新疆考生:ACCA考试内容是什么?难度和专业课相比怎样?
发布时间:2020-01-09
第一次听闻ACCA考试的同学可能只知道其证书的含金量是十分高的,但当听到ACCA考试的考试科目多达13科的时候,可能有些同学就会打退堂鼓了。其实,51题库考试学习网想告诉大家的是,ACCA考试并不是高不可攀的,任何一场考试他都是有难度的,但只要自己付出过汗水,努力过,即使没有通过也不会留下遗憾。可能这样说大家还是感觉到很空洞吧,那么51题库考试学习网就结合当下同学们目前正在学习的学校专业课程与ACCA考试的科目进行比较,让你们更加直观地感受ACCA考试的具体内容。
和大学课程相比,ACCA的难度如何?
相比较国内会计师考试,ACCA对于报考要求很低,最明显的一点就是它不要求你需要从事此行业到一定年限才可以报考,即使是没接触过会计学科知识的人,通过ACCA的考试的系统化的学习、记忆和理解,也能建立起系统的会计学科知识。
ACCA考试分为基础阶段和专业阶段。因为ACCA总部是在英国,所以考试的难度是以英国大学学位考试的难度为标准,换到国内的水平就是:基础课程的难度相当于学士学位高年级课程的考试难度,专业阶段课程的考试相当于硕士学位的考试。再说简单点就是,基础阶段是国内大学水平,专业阶段是国内硕士水平。所以更大学的专业课程相比,基础阶段的知识还能勉强用大学所学的知识应付,而到了专业阶段就可能不适用了,因此必须要去学习专业阶段的知识。ACCA的课程使学员全面掌握财务、财务管理、审计、税务及经营战略等方面的专业知识,提升分析能力并拓宽战略思维。
与国内注会拔高式的考试内容不同,ACCA的知识体系是呈阶梯式递进的。难度也是层层递进的,因此即便是非财会专业出身,也不必担心吃不透某个基础概念的状况。如果你是财会专业出身,ACCA学起来不但更为轻松,高级阶段教授的知识内容也能你让你提前领会在校期间学不到的商业奥义。
考完ACCA需要多长时间呢?
听到考试科目多达13科目是不是被吓到了?一次性同时备考13个科目压力还是太大了。所以,ACCA官方给了你7年时间去完成整个考试,不过大家不要怕,基本上大多数学生只需要花2-4年的时间就可以全部考完。当然前提是你每个阶段都是认真学习的情况下。
英语不好学ACCA会不会困难?
简单来说,ACCA里的英文水准可能等同于国家三级水准,只要在大学考试通过了CET-4的同学,一般来说没什么参加ACCA考试不会吃看不懂单词的亏。学ACCA不是学英语,只要表述没有问题,考官不会在意你用的是什么华丽的句式或者无伤大雅的语病。而且语感这东西,在学习的过程中是能逐渐培养出来的,也就是所谓的“套路”。
需要注意的地方是:ACCA里很多是会计专业词汇,我们平时学的英语单词很少用上。而且在ACCA培训班,老师解释的时候都用中文,这样字典也不用查了,况且不少专业词汇的用法在普通字典里是查不到的,比如premium既可以解释为“溢价”,又可以解释为“定金/押金”,普通字典查不到这种解释,大学四六级雅思什么的也没有这种解释。所以说,51题库考试学习网建议大家购买专业的英文字典,可以去ACCA官网了解一下相关字典是通过何种渠道获得的。
ACCA能否通过,要看你付出到什么程度。
ACCA考试虽然有一定的难度,但是绝对是在大家能力范围之内的——只要你努力。如果你想不花精力和时间就通过ACCA的话,通过考试也只是痴人说梦。想要通过ACCA肯定是要做出一定的牺牲的。俗话说,贵在坚持,也就是说,ACCA的难度其实取决于你自己。通过率的高低其实与我们没有太大的关系,通过率再高,你不认真学习,也是通不过的。
如何平衡ACCA考试与大学生活
在大学生活中,如果备考ACCA考试,那么首先要面临的问题就是如何平衡考试与大学生活了。大学专业课的绩点与排名,对自己能否拿到学位证和学历证以及对今后的考研或出国来说,还是有着至关重要影响的,所以51题库考试学习网建议在ACCA的复习备考的基础上要首先完善好大学的相关课程和作业,因为毕竟ACCA考试的年限长达7年,而大学也就4年左右。所以,该做取舍的时候就还是可以做取舍的。建议大家在大学期间每一个考季不用报考满4个科目,根据自己的学习时间来制定相应的计划就可以了。
另外,合理利用自己周末的时间,这就是大学生复习时间的主要来源。对当天所讲的内容进行全面的复习与刷题会比较困难,所以我个人建议,对于一些难度大的知识点要确保在讲授当天及时复习巩固,其他的知识点如果来不及,可以分散到周一到周五去抽一定的时间复习,并保证一定的刷题量,这样才能加深对相应知识点的印象,提高复习的效率,减轻备考时的工作量。
在文章的最后,51题库考试学习网想与大家分享一句话:“人不能漂泊一辈子,但在声嘶力竭之前就安居乐业也未免可惜。”既然选择了报考ACCA这条道路,那就坚持下去,让生命在汗水与努力中呐喊出最灿烂的色彩,大家加油~。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
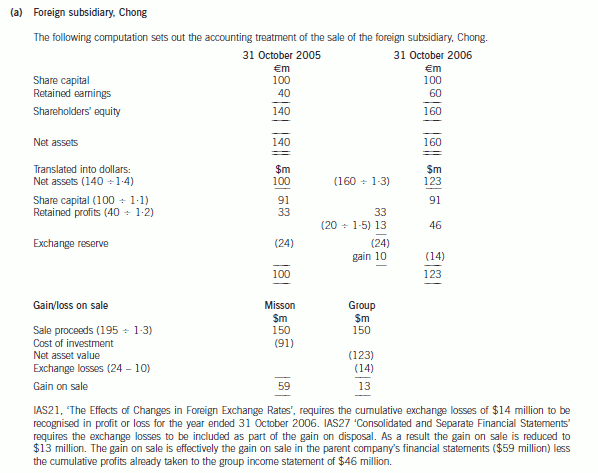
2 Misson, a public limited company, has carried out transactions denominated in foreign currency during the financial
year ended 31 October 2006 and has conducted foreign operations through a foreign entity. Its functional and
presentation currency is the dollar. A summary of the foreign currency activities is set out below:
(a) Misson has a 100% owned foreign subsidiary, Chong, which was formed on 1 November 2004 with a share
capital of 100 million euros which has been taken as the cost of the investment. The total shareholders’ equity
of the subsidiary as at 31 October 2005 and 31 October 2006 was 140 million euros and 160 million euros
respectively. Chong has not paid any dividends to Misson and has no other reserves than retained earnings in its
financial statements. The subsidiary was sold on 31 October 2006 for 195 million euros.
Misson would like to know how to treat the sale of the subsidiary in the parent and group accounts for the year
ended 31 October 2006. (8 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above transactions in accordance with the advice required by the
directors.
(Candidates should show detailed workings as well as a discussion of the accounting treatment used.)
(iv) critiques the performance measurement system at TSC. (5 marks
(iv) The performance measurement system used by TSC appears simplistic. However, it may be considered to be measuring
the right things since the specific measures used cover a range of dimensions designed to focus the organisation on
factors thought to be central to corporate success, and not confined to traditional financial measures.
Internal benchmarking is used at TSC in order to provide sets of absolute standards that all depots are expected to attain.
This should help to ensure that there is a continual focus upon the adoption of ‘best practice’ at all depots. Benchmarks
on delivery performance place an emphasis upon quality of service whereas benchmarks on profitability are focused
solely upon profitability!
Incentive schemes are used throughout the business, linking the achievement of company targets with financial rewards.
It might well be the case that the profit incentive would act as a powerful motivator to each depot management team.
However, what is required for the prosperity of TSC is a focus of management on the determinants of success as opposed
to the results of success.
(Alternative relevant discussion would be acceptable)
John Pentanol was appointed as risk manager at H&Z Company a year ago and he decided that his first task was to examine the risks that faced the company. He concluded that the company faced three major risks, which he assessed by examining the impact that would occur if the risk were to materialise. He assessed Risk 1 as being of low potential impact as even if it materialised it would have little effect on the company’s strategy. Risk 2 was assessed as being of medium potential impact whilst a third risk, Risk 3, was assessed as being of very high potential impact.
When John realised the potential impact of Risk 3 materialising, he issued urgent advice to the board to withdraw from the activity that gave rise to Risk 3 being incurred. In the advice he said that the impact of Risk 3 was potentially enormous and it would be irresponsible for H&Z to continue to bear that risk.
The company commercial director, Jane Xylene, said that John Pentanol and his job at H&Z were unnecessary and that risk management was ‘very expensive for the benefits achieved’. She said that all risk managers do is to tell people what can’t be done and that they are pessimists by nature. She said she wanted to see entrepreneurial risk takers in H&Z and not risk managers who, she believed, tended to discourage enterprise.
John replied that it was his job to eliminate all of the highest risks at H&Z Company. He said that all risk was bad and needed to be eliminated if possible. If it couldn’t be eliminated, he said that it should be minimised.
(a) The risk manager has an important role to play in an organisation’s risk management.
Required:
(i) Describe the roles of a risk manager. (4 marks)
(ii) Assess John Pentanol’s understanding of his role. (4 marks)
(b) With reference to a risk assessment framework as appropriate, criticise John’s advice that H&Z should
withdraw from the activity that incurs Risk 3. (6 marks)
(c) Jane Xylene expressed a particular view about the value of risk management in H&Z Company. She also said that she wanted to see ‘entrepreneurial risk takers’.
Required:
(i) Define ‘entrepreneurial risk’ and explain why it is important to accept entrepreneurial risk in business
organisations; (4 marks)
(ii) Critically evaluate Jane Xylene’s view of risk management. (7 marks)
(a) (i) Roles of a risk manager
Providing overall leadership, vision and direction, involving the establishment of risk management (RM) policies,
establishing RM systems etc. Seeking opportunities for improvement or tightening of systems.
Developing and promoting RM competences, systems, culture, procedures, protocols and patterns of behaviour. It is
important to understand that risk management is as much about instituting and embedding risk systems as much as
issuing written procedure. The systems must be capable of accurate risk assessment which seem not to be the case at
H&Z as he didn’t account for variables other than impact/hazard.
Reporting on the above to management and risk committee as appropriate. Reporting information should be in a form
able to be used for the generation of external reporting as necessary. John’s issuing of ‘advice’ will usually be less useful
than full reporting information containing all of the information necessary for management to decide on risk policy.
Ensuring compliance with relevant codes, regulations, statutes, etc. This may be at national level (e.g. Sarbanes Oxley)
or it may be industry specific. Banks, oil, mining and some parts of the tourism industry, for example, all have internal
risk rules that risk managers are required to comply with.
[Tutorial note: do not reward bullet lists. Study texts both use lists but question says ‘describe’.]
(ii) John Pentanol’s understanding of his role
John appears to misunderstand the role of a risk manager in four ways.
Whereas the establishment of RM policies is usually the most important first step in risk management, John launched
straight into detailed risk assessments (as he saw it). It is much more important, initially, to gain an understanding of
the business, its strategies, controls and risk exposures. The assessment comes once the policy has been put in place.
It is important for the risk manager to report fully on the risks in the organisation and John’s issuing of ‘advice’ will usually
be less useful than full reporting information. Full reporting would contain all of the information necessary for
management to decide on risk policy.
He told Jane Xylene that his role as risk manager involved eliminating ‘all of the highest risks at H&Z Company’ which
is an incorrect view. Jane Xylene was correct to say that entrepreneurial risk was important, for example.
The risk manager is an operational role in a company such as H&Z Company and it will usually be up to senior
management to decide on important matters such as withdrawal from risky activities. John was being presumptuous
and overstepping his role in issuing advice on withdrawal from Risk 3. It is his job to report on risks to senior
management and for them to make such decisions based on the information he provides.
(b) Criticise John’s advice
The advice is based on an incomplete and flawed risk assessment. Most simple risk assessment frameworks comprise at least
two variables of which impact or hazard is only one. The other key variable is probability. Risk impact has to be weighed
against probability and the fact that a risk has a high potential impact does not mean the risk should be avoided as long as
the probability is within acceptable limits. It is the weighted combination of hazard/impact and probability that forms the basis
for meaningful risk assessment.
John appears to be very certain of his impact assessments but the case does not tell us on what information the assessment
is made. It is important to recognise that ‘hard’ data is very difficult to obtain on both impact and probability. Both measures
are often made with a degree of assumption and absolute measures such as John’s ranking of Risks 1, 2 and 3 are not as
straightforward as he suggests.
John also overlooks a key strategic reason for H&Z bearing the risks in the first place, which is the return achievable by the
bearing of risk. Every investment and business strategy carries a degree of risk and this must be weighed against the financial
return that can be expected by the bearing of the risk.
(c) (i) Define ‘entrepreneurial risk’
Entrepreneurial risk is the necessary risk associated with any new business venture or opportunity. It is most clearly seen
in entrepreneurial business activity, hence its name. In ‘Ansoff’ terms, entrepreneurial risk is expressed in terms of the
unknowns of the market/customer reception of a new venture or of product uncertainties, for example product design,
construction, etc. There is also entrepreneurial risk in uncertainties concerning the competences and skills of the
entrepreneurs themselves.
Entrepreneurial risk is necessary, as Jane Xylene suggested, because it is from taking these risks that business
opportunities arise. The fact that the opportunity may not be as hoped does not mean it should not be pursued. Any
new product, new market development or new activity is a potential source of entrepreneurial risk but these are also the
sources of future revenue streams and hence growth in company value.
(ii) Critically evaluate Jane Xylene’s view of risk management
There are a number of arguments against risk management in general. These arguments apply against the totality of risk
management and also of the employment of inappropriate risk measures.
There is a cost associated with all elements of risk management which must obviously be borne by the company.
Disruption to normal organisational practices and procedures as risk systems are complied with.
Slowing (introducing friction to) the seizing of new business opportunities or the development of internal systems as they
are scrutinised for risk.
‘STOP’ errors can occur as a result of risk management systems where a practice or opportunity has been stopped on
the grounds of its risk when it should have been allowed to proceed. This may be the case with Risk 3 in the case.
(Contrast with ‘GO’ errors which are the opposite of STOP errors.)
There are also arguments for risk management people and systems in H&Z. The most obvious benefit is that an effective
risk system identifies those risks that could detract from the achievements of the company’s strategic objectives. In this
respect, it can prevent costly mistakes by advising against those actions that may lose the company value. It also has
the effect of reassuring investors and capital markets that the company is aware of and is in the process of managing
its risks. Where relevant, risk management is necessary for compliance with codes, listing rules or statutory instruments.
2 (a) Explain the term ‘backflush accounting’ and the circumstances in which its use would be appropriate.
(6 marks)
(a) Backflush accounting focuses upon output of an organisation and then works backwards when allocating costs between cost
of goods sold and inventories. It can be argued that backflush accounting simplifies costing since it ignores both labour
variances and work-in-progress. Whilst in a perfect just-in-time environment there would be no work-in-progress at all, there
will in practice be a small amount of work-in-progress in the system at any point in time. This amount, however, is likely to
be negligible in quantity and therefore not significant in terms of value. Thus, a backflush accounting system simplifies the
accounting records by avoiding the need to follow the movement of materials and work-in-progress through the manufacturing
process within the organisation.
The backflush accounting system is likely to involve the maintenance of a raw materials and work-in–progress account
together with a finished goods account. The use of standard costs and variances is likely to be incorporated into the
accounting entries. Transfers from raw materials and work-in-progress account to finished goods (or cost of sales) will probably
be made at standard cost. The difference between the actual inputs and the standard charges from the raw materials and
work-in-progress account will be recorded as a residual variance, which will be recorded in the profit and loss account. Thus,
it is essential that standard costs are a good surrogate for actual costs if large variances are to be avoided. Backflush
accounting is ideally suited to a just-in-time philosophy and is employed where the overall cycle time is relatively short and
inventory levels are low. Naturally, management will still be eager to ascertain the cause of any variances that arise from the
inefficient usage of materials, labour and overhead. However investigations are far more likely to be undertaken using nonfinancial
performance indicators as opposed to detailed cost variances.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-05-13
- 2020-05-21
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-05
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-15
- 2020-02-06
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-10