你知道ACCA什么时候全面机考吗?
发布时间:2020-04-18
相信大家都或多或少的听说过ACCA。那么什么是ACCA呢?由51题库考试学习网为您进行解答。ACCA是目前财经领域认可度最高的资格证书,也是世界上拥有学员和会员最多的,为此还被我国称之为“国际注册会计师”。最近,听说ACCA 将要全面实施机考考试,那不知道的朋友们快跟着51题库考试学习网给大家带来的这篇文章吧!
截止到2020年,ACCA专业阶段考试仍在我国国内全面推行着笔考考试,但近日官方又发布重要改革信息,从2021年3月考试季开始,将在我国全面施行战略性专业课程的机考考试。根据查询结果显示,ACCA SP阶段机考考试的大体时间为2021年3月,香港地区为2021年9月。当然也有部分地区并没有确定大概的时间,例如:澳大利亚。在全面机考的大形势下,运用崭新的机考答题技巧已成为我们能否正常发挥,甚至超常发挥个人ACCA水平的重要因素。
看了ACCA的一些政策后,那关于ACCA的其他内容你知道吗?要不接着看下去吧!
缴费情况:
在ACCA官网缴费是支持使用银联卡和支付宝的。但ACCA总部推荐学员使用双币信用卡在线考试报名。这样将可以及时确认报名成功并且可以享受提前考试报名时段的优惠价格。 但如果在我们缴纳ACCA报名费时,网页显示报名成功,但未收到银行扣款通知怎么办?如果其他步骤都没有出错,并且有显示报考成功的话,有可能是由于因为报名时ACCA使用的信用卡预授权消费,信用卡发卡行会先把你这笔缴费款冻结住,一般银行过1-2个工作日会跟ACCA官方对账,确定这笔款项真的没问题时,才会把费用真正扣除。所以,当出现上述情况时,先检查自己的各项信息,没错的话,可以过两天再查询具体情况吧!
就业前景:
国际知名机构建立了密切的合作关系,包括跨国企业、各国地方企业、其他会计师组织、教育机构、以及联合国、世界银行等世界性组织。全球共有7000多家ACCA认证雇主,其中在中国有超过700家ACCA认证雇主,这些认证雇主企业将优先录用及提升ACCA会员及毕业生。
ACCA未来的就业方向和行业主要集中在以下公司:
国际国内大型银行及投资银行:花旗银行、汇丰银行、渣打银行、中国工商银行、中国银行等。
保险及金融投资机构:中国国际金融公司、美国高盛、美国友邦保险、鼎辉投资等。
国际知名企业:可口可乐(中国)有限公司、微软(中国)有限公司、西门子中国有限公司等。
中国大型国有及民营企业:中国移动通信集团、中国石油天然气集团、阿里巴巴、联想集团等。
国际知名咨询企业及会计师事务所:麦肯锡、埃森哲、四大国际会计师事务所。
以上就是由51题库考试学习网为您带来的有关AACA的相关信息了,想要获取更多信息的同学,请持续关注51题库考试学习网。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
2 Clifford and Amanda, currently aged 54 and 45 respectively, were married on 1 February 1998. Clifford is a higher
rate taxpayer who has realised taxable capital gains in 2007/08 in excess of his capital gains tax annual exemption.
Clifford moved into Amanda’s house in London on the day they were married. Clifford’s own house in Oxford, where
he had lived since acquiring it for £129,400 on 1 August 1996, has been empty since that date although he and
Amanda have used it when visiting friends. Clifford has been offered £284,950 for the Oxford house and has decided
that it is time to sell it. The house has a large garden such that Clifford is also considering an offer for the house and
a part only of the garden. He would then sell the remainder of the garden at a later date as a building plot. His total
sales proceeds will be higher if he sells the property in this way.
Amanda received the following income from quoted investments in 2006/07:
£
Dividends in respect of quoted trading company shares 1,395
Dividends paid by a Real Estate Investment Trust out of tax exempt property income 485
On 1 May 2006, Amanda was granted a 22 year lease of a commercial investment property. She paid the landlord
a premium of £6,900 and also pays rent of £2,100 per month. On 1 June 2006 Amanda granted a nine year
sub-lease of the property. She received a premium of £14,700 and receives rent of £2,100 per month.
On 1 September 2006 Amanda gave quoted shares with a value of £2,200 to a registered charity. She paid broker’s
fees of £115 in respect of the gift.
Amanda began working for Shearer plc, a quoted company, on 1 June 2006 having had a two year break from her
career. She earns an annual salary of £38,600 and was paid a bonus of £5,750 in August 2006 for agreeing to
come and work for the company. On 1 August 2006 Amanda was provided with a fully expensed company car,
including the provision of private petrol, which had a list price when new of £23,400 and a CO2 emissions rate of
187 grams per kilometre. Amanda is required to pay Shearer plc £22 per month in respect of the private use of the
car. In June and July 2006 Amanda used her own car whilst on company business. She drove 720 business miles
during this two month period and was paid 34 pence per mile. Amanda had PAYE of £6,785 deducted from her gross
salary in the tax year 2006/07.
After working for Shearer plc for a full year, Amanda becomes entitled to the following additional benefits:
– The opportunity to purchase a large number of shares in Shearer plc on 1 July 2007 for £3·30 per share. It is
anticipated that the share price on that day will be at least £7·50 per share. The company will make an interestfree
loan to Amanda equal to the cost of the shares to be repaid in two years.
– Exclusive free use of the company sailing boat for one week in August 2007. The sailing boat was purchased by
Shearer plc in January 2005 for use by its senior employees and costs the company £1,400 a week in respect
of its crew and other running expenses.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate Clifford’s capital gains tax liability for the tax year 2007/08 on the assumption that the Oxford
house together with its entire garden is sold on 31 July 2007 for £284,950. Comment on the relevance
to your calculations of the size of the garden; (5 marks)
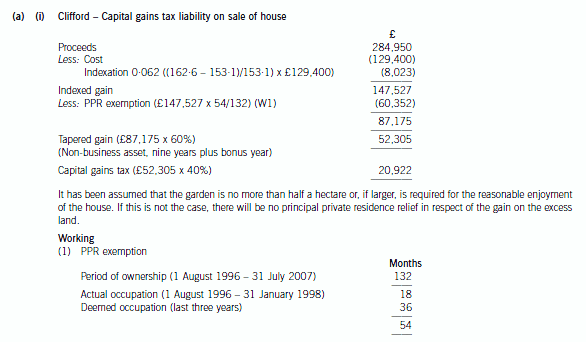
(c) Critically discuss the statement (in note 12) of the managing director of GBC and suggest how the company
could calculate the value of the service provision to the population of the Western region. (6 marks)
(c) It would appear that in operating a bus service to the Western region of Geeland that GBC is fulfilling a social objective since
a contribution loss amounting to $38,400 ($230,400 – $268,800) was made as a consequence of operating the route to
the Western region during 2007. As an organisation which is partially funded by the government it is highly probable that
GBC has objectives which differ from those of TTC which is a profit-seeking organisation.
The value of a social service such as the provision of public transport can be quantified, albeit, in non-financial times. It is
possible to apply quantitative measures to the bus service itself, the most obvious ones being the number of passengers
carried and the number of passenger miles travelled.
The cost of the provision of alternative transport to the Western region might also enable a value to be placed on the current
service by GBC.
It might be possible to estimate quantitatively some of the social benefits resulting from the provision of the transport facility
to and from the Western region. For example, GBC could undertake a survey of the population of the Western region in order
to help estimate the extent to which rural depopulation would otherwise have occurred had the transport facility not been
made.
The application of the technique of cost-benefit analysis makes it possible to estimate money values for non-monetary
benefits. Social benefits can therefore be expressed in financial terms. It is highly probable that the fact that the Western region
is served by GBC will increase the attractiveness of living in a rural area, which may in turn precipitate an increase in property
values in the Western region and the financial benefit could be expressed in terms of the aggregate increase in property values
in the region as a whole.
The following financial information relates to HGR Co:
Statement of financial position at the current date (extracts)
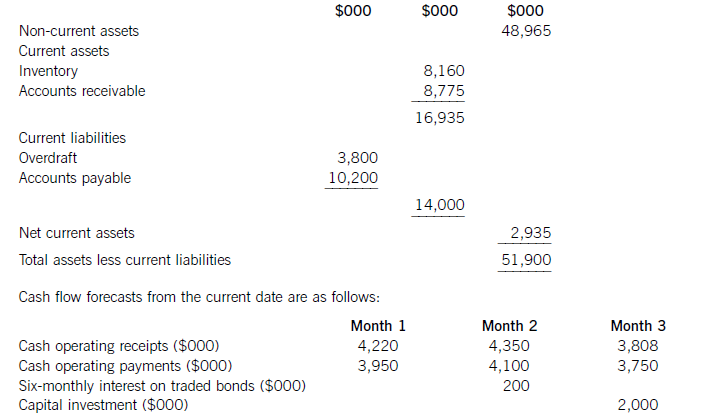
The finance director has completed a review of accounts receivable management and has proposed staff training and operating procedure improvements, which he believes will reduce accounts receivable days to the average sector value of 53 days. This reduction would take six months to achieve from the current date, with an equal reduction in each month. He has also proposed changes to inventory management methods, which he hopes will reduce inventory days by two days per month each month over a three-month period from the current date. He does not expect any change in the current level of accounts payable.
HGR Co has an overdraft limit of $4,000,000. Overdraft interest is payable at an annual rate of 6·17% per year, with payments being made each month based on the opening balance at the start of that month. Credit sales for the year to the current date were $49,275,000 and cost of sales was $37,230,000. These levels of credit sales and cost of sales are expected to be maintained in the coming year. Assume that there are 365 working days in each year.
Required:
(a) Discuss the working capital financing strategy of HGR Co. (7 marks)
(b) For HGR Co, calculate:
(i) the bank balance in three months’ time if no action is taken; and
(ii) the bank balance in three months’ time if the finance director’s proposals are implemented.
Comment on the forecast cash flow position of HGR Co and recommend a suitable course of action.
(10 marks)
(c) Discuss how risks arising from granting credit to foreign customers can be managed and reduced.
(8 marks)
(a)Whenconsideringthefinancingofworkingcapital,itisusefultodividecurrentassetsintofluctuatingcurrentassetsandpermanentcurrentassets.Fluctuatingcurrentassetsrepresentchangesinthelevelofcurrentassetsduetotheunpredictabilityofbusinessactivity.Permanentcurrentassetsrepresentthecorelevelofinvestmentincurrentassetsneededtosupportagivenlevelofturnoverorbusinessactivity.Asturnoverorlevelofbusinessactivityincreases,thelevelofpermanentcurrentassetswillalsoincrease.Thisrelationshipcanbemeasuredbytheratioofturnovertonetcurrentassets.Thefinancingchoiceasfarasworkingcapitalisconcernedisbetweenshort-termandlong-termfinance.Short-termfinanceismoreflexiblethanlong-termfinance:anoverdraft,forexample,isusedbyabusinessorganisationastheneedarisesandvariableinterestischargedontheoutstandingbalance.Short-termfinanceisalsomoreriskythanlong-termfinance:anoverdraftfacilitymaybewithdrawn,orashort-termloanmayberenewedonlessfavourableterms.Intermsofcost,thetermstructureofinterestratessuggeststhatshort-termdebtfinancehasalowercostthanlong-termdebtfinance.Thematchingprinciplesuggeststhatlong-termfinanceshouldbeusedforlong-terminvestment.Applyingthisprincipletoworkingcapitalfinancing,long-termfinanceshouldbematchedwithpermanentcurrentassetsandnon-currentassets.Afinancingpolicywiththisobjectiveiscalleda‘matchingpolicy’.HGRCoisnotusingthisfinancingpolicy,sinceofthe$16,935,000ofcurrentassets,$14,000,000or83%isfinancedfromshort-termsources(overdraftandtradepayables)andonly$2,935,000or17%isfinancedfromalong-termsource,inthiscaseequityfinance(shareholders’funds)ortradedbonds.ThefinancingpolicyorapproachtakenbyHGRCotowardsthefinancingofworkingcapital,whereshort-termfinanceispreferred,iscalledanaggressivepolicy.Relianceonshort-termfinancemakesthisriskierthanamatchingapproach,butalsomoreprofitableduetothelowercostofshort-termfinance.Followinganaggressiveapproachtofinancingcanleadtoovertrading(undercapitalisation)andthepossibilityofliquidityproblems.(b)Bankbalanceinthreemonths’timeifnoactionistaken:Workings:ReductioninaccountsreceivabledaysCurrentaccountsreceivabledays=(8,775/49,275)x365=65daysReductionindaysoversixmonths=65–53=12daysMonthlyreduction=12/6=2daysEachreceivablesdayisequivalentto8,775,000/65=$135,000(Alternatively,eachreceivablesdayisequivalentto49,275,000/365=$135,000)Monthlyreductioninaccountsreceivable=2x135,000=$270,000ReductionininventorydaysCurrentinventorydays=(8,160/37,230)x365=80daysEachinventorydayisequivalentto8,160,000/80=$102,000(Alternatively,eachinventoryday=37,230,000/365=$102,000)Monthlyreductionininventory=102,000x2=$204,000OverdraftinterestcalculationsMonthlyoverdraftinterestrate=1·06171/12=1·005or0·5%Ifnoactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0·005=$19,000Period2interest=3,549,000x0·005=$17,745or$18,000Period3interest=3,517,000x0·005=$17,585or$18,000Ifactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0.005=$19,000Period2interest=3,075,000x0.005=$15,375or$15,000Period3interest=2,566,000x0.005=$12,830or$13,000DiscussionIfnoactionistaken,thecashflowforecastshowsthatHGRCowillexceeditsoverdraftlimitof$4millionby$1·48millioninthreemonths’time.Ifthefinancedirector’sproposalsareimplemented,thereisapositiveeffectonthebankbalance,buttheoverdraftlimitisstillexceededinthreemonths’time,althoughonlyby$47,000ratherthanby$1·47million.Ineachofthethreemonthsfollowingthat,thecontinuingreductioninaccountsreceivabledayswillimprovethebankbalanceby$270,000permonth.Withoutfurtherinformationonoperatingreceiptsandpayments,itcannotbeforecastwhetherthebankbalancewillreturntolessthanthelimit,orevencontinuetoimprove.Themainreasonfortheproblemwiththebankbalanceisthe$2millioncapitalexpenditure.Purchaseofnon-currentassetsshouldnotbefinancedbyanoverdraft,butalong-termsourceoffinancesuchasequityorbonds.Ifthecapitalexpenditurewereremovedfromtheareaofworkingcapitalmanagement,theoverdraftbalanceattheendofthreemonthswouldbe$3·48millionifnoactionweretakenand$2·05millionifthefinancedirector’sproposalswereimplemented.GiventhatHGRCohasalmost$50millionofnon-currentassetsthatcouldpossiblybeusedassecurity,raisinglong-termdebtthrougheitherabankloanorabondissueappearstobesensible.Assumingabondinterestrateof10%peryear,currentlong-termdebtintheform.oftradedbondsisapproximately($200mx2)/0·1=$4m,whichismuchlessthantheamountofnoncurrentassets.AsuitablecourseofactionforHGRCotofollowwouldthereforebe,firstly,toimplementthefinancedirector’sproposalsand,secondly,tofinancethecapitalexpenditurefromalong-termsource.Considerationcouldalsobegiventousingsomelong-termdebtfinancetoreducetheoverdraftandtoreducethelevelofaccountspayable,currentlystandingat100days.(c)Whencreditisgrantedtoforeigncustomers,twoproblemsmaybecomeespeciallysignificant.First,thelongerdistancesoverwhichtradetakesplaceandthemorecomplexnatureoftradetransactionsandtheirelementsmeansforeignaccountsreceivableneedmoreinvestmentthantheirdomesticcounterparts.Longertransactiontimesincreaseaccountsreceivablebalancesandhencetheleveloffinancingandfinancingcosts.Second,theriskofbaddebtsishigherwithforeignaccountsreceivablethanwiththeirdomesticcounterparts.Inordertomanageandreducecreditrisks,therefore,exportersseektoreducetheriskofbaddebtandtoreducethelevelofinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivable.Manyforeigntransactionsareon‘openaccount’,whichisanagreementtosettletheamountoutstandingonapredetermineddate.Openaccountreflectsagoodbusinessrelationshipbetweenimporterandexporter.Italsocarriesthehighestriskofnon-payment.Onewaytoreduceinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableistoagreeearlypaymentwithanimporter,forexamplebypaymentinadvance,paymentonshipment,orcashondelivery.Thesetermsoftradeareunlikelytobecompetitive,however,anditismorelikelythatanexporterwillseektoreceivecashinadvanceofpaymentbeingmadebythecustomer.Onewaytoacceleratecashreceiptsistousebillfinance.Billsofexchangewithasignedagreementtopaytheexporteronanagreedfuturedate,supportedbyadocumentaryletterofcredit,canbediscountedbyabanktogiveimmediatefunds.Thisdiscountingiswithoutrecourseifbillsofexchangehavebeencountersignedbytheimporter’sbank.Documentarylettersofcreditareapaymentguaranteebackedbyoneormorebanks.Theycarryalmostnorisk,providedtheexportercomplieswiththetermsandconditionscontainedintheletterofcredit.Theexportermustpresentthedocumentsstatedintheletter,suchasbillsoflading,shippingdocuments,billsofexchange,andsoon,whenseekingpayment.Aseachsupportingdocumentrelatestoakeyaspectoftheoveralltransaction,lettersofcreditgivesecuritytotheimporteraswellastheexporter.Companiescanalsomanageandreduceriskbygatheringappropriateinformationwithwhichtoassessthecreditworthinessofnewcustomers,suchasbankreferencesandcreditreports.Insurancecanalsobeusedtocoversomeoftherisksassociatedwithgivingcredittoforeigncustomers.Thiswouldavoidthecostofseekingtorecovercashduefromforeignaccountsreceivablethroughaforeignlegalsystem,wheretheexportercouldbeatadisadvantageduetoalackoflocalorspecialistknowledge.Exportfactoringcanalsobeconsidered,wheretheexporterpaysforthespecialistexpertiseofthefactorasawayofreducinginvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableandreducingtheincidenceofbaddebts.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-05
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-02
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-03-15
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-04-04
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-12
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-04-17
- 2020-05-06
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-03-29
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-01