ACCA考试F4考试模拟试题(2020-08-13)
发布时间:2020-08-13
备考ACCA考试,好的学习方法很重要,但是练习也很重要,下面51题库考试学习网就给大家分享一些,ACCA考试F4考试模拟试题,备考的小伙伴赶紧来练练手吧。
8 Mr Ding picked up a handbag lost by
somebody when he was walking in the park. There was lots of cash, some bills of
exchange and a set of commercial documents in the handbag. Mr Ding found, from
the information on the documents, the owner of this handbag was Ms Liang and
contacted her.
On the day, as fixed by Mr Ding and Ms
Liang via exchange of communications, Ms Liang went to Mr Ding’s home to take
back the handbag. Before handing over the handbag to Ms Liang, however, Mr Ding
requested a sum of cash as a reward for his kindness and efforts to return the
lost handbag. Ms Liang refused to give the reward.
Required:
Answer the following questions in
accordance with the Property Law, and give your reasons for your answer:
(a) state whether Mr Ding was entitled to
request a reward for returning the lost handbag;
(b) if Ms Liang had put up an advertisement
offering a reward for the successful find of the lost property, state whether
she could refuse to grant the reward if she learnt that Mr Ding did not see the
advertisement;
(c) assuming Mr Ding could not find the
owner and turned the handbag over to the police who then published an
announcement of finding of the lost property in the newspaper, state how to
deal with the handbag where nobody claimed it.
答案:
8 This question requires candidates to deal
with the legal issues relevant to the lost-and-found object under the Property
Law.
(a) In accordance with Articles 109 and 112
of the Property Law, a lost-and-found object shall be returned to the right
holder and the right holder, when obtaining the lost-and-found object, shall
pay the person who finds the object such necessary expenses as the cost for
safekeeping the object. The Property Law does not stipulate that a person is
entitled to request a reward for finding the lost object. Therefore, Mr Ding
could not request the reward from Ms Liang for returning the handbag.
(b) In accordance with Article 112 of the
Property Law, where the right holder publicly offers a reward for the lost
object, he or she shall keep the promise when claiming the lost-and-found
object. An offer of reward for the lost object is an offer to a non-specific
offeree and an unilateral act. Whenever the offer takes effect, the offeror is
bound by such an expression.
Therefore, Ms Liang could not refuse to
grant the reward on the ground that Mr Ding did not see the particular
advertisement.
(c) In accordance with Article 113 of the
Property Law, where a lost-and-found object fails to be claimed within six
months as of the date when the claiming announcement is published, it shall be
owned by the State. Since the police published an announcement in the newspaper
and received no claiming from Ms Liang, therefore, the handbag found by Mr Ding
should become the property of the State when six months expired.
以上就是本次51题库考试学习网带给大家的内容,希望可以帮助到备考的小伙伴。如果大家想了解更多关于ACCA考试的试题,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
2 Clifford and Amanda, currently aged 54 and 45 respectively, were married on 1 February 1998. Clifford is a higher
rate taxpayer who has realised taxable capital gains in 2007/08 in excess of his capital gains tax annual exemption.
Clifford moved into Amanda’s house in London on the day they were married. Clifford’s own house in Oxford, where
he had lived since acquiring it for £129,400 on 1 August 1996, has been empty since that date although he and
Amanda have used it when visiting friends. Clifford has been offered £284,950 for the Oxford house and has decided
that it is time to sell it. The house has a large garden such that Clifford is also considering an offer for the house and
a part only of the garden. He would then sell the remainder of the garden at a later date as a building plot. His total
sales proceeds will be higher if he sells the property in this way.
Amanda received the following income from quoted investments in 2006/07:
£
Dividends in respect of quoted trading company shares 1,395
Dividends paid by a Real Estate Investment Trust out of tax exempt property income 485
On 1 May 2006, Amanda was granted a 22 year lease of a commercial investment property. She paid the landlord
a premium of £6,900 and also pays rent of £2,100 per month. On 1 June 2006 Amanda granted a nine year
sub-lease of the property. She received a premium of £14,700 and receives rent of £2,100 per month.
On 1 September 2006 Amanda gave quoted shares with a value of £2,200 to a registered charity. She paid broker’s
fees of £115 in respect of the gift.
Amanda began working for Shearer plc, a quoted company, on 1 June 2006 having had a two year break from her
career. She earns an annual salary of £38,600 and was paid a bonus of £5,750 in August 2006 for agreeing to
come and work for the company. On 1 August 2006 Amanda was provided with a fully expensed company car,
including the provision of private petrol, which had a list price when new of £23,400 and a CO2 emissions rate of
187 grams per kilometre. Amanda is required to pay Shearer plc £22 per month in respect of the private use of the
car. In June and July 2006 Amanda used her own car whilst on company business. She drove 720 business miles
during this two month period and was paid 34 pence per mile. Amanda had PAYE of £6,785 deducted from her gross
salary in the tax year 2006/07.
After working for Shearer plc for a full year, Amanda becomes entitled to the following additional benefits:
– The opportunity to purchase a large number of shares in Shearer plc on 1 July 2007 for £3·30 per share. It is
anticipated that the share price on that day will be at least £7·50 per share. The company will make an interestfree
loan to Amanda equal to the cost of the shares to be repaid in two years.
– Exclusive free use of the company sailing boat for one week in August 2007. The sailing boat was purchased by
Shearer plc in January 2005 for use by its senior employees and costs the company £1,400 a week in respect
of its crew and other running expenses.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate Clifford’s capital gains tax liability for the tax year 2007/08 on the assumption that the Oxford
house together with its entire garden is sold on 31 July 2007 for £284,950. Comment on the relevance
to your calculations of the size of the garden; (5 marks)
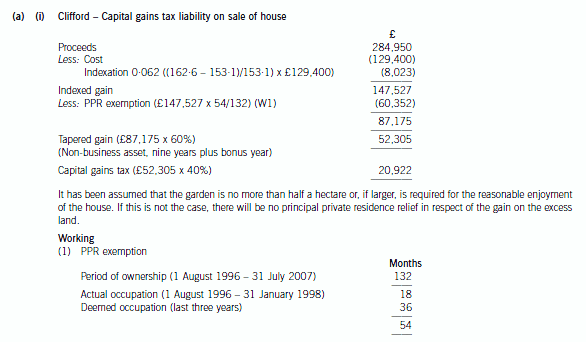
1 Oliver Hoppe has been working at Hoopers and Henderson accountancy practice for eighteen months. He feels that
he fits in well, especially with his colleagues and has learnt a lot from them. However, he feels that the rules and
regulations governing everyday activities and time keeping are not clear.
Oliver does not get on well with his line manager, David Morgan. There appears to be a clash of personalities and
reluctance on David Morgan’s part to deal with the icy atmosphere between them after David was asked by one of
the accounting partners to give Oliver a job. For the past three months Oliver has gone to lunch with his fellow workers
and always returned to work with them or before them. In fact they all have returned to work about ten minutes late
on several previous occasions. After the third time, Oliver was called into David Morgan’s office and given an oral
warning about his time keeping.
Oliver was not permitted to argue his case and none of the other staff who returned late were disciplined in this way.
On the next occasion the group was late returning from lunch, David Morgan presented Oliver with a written warning
about his time keeping.
Yesterday, Oliver was five minutes late returning to work. His colleagues returned after him. David Morgan gave Oliver
notice and told him to work until the end of the week and then collect his salary, the necessary paperwork and to
leave the practice.
There is a partner responsible for human resources. Oliver has come to see the partner to discuss the grievance
procedures against David Morgan for his treatment and about what Oliver regards as unfair dismissal.
Required:
(a) Describe the six stages of a formal disciplinary procedure that an organisation such as Hoopers and
Henderson should have in place. (12 marks)
1 Overview
A grievance occurs when an individual thinks that he or she has been wrongly treated by colleagues or management, especially
in disciplinary matters. An unresolved feeling of grievance can often lead to further problems for the organisation. The purpose of
procedures is to resolve disciplinary and grievance issues to the satisfaction of all concerned and as early as possible.
If a grievance perceived by an employee is not resolved, then conflict and discontent can arise that will affect the work of the
individual and the organisation. Accountants as managers need to be aware of the need to resolve grievances satisfactorily and
professionally.
The fundamental basis of organisational disciplinary and grievance procedures is that they must be explicitly clear and accessible
to all.
Part (a):
An official and correctly applied disciplinary procedure has six steps which should be followed in the correct order and applied
equitably.
The Informal Talk.
This is the first step. If the disciplinary matter is of a minor nature and the individual has had until this occasion a good record,
then an informal meeting can often resolve the issue.
Reprimand or Oral Warning.
Here the manager draws the attention of the employee to unsatisfactory behaviour, a repeat of which could lead to formal
disciplinary proceedings.
Official or Written Warning.
A written warning is a serious matter. It draws the attention of the offending employee to a serious breach of conduct and remains
a recorded document on the employee’s employment history.
Such written documents can be used as evidence if further action is taken, especially dismissal.
Suspension or Lay-off.
If an offence is of a serious nature, if the employee has repeated an earlier offence or if there have been repeated problems then
an employee may be suspended from work for a period of time without pay.
Demotion.
This is a situation where an employee is demoted to a lower salary or position within an organisation. This is a very serious step
to take and can be regarded as a form. of internal dismissal. This course of action can have negative repercussions because the
employee concerned will feel dissatisfied and such feelings can affect their own work and that of others.
Dismissal.
This is the ultimate disciplinary measure and should be used only in the most extreme cases. As with demotion, the dismissal of
a staff member can lead to wider dissatisfaction amongst the employees.
The employee may nominate a representative at any stage of the procedure, especially at the more serious stages.
(b) Discuss the nature of the following issues in developing IFRSs for SMEs.
(i) The purpose of the standards and the type of entity to whom they should apply. (7 marks)
(b) There are several issues which need to be addressed when developing IFRSs for SMEs:
(i) The purpose of the standards and type of entity
The principal aim of the development of an accounting framework for SMEs is to provide a framework which generates
relevant, reliable and useful information. The standards should provide high quality and understandable accounting
standards suitable for SMEs globally. Additionally they should meet the needs set out in (a) above. For example reduce
the financial reporting burden for SMEs. It is unlikely that one of the objectives would be to provide information for
management or meet the needs of the tax authorities as these bodies will have specific requirements which would be
difficult to meet in an accounting standard. However, it is likely that the standards for SMEs will be a modified version
of the full IFRSs and not an independently developed set of standards in order that they are based on the same
conceptual framework and will allow easier transition to full IFRS if the SME grows or decides to become a publicly listed
entity.
It is important to define the type of entity for which the standards are intended. Companies who have issued shares to
the public would be expected to use full IFRS. The question arises as to whether SME standards should apply to all
unlisted entities or just those listed entities below a certain size threshold. The difficulty with size criteria is that it would
have to apply worldwide and it would be very difficult to specify such criteria. Additionally some unlisted companies, for
example public utilities, have a reporting obligation that is equivalent to that of a listed company and should follow full
IFRS.
The main characteristic which distinguishes SMEs from other entities is the degree of public accountability. Thus the
definition of what constitutes an SME could revolve around those entities that do not have public accountability.
Indicators of public accountability will have to be developed. For example, a listed company or companies holding assets
in a fiduciary capacity (bank), or a public utility, or an entity with economic significance in its country. Thus all entities
that do not have public accountability may be considered as potential users of IFRSs for SMEs.
Size may not be the best way to determine what is an SME. SMEs could be defined by reference to ownership and themanagement of the entity. SMEs are not necessarily just smaller versions of public companies.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2019-03-21
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-05
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-10-11