香港考生想知道ACCA的科目F2怎么备考?
发布时间:2020-01-10
学习ACCA,不仅是为了给自己的简历上增添一个拿的出手的证书,更是因为ACCA完整的知识体系,充实自己的大学生活。我认为,每一份努力都会有回报,只要功夫下的多,就没有什么事情做不好。这一份ACCA MA(F2)的备考技巧请大家收藏起来哦~
报考建议
F2的考试一般建议大家在结课之后一个月左右考试,因为F2是一门刷题型的科目,需要留出足够的做题,并且考前也需要模拟考进行练习;但也不宜太晚考,有些需要记忆的知识点容易遗忘。因此,F2最简单也是最直截了当的复习技巧就是题海战术,当然大家可以根据自己的实际情况进行调整,如果备考时间充裕,也可以缩短备考时间,如果碰上了学校的考试周,或者有自己的比较忙的事情,也可以适当拉长。
备考建议
① 备考初期:F2主要以刷题为主。F2是管理会计,偏计算,但是计算水平要求其实也很低,重要的是细心点,把题看懂。
在ACCA的官网中也有样卷与模考卷可以练习,其中样卷是可以免费进入,进行练习的,模考卷的练习是需要付7英镑的费用。:
② 临考准备:如果大家已经看完网课,也做了一定量的习题了后,这个时候应该要明确自己薄弱的地方在哪里。哪部分知识点比较薄弱,就花费多一点的时间去复习,反之就少花费一点时间。建议大家可以像考试一样,在电脑上认真地花两个小时做一套模拟卷,并且进行批改,看看自己在考试中会遇到什么问题。
如果觉得两个小时的时间不够,做不完,说明做题的速度不够,需要提高做题速度。那么再做一遍题库,或者找其他的练习册再进行题海战略是必要的。
如果发现某个知识点的题目都需要花特别多的时间,或错误率非常高,那么说明对这部分的知识掌握的并不是很好,需要再次反复去巩固这部分的知识点,这部分有关的网课以及习题是需要再重新回顾1-2遍的。
如果觉得用电脑看题自己非常不适应,会非常影响自己的思路和速度,那么平时就不要在纸质的练习册上做题了,应该多练练,比如可以在电脑上做电子版的练习册或题库,使自己更适应机考。
总之大家可以通过模拟考的形式明确自己的弱点,进行加强后再在考试前练习一次,这样考试前就不会太紧张。但考试紧张也是会在所难的,所以就要要求大家及时调整心态,快速找回考试状态。
F2知识点总结
1. Data
and information:
Unprocessed
--->data; Processed --->information
2.
Quality of good information
“ACCURATE”
3.
Mission statement(abstract) ---> Objective(SMART) --->Strategy(Possible
course of action)
4.
Planning (establishing the objectives& selecting appropriate strategies)
5.
Control(compare plans with actual results, reviewed and made changes)
6. The
relationship between planning, decision making and control
7.
Management information Strategic information
幻想一步成功者突遭失败,会觉得浪费了时间,付出了精力,却认为没有任何收获;在失败面前,懦弱者痛苦迷茫,彷徨畏缩;而强者却坚持不懈,紧追不舍。各位ACCAer们加油,期待听到你们3月份考试成功的好消息~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) In April 2006, Keffler was banned by the local government from emptying waste water into a river because the
water did not meet minimum standards of cleanliness. Keffler has made a provision of $0·9 million for the
technological upgrading of its water purifying process and included $45,000 for the penalties imposed in ‘other
provisions’. (5 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
(c) Ban on emptying waste water
(i) Matter
■ $0·9m provision for upgrading the process represents 45% PBT and is very material. This provision is also
material to the balance sheet (2·7% of total assets).
■ The provision for penalties is immaterial (2·2% PBT and 0·1% total assets).
■ The ban is an adjusting post balance sheet event in respect of the penalties (IAS 10). It provides evidence that at
the balance sheet date Keffler was in contravention of local government standards. Therefore it is correct (in
accordance with IAS 37) that a provision has been made for the penalties. As the matter is not material inclusion
in ‘other provisions’ is appropriate.
■ However, even if Keffler has a legal obligation to meet minimum standards, there is no obligation for upgrading the
purifying process at 31 March 2006 and the $0·9m provision should be written back.
■ If the provision for upgrading is not written back the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ (disagreement).
■ Keffler does not even have a contingent liability for upgrading the process because there is no present obligation to
do so. The obligation is to stop emptying unclean water into the river. Nor is there a possible obligation whose
existence will be confirmed by an uncertain future event not wholly within Keffler’s control.
Tutorial note: Consider that Keffler has alternatives wholly within its control. For example, it could ignore the ban
and incur fines, or relocate/close this particular plant/operation or perhaps dispose of the water by alternative
means.
■ The need for a technological upgrade may be an indicator of impairment. Management should have carried out
an impairment test on the carrying value of the water purifying process and recognised any impairment loss in the
profit for the year to 31 March 2006.
■ Management’s intention to upgrade the process is more appropriate to an environmental responsibility report (if
any).
■ Whether there is any other information in documents containing financial statements.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Penalty notices of fines received to confirm amounts and period/dates covered.
■ After-date payment of fines agreed to the cash book.
■ A copy of the ban and any supporting report on the local government’s findings.
■ Minutes of board meetings at which the ban was discussed confirming management’s intentions (e.g. to upgrade
the process).
Tutorial note: This may be disclosed in the directors’ report and/or as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event.
■ Any tenders received/costings for upgrading.
Tutorial note: This will be relevant if, for example, capital commitment authorised (by the board) but not
contracted for at the year end are disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
■ Physical inspection of the emptying point at the river to confirm that Keffler is not still emptying waste water into
it (unless the upgrading has taken place).
Tutorial note: Thereby incurring further penalties.
5 Crusoe has contacted you following the death of his father, Noland. Crusoe has inherited the whole of his father’s
estate and is seeking advice on his father’s capital gains tax position and the payment of inheritance tax following his
death.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from telephone conversations with Crusoe.
Noland – personal information:
– Divorcee whose only other relatives are his sister, Avril, and two grandchildren.
– Died suddenly on 1 October 2007 without having made a will.
– Under the laws of intestacy, the whole of his estate passes to Crusoe.
Noland – income tax and capital gains tax:
– Has been a basic rate taxpayer since the tax year 2000/01.
– Sales of quoted shares resulted in:
– Chargeable gains of £7,100 and allowable losses of £17,800 in the tax year 2007/08.
– Chargeable gains of approximately £14,000 each tax year from 2000/01 to 2006/07.
– None of the shares were held for long enough to qualify for taper relief.
Noland – gifts made during lifetime:
– On 1 December 1999 Noland gave his house to Crusoe.
– Crusoe has allowed Noland to continue living in the house and has charged him rent of £120 per month
since 1 December 1999. The market rent for the house would be £740 per month.
– The house was worth £240,000 at the time of the gift and £310,000 on 1 October 2007.
– On 1 November 2004 Noland transferred quoted shares worth £232,000 to a discretionary trust for the benefit
of his grandchildren.
Noland – probate values of assets held at death: £
– Portfolio of quoted shares 370,000
Shares in Kurb Ltd 38,400
Chattels and cash 22,300
Domestic liabilities including income tax payable (1,900)
– It should be assumed that these values will not change for the foreseeable future.
Kurb Ltd:
– Unquoted trading company
– Noland purchased the shares on 1 December 2005.
Crusoe:
– Long-standing personal tax client of your firm.
– Married with two young children.
– Successful investment banker with very high net worth.
– Intends to gift the portfolio of quoted shares inherited from Noland to his aunt, Avril, who has very little personal
wealth.
Required:
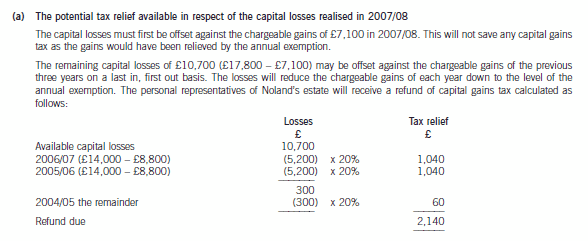
(a) Prepare explanatory notes together with relevant supporting calculations in order to quantify the tax relief
potentially available in respect of Noland’s capital losses realised in 2007/08. (4 marks)
15 A trader who fixes her prices by adding 50% to cost actually achieved a mark-up of 45%.
Which of the following factors could account for the shortfall?
1 Sales were lower than expected.
2 The opening inventories had been overstated.
3 The closing inventories of the business were higher than the opening inventories.
4 Goods taken from inventories by the proprietor were recorded by debiting drawings and crediting purchases with
the cost of the goods.
A All four factors
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2 only
D 3 and 4 only
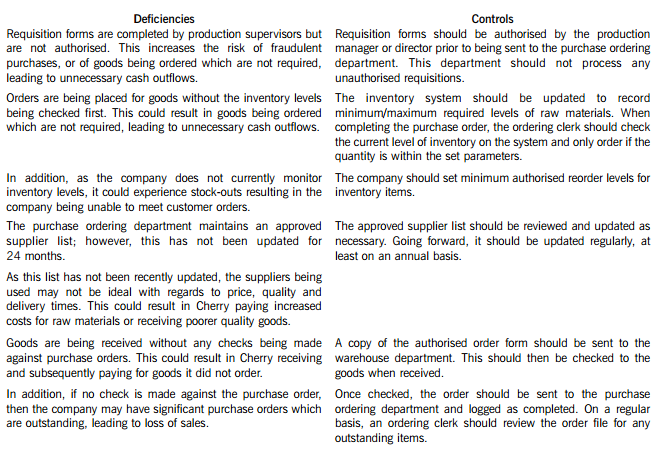
Cherry Blossom Co (Cherry) manufactures custom made furniture and its year end is 30 April. The company purchases its raw materials from a wide range of suppliers. Below is a description of Cherry’s purchasing system.
When production supervisors require raw materials, they complete a requisition form. and this is submitted to the purchase ordering department. Requisition forms do not require authorisation and no reference is made to the current inventory levels of the materials being requested. Staff in the purchase ordering department use the requisitions to raise sequentially numbered purchase orders based on the approved suppliers list, which was last updated 24 months ago. The purchasing director authorises the orders prior to these being sent to the suppliers.
When the goods are received, the warehouse department verifies the quantity to the suppliers despatch note and checks that the quality of the goods received are satisfactory. They complete a sequentially numbered goods received note (GRN) and send a copy of the GRN to the finance department.
Purchase invoices are sent directly to the purchase ledger clerk, who stores them in a manual file until the end of each week. He then inputs them into the purchase ledger using batch controls and gives each invoice a unique number based on the supplier code. The invoices are reviewed and authorised for payment by the finance director, but the actual payment is only made 60 days after the invoice is input into the system.
Required:
In respect of the purchasing system of Cherry Blossom Co:
(i) Identify and explain FIVE deficiencies; and
(ii) Recommend a control to address each of these deficiencies.
Note: The total marks will be split equally between each part.
Cherry Blossom Co’s (Cherry) purchasing system deficiencies and controls

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-21
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-01-05
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-01-04
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-14