,665
i.e. £40,000.
(3) The taper relief is effectively wasted, having restricted losses b/f to preserve the annual exemption.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-05-12
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-05-15
- 2021-06-13
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-02-06
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-07
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-04-04
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-04
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-02-13
- 2020-02-06
- 2021-05-23