如何帮助云南省考生高效的学习ACCA考试?
发布时间:2020-01-10
2020年已经到来,第一次ACCAer们对考试已经了解了多少了呢?一点也不了解也不用担心,51题库考试学习网帮助大家收集到了一些关于考试的高效学习技巧,希望对备考的你有多帮助,现在且随51题库考试学习网,告诉你怎有哪些技巧吧:
复习的首要任务是巩固和加深对所学知识的理解和记忆。首先,要根据教材的知识体系确定好一个中心内容,把主要精力集中在教材的中心、重点和难点上,不真正搞懂,决不放松。其次,要及时巩固,防止遗忘。复习最好在遗忘之前,倘若在遗忘之后,效率就低了。复习还要经常,不能一曝十寒。
对于一个新人而言,刚刚学ACCA,肯定都在想:我是报班呢还是报班呢?报班的话该选择什么样的辅导班?其次,如果自学的话有没有希望?
首先,明确一点,无论是否报班学习,最终决定成败的还是自己。
其次ACCA学习是一个由浅入深、由简到难的过程。对于学习能力好的大神来说,选择自学也是没有问题的!但是这个过程会耗时耗力,难抓住重点,如果有高顿经验丰富的老师身经百战总结出来的重要知识点,将会如虎添翼!
最后自学备考ACCA的过程重在坚持,但是大多数人都会被周围的事情分散注意力而导致备考意志力不够坚定,最后的结果也很失败。而报高顿ACCA面授课,除了有专业讲师系统性的讲解,针对性的答疑,能遇到许多志同道合的小伙伴,互相鼓励,互相监督,更有负责的学管团队全程及时提醒沟通,帮你克服意志力薄弱的问题,早日全科通关。
学习acca是否有必要参加辅导班
根据每个人的基础来判别,有些基础比较好的考生,简单的科目完全自学,难点科目自己看看网课就可以顺利通过了;基础一般的同学大部分科目需要借助网课的帮助来通过考试;基础较差的同学可能就需要面授课老师来帮忙了。不管哪个级别的考生,基本上是不太可能不借助任何辅导通过的。
基础较差的考生参加ACCA辅导班跟着老师学习,会轻松很多,也会节省很多时间,自己自学不知道重点,遇到知识点要弄很久才弄明白,比较费劲。
所以考生们可以根据自己的情况来安排辅导的力度哦。
具体的备考步骤分为以下四步:
第一步是拿2-3套ACCA真题,自己扫一遍所有的题干,可以不看题目,然后用这几套真题总结一下出题的套路和重点的知识点。ACCA的考试中重要的知识点一定是每年都出的,用这几套完全可以总结出重要知识点。当然如果真的基础不错,可以拿一套真题先做一下,然后你就有动力去进行后续的复习了。
第二步是看书,不过是先根据课本的目录,给自己梳理出来一个框架图,然后结合第一步的总结,所有的重点都一目了然。
第三步就是看书了,ACCA的教材一般会分为16-18个章节,一个章节如果完全投入进去阅读,两个小时完全可以搞明白。更何况最开始还整理出来了重点,那么复习详略得当,这个时间是足够的。还要注意一下就是每个章节如果真题中有考到这个章节的知识点,BPP的教材是会给出提示的,务必保证每个章节在学习完做一道题,总结答题思路。
最后一步是真题,一具体就要做的真题数目决定。51题库考试学习网建议大家有时间就尽量多做题,虽然题海战术不算什么高端的战术,但它却是最有用的。用来检测知识点是否掌握,如果是重要知识点没掌握,务必要回去复习了。
总结必考题的答题套路,就想F7/P2的合并报表,一定有它必备的一些步骤一样,这些必考题一定有每年都要做的相同部分。
完全的考前模拟,看看考试的时候如何安排时间比较合理。
以上就是关于备考ACCA考试的相关经验分享,你Get到了吗?俗话说,好的开始是成功的一半,大家要积极地认真地备考ACCA考试哦,要相信你所付出的一定会得到结果的~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Explain the benefits of performance-related pay in rewarding directors and critically evaluate the implications
of the package offered to Choo Wang. (8 marks)
(c) Choo Wang’s remuneration package
Benefits of PRP
In general terms, performance-related pay serves to align directors’ and shareholders’ interests in that the performancerelated
element can be made to reflect those things held to be important to shareholders (such as financial targets). This, in
turn, serves to motivate directors, especially if they are directly responsible for a cost or revenue/profit budget or centre. The
possibility of additional income serves to motivate directors towards higher performance and this, in turn, can assist in
recruitment and retention. Finally, performance-related pay can increase the board’s control over strategic planning and
implementation by aligning rewards against strategic objectives.
Critical evaluation of Choo Wang’s package
Choo Wang’s package appears to have a number of advantages and shortcomings. It was strategically correct to include some
element of pay linked specifically to Southland success. This will increase Choo’s motivation to make it successful and indeed,
he has said as much – he appears to be highly motivated and aware that additional income rests upon its success. Against
these advantages, it appears that the performance-related component does not take account of, or discount in any way for,
the risk of the Southland investment. The bonus does not become payable on a sliding scale but only on a single payout basis
when the factory reaches an ‘ambitious’ level of output. Accordingly, Choo has more incentive to be accepting of risk with
decisions on the Southland investment than risk averse. This may be what was planned, but such a bias should be pointed
out. Clearly, the company should accept some risk but recklessness should be discouraged. In conclusion, Choo’s PRP
package could have been better designed, especially if the Southland investment is seen as strategically risky.
2 Your audit client, Prescott Co, is a national hotel group with substantial cash resources. Its accounting functions are
well managed and the group accounting policies are rigorously applied. The company’s financial year end is
31 December.
Prescott has been seeking to acquire a construction company for some time in order to bring in-house the building
and refurbishment of hotels and related leisure facilities (e.g. swimming pools, squash courts and restaurants).
Prescott’s management has recently identified Robson Construction Co as a potential target and has urgently requested
that you undertake a limited due diligence review lasting two days next week.
Further to their preliminary talks with Robson’s management, Prescott has provided you with the following brief on
Robson Construction Co:
The chief executive, managing director and finance director are all family members and major shareholders. The
company name has an established reputation for quality constructions.
Due to a recession in the building trade the company has been operating at its overdraft limit for the last 18
months and has been close to breaching debt covenants on several occasions.
Robson’s accounting policies are generally less prudent than those of Prescott (e.g. assets are depreciated over
longer estimated useful lives).
Contract revenue is recognised on the percentage of completion method, measured by reference to costs incurred
to date. Provisions are made for loss-making contracts.
The company’s management team includes a qualified and experienced quantity surveyor. His main
responsibilities include:
(1) supervising quarterly physical counts at major construction sites;
(2) comparing costs to date against quarterly rolling budgets; and
(3) determining profits and losses by contract at each financial year end.
Although much of the labour is provided under subcontracts all construction work is supervised by full-time site
managers.
In August 2005, Robson received a claim that a site on which it built a housing development in 2002 was not
properly drained and is now subsiding. Residents are demanding rectification and claiming damages. Robson
has referred the matter to its lawyers and denied all liability, as the site preparation was subcontracted to Sarwar
Services Co. No provisions have been made in respect of the claims, nor has any disclosure been made.
The auditor’s report on Robson’s financial statements for the year to 30 June 2005 was signed, without
modification, in March 2006.
Required:
(a) Identify and explain the specific matters to be clarified in the terms of engagement for this due diligence
review of Robson Construction Co. (6 marks)
2 PRESCOTT CO
(a) Terms of engagement – matters to be clarified
Tutorial note: This one-off assignment requires a separate letter of engagement. Note that, at this level, a standard list of
contents will earn few, if any, marks. Any ‘ideas list’ must be tailored to generate answer points specific to the due diligence
review of this target company.
■ Objective of the review: for example, to find and report facts relevant to Prescott’s decision whether to acquire Robson.
The terms should confirm whether Prescott’s interest is in acquiring the company (i.e. the share capital) or its trading
assets (say), as this will affect the nature and scope of the review.
Tutorial note: This is implied as Prescott ‘has been seeking to acquire ... to bring building … in-house’.
■ Prescott’s management will be solely responsible for any decision made (e.g. any offer price made to purchase Robson).
■ The nature and scope of the review and any standards/guidelines in accordance with which it will be conducted. That
investigation will consist of enquiry (e.g. of the directors and the quantity surveyor) and analytical procedures (e.g. on
budgeted information and prior period financial statements).
Tutorial note: This is not going to be a review of financial statements. The prior year financial statements have only
recently been audited and financial statements for the year end 30 June 2006 will not be available in time for the
review.
■ The level of assurance will be ‘negative’. That is, that the material subject to review is free of material misstatement. It
should be stated that an audit is not being performed and that an audit opinion will not be expressed.
■ The timeframe. for conducting the investigation (two days next week) and the deadline for reporting the findings.
■ The records, documentation and other information to which access will be unrestricted. This will be the subject of
agreement between Prescott and Robson.
■ A responsibility/liability disclaimer that the engagement cannot be relied upon to disclose errors, illegal acts or other
irregularities (e.g. fraudulent financial reporting or misappropriations of Robson’s assets).
Tutorial note: Third party reliance on the report seems unlikely as Prescott has ‘substantial cash resources’ and may not
need to obtain loan finance.
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
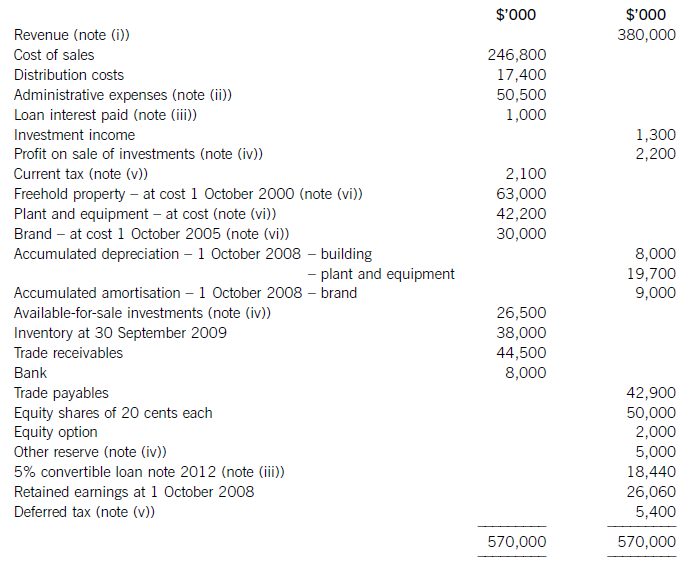
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities.
1 The board of Worldwide Minerals (WM) was meeting for the last monthly meeting before the publication of the yearend
results. There were two points of discussion on the agenda. First was the discussion of the year-end results;
second was the crucial latest minerals reserves report.
WM is a large listed multinational company that deals with natural minerals that are extracted from the ground,
processed and sold to a wide range of industrial and construction companies. In order to maintain a consistent supply
of minerals into its principal markets, an essential part of WM’s business strategy is the seeking out of new sources
and the measurement of known reserves. Investment analysts have often pointed out that WM’s value rests principally
upon the accuracy of its reserve reports as these are the best indicators of future cash flows and earnings. In order to
support this key part of its strategy, WM has a large and well-funded geological survey department which, according
to the company website, contains ‘some of the world’s best geologists and minerals scientists’. In its investor relations
literature, the company claims that:
‘our experts search the earth for mineral reserves and once located, they are carefully measured so that the company
can always report on known reserves. This knowledge underpins market confidence and keeps our customers
supplied with the inventory they need. You can trust our reserve reports – our reputation depends on it!’
At the board meeting, the head of the geological survey department, Ranjana Tyler, reported that there was a problem
with the latest report because one of the major reserve figures had recently been found to be wrong. The mineral in
question, mallerite, was WM’s largest mineral in volume terms and Ranjana explained that the mallerite reserves in
a deep mine in a certain part of the world had been significantly overestimated. She explained that, based on the
interim minerals report, the stock market analysts were expecting WM to announce known mallerite reserves of
4·8 billion tonnes. The actual figure was closer to 2·4 billion tonnes. It was agreed that this difference was sufficient
to affect WM’s market value, despite the otherwise good results for the past year. Vanda Monroe, the finance director,
said that the share price reflects market confidence in future earnings. She said that an announcement of an incorrect
estimation like that for mallerite would cause a reduction in share value. More importantly for WM itself, however, it
could undermine confidence in the geological survey department. All agreed that as this was strategically important
for the company, it was a top priority to deal with this problem.
Ranjana explained how the situation had arisen. The major mallerite mine was in a country new to WM’s operations.
The WM engineer at the mine said it was difficult to deal with some local people because, according to the engineer,
‘they didn’t like to give us bad news’. The engineer explained that when the mine was found to be smaller than
originally thought, he was not told until it was too late to reduce the price paid for the mine. This was embarrassing
and it was agreed that it would affect market confidence in WM if it was made public.
The board discussed the options open to it. The chairman, who was also a qualified accountant, was Tim Blake. He
began by expressing serious concern about the overestimation and then invited the board to express views freely. Gary
Howells, the operations director, said that because disclosing the error to the market would be so damaging, it might
be best to keep it a secret and hope that new reserves can be found in the near future that will make up for the
shortfall. He said that it was unlikely that this concealment would be found out as shareholders trusted WM and they
had many years of good investor relations to draw on. Vanda Monroe, the finance director, reminded the board that
the company was bound to certain standards of truthfulness and transparency by its stock market listing. She pointed
out that they were constrained by codes of governance and ethics by the stock market and that colleagues should be
aware that WM would be in technical breach of these if the incorrect estimation was concealed from investors. Finally,
Martin Chan, the human resources director, said that the error should be disclosed to the investors because he would
not want to be deceived if he were an outside investor in the company. He argued that whatever the governance codes
said and whatever the cost in terms of reputation and market value, WM should admit its error and cope with
whatever consequences arose. The WM board contains three non-executive directors and their views were also
invited.
At the preliminary results presentation some time later, one analyst, Christina Gonzales, who had become aware of
the mallerite problem, asked about internal audit and control systems, and whether they were adequate in such a
reserve-sensitive industry. WM’s chairman, Tim Blake, said that he intended to write a letter to all investors and
analysts in the light of the mallerite problem which he hoped would address some of the issues that Miss Gonzales
had raised.
Required:
(a) Define ‘transparency’ and evaluate its importance as an underlying principle in corporate governance and in
relevant and reliable financial reporting. Your answer should refer to the case as appropriate. (10 marks)
(a) Transparency and its importance at WM
Define transparency
Transparency is one of the underlying principles of corporate governance. As such, it is one of the ‘building blocks’ that
underpin a sound system of governance. In particular, transparency is required in the agency relationship. In terms of
definition, transparency means openness (say, of discussions), clarity, lack of withholding of relevant information unless
necessary and a default position of information provision rather than concealment. This is particularly important in financial
reporting, as this is the primary source of information that investors have for making effective investment decisions.
Evaluation of importance of transparency
There are a number of benefits of transparency. For instance, it is part of gaining trust with investors and state authorities
(e.g. tax people). Transparency provides access for investors and other stakeholders to company information thereby dispelling
suspicion and underpinning market confidence in the company through truthful and fair reporting. It also helps to manage
stakeholder claims and reduces the stresses caused by stakeholders (e.g. trade unions) for whom information provision is
important. Reasons for secrecy/confidentiality include the fact that it may be necessary to keep strategy discussions secret
from competitors. Internal issues may be private to individuals, thus justifying confidentiality. Finally, free (secret or
confidential) discussion often has to take place before an agreed position is announced (cabinet government approach).
Reference to case
At Worldwide Minerals, transparency as a principle is needed to deal with the discussion of concealment. Should a discussion
of possible concealment even be taking place? Truthful, accurate and timely reporting underpins investor confidence in all
capital-funded companies including WM. The issue of the overestimation of the mallerite reserve is clearly a matter of concern
to shareholders and so is an example of where a default assumption of transparency would be appropriate.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-29
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-04-29
- 2021-06-26
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-03-29
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10