ACCA F1考试历年真题(2019-01-05)
发布时间:2019-01-05
Which
two of the following statements are not consistent with Handy's shamrock
organisation?
A.Self-employed technicians should be hired
on a project-by-project basis
B.The contingent work force consists of employees
on long-term contracts
C.The professional core should consist of
full-time, fixed salary employees
D.The organisation looks for ways that
consumers can do part of the work of the organisation
【答案】BC
【解析】
以下选项中,哪两个陈述与Handy 的三叶草组织不符?
在该理论中:
(1)第一片叶子代表核心专家系统,由资深专家、技术人员和管理人员组成。他们的薪水不是固定的,而是根据performance,表现得好,做的贡献大,薪水才高。这片叶子对应的是C选项,C中的 “fixed salary”是错误的。
(2)第二片叶子由与企业存在合同关系的个人或组织构成,通常还包括一些曾经为企业工作过,但现在为其提供服务的专家。他们中许多人曾经是中心组织的雇员,是从核心层退下来的或是喜欢从事个体职业的那部分自由的人。指的是A选项。
(3)第三片叶子代表的是具有很大弹性的劳动力,如兼职工和临时工等。这一片叶子对应的是B选项。这些员工通常是short-term的,B的 “long-term”错了。
(4)Handy还提到过,在三叶草之外还有第四片叶子的存在,指的是让客户承担价值链的一个环节,“产销合一”,组织无需提供成本。比如宜家的产品设计简约时尚,顾客能够自行组装拆卸,在组装与拆卸的过程中享受愉悦的消费体验,这些组装拆卸就不用劳烦宜家。这对应的就是D选项。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
Section B – TWO questions ONLY to be attempted
Perkin manufactures electronic components for export worldwide, from factories in Ceeland, for use in smartphones and hand held gaming devices. These two markets are supplied with similar components by two divisions, Phones Division (P) and Gaming Division (G). Each division has its own selling, purchasing, IT and research and development functions, but separate IT systems. Some manufacturing facilities, however, are shared between the two divisions.
Perkin’s corporate objective is to maximise shareholder wealth through innovation and continuous technological improvement in its products. The manufacturers of smartphones and gaming devices, who use Perkin’s components, update their products frequently and constantly compete with each other to launch models which are technically superior.
Perkin has a well-established incremental budgeting process. Divisional managers forecast sales volumes and costs months in advance of the budget year. These divisional budgets are then scrutinised by the main board, and revised significantly by them in line with targets they have set for the business. The finalised budgets are often approved after the start of the accounting year. Under pressure to deliver consistent returns to institutional shareholders, the board does not tolerate failure by either division to achieve the planned net profit for the year once the budget is approved. Last year’s results were poor compared to the annual budget. Divisional managers, who are appraised on the financial performance of their own division, have complained about the length of time that the budgeting process takes and that the performance of their divisions could have been better but was constrained by the budgets which were set for them.
In P Division, managers had failed to anticipate the high popularity of a new smartphone model incorporating a large screen designed for playing games, and had not made the necessary technical modifications to the division’s own components. This was due to the high costs of doing so, which had not been budgeted for. Based on the original sales forecast, P Division had already committed to manufacturing large quantities of the existing version of the component and so had to heavily discount these in order to achieve the planned sales volumes.
A critical material in the manufacture of Perkin’s products is silver, which is a commodity which changes materially in price according to worldwide supply and demand. During the year supplies of silver were reduced significantly for a short period of time and G Division paid high prices to ensure continued supply. Managers of G Division were unaware that P Division held large inventories of silver which they had purchased when the price was much lower.
Initially, G Division accurately forecasted demand for its components based on the previous years’ sales volumes plus the historic annual growth rate of 5%. However, overall sales volumes were much lower than budgeted. This was due to a fire at the factory of their main customer, which was then closed for part of the year. Reacting to this news, managers at G Division took action to reduce costs, including closing one of the three R&D facilities in the division.
However, when the customer’s factory reopened, G Division was unwilling to recruit extra staff to cope with increased demand; nor would P Division re-allocate shared manufacturing facilities to them, in case demand increased for its own products later in the year. As a result, Perkin lost the prestigious preferred supplier status from their main customer who was unhappy with G Division’s failure to effectively respond to the additional demand. The customer had been forced to purchase a more expensive, though technically superior, component from an alternative manufacturer.
The institutional shareholders’ representative, recently appointed to the board, has asked you as a performance management expert for your advice. ‘We need to know whether Perkin’s budgeting process is appropriate for the business, and how this contributed to last year’s poor performance’, she said, ‘and more importantly, how do we need to change the process to prevent this happening in the future, such as a move to beyond budgeting.’
Required:
(a) Evaluate the weaknesses in Perkin’s current budgeting system and whether it is suitable for the environment in which Perkin operates. (13 marks)
(b) Evaluate the impact on Perkin of moving to beyond budgeting. (12 marks)
Tutor note: This is a detailed solution and candidates would not be expected to produce an answer of this length.
(a) Weaknesses in the current budget process at Perkin
Perkin uses a traditional approach to budgeting, which has a number of weaknesses.
First of all the budgeting system does not seem aligned with Perkin’s corporate objective which focuses on innovation and continuous product improvement. Innovation is a key competitive advantage to both component and device manufacturers in this industry and the products which incorporate Perkin’s components are subject to rapid technological change as well as changes in consumer trends. The markets in which the two divisions operate appear to be evolving, as seen by the high popularity of the smartphone model which was designed for playing games. This may mean the distinction between smartphone and gaming devices could be becoming less clear cut. Management time would probably be better spent considering these rapid changes and currently the budgeting process does not facilitate that.
In reality, the budget process at Perkin is time consuming and probably therefore a costly exercise. Divisional budgets go through a lengthy process of drafting and then revision by the main board before they are approved. The approval often happens after the start of the period to which they relate, at which point the budgets are already out of date. This also means divisional managers are trying to plan activities for the next financial year without a set of finalised targets agreed, which could impact the effectiveness of decisions made.
Another weakness is that the budgets are only prepared annually, which is clearly too infrequent for a business such as Perkin. The process is also rigid and inflexible as deviations from the planned targets are not tolerated. Sticking to rigid, annual budgets can lead to problems such as P Division not being able to cope with increasing popularity of a particular product and even other short-term changes in demand like those driven by seasonal factors, or one-off events such as the factory fire. Linked to this problem of budgetary constraints is that to cut costs to achieve the budgeted net profit, managers closed one of the three research and development facilities in G Division. As identified at the outset, a successful research and development function is a key source of long-term competitive advantage to Perkin.
It also appears that Perkin fails to flex the budgets and consequently the fixed budgets had discouraged divisional managers from deviating from the original plan. P Division did not make technical modifications to its components due to the cost of doing so, which meant they were unable to supply components for use in the new model of smartphone and had to discount the inventories of the old version. It is unclear why G Division did not take on additional staff to cope with increased demand following reopening of their customer’s factory, but it may be because managers felt constrained by the budget. This then caused long-term detriment to Perkin as they lost the preferred supplier status with their main customer.
Another problem created by annual budgeting is the management of short-term changes in costs and prices. A key component of Perkin’s products is silver, which fluctuates in price, and though it is not clear how much effect this has on Perkin’s costs, any problems in supply could disrupt production even if only a small amount of silver were required. Also Perkin exports goods worldwide and probably also purchases materials, including silver, from overseas. The business is therefore exposed to short-term movements in foreign currency exchange rates which may affect costs and selling prices.
Similarly, there also seems to be considerable uncertainty in sales volumes and prices which creates problems in the forecasting process for the two divisions. P Division did not anticipate the high demand for the new component which meant P Division had to discount products it had already manufactured in order to achieve its forecast sales volumes. G Division did correctly forecast the demand, but based on past growth in the market which may be too simplistic in a rapidly changing industry. Lack of up-to-date information will hinder decision-making and overall performance at Perkin. Perkin would perhaps be better adopting a rolling basis for forecasting.
The two divisions share manufacturing facilities and are likely to compete for other resources during the budgeting process. The current budgeting system does not encourage resource, information or knowledge sharing, for example, expertise in forecasting silver requirements. Divisional managers are appraised on the financial performance of their own division and hence are likely to prioritise the interests of their own division above those of Perkin as a whole. P Division would not re-allocate its manufacturing facilities to G Division, even though G Division needed this to cope with extra demand following reopening of the customer’s factory. The current system is therefore not encouraging goal congruence between the divisions and Perkin as a whole and a budgeting system, if done effectively, should encourage co-ordination and co-operation.
Managers may find the budgeting process demotivating because it is time-consuming for them and then the directors override the forecast which they had made. It is also unfair and demotivating to staff to appraise them on factors which are outside their control. This also identifies another weakness in Perkin’s budgeting system related to control as there does not seem to be any planning and operating variance analysis performed to assess exactly where performance is lacking and so no appropriate management information is provided. In fact it is not even clear just how often divisional managers receive reports on performance throughout the year. Any budgeting system without regular feedback would be ineffective. It should even be noted that for the industry in which Perkin operates the use of only budgetary targets as a measure of performance is narrow and internal. It should be utilising information from external sources as well to assess performance in a more relevant and contextual way.
Given the rapidly changing external environment and the emphasis on innovation and continuous product development, the current traditional budgeting method does not seem appropriate for Perkin.
(b) Beyond budgeting moves away from traditional budgeting processes and is suitable for businesses operating in a rapidly changing external environment and has the following features:
1. Encourages management to focus on the present and the future. Performance is assessed by reference to external benchmarks, utilising rolling forecasts and more non-financial information. This encourages a longer term view.
2. More freedom is given to managers to make decisions, which are consistent with the organisation’s goals and achieving competitive success.
3. Resources are made available on demand, for example, to enable a division to take advantage of an opportunity in the market, rather than being constrained by budgets.
4. Management focus is switched to the customer and managers are motivated towards actions which benefit the whole organisation, not just their own divisions.
5. Effective information systems are required to provide fast and easily accessible information across the whole organisation to allow for robust planning and control at all levels.
Taking each of the elements of beyond budgeting in turn, the impact of introducing this technique into Perkin can be assessed.
At Perkin, there are rapid technological changes in the products being produced by customers and competitors as a result of changes demanded by the market, which mean that Perkin must respond and continuously innovate and develop its products. This will support Perkin’s corporate objective. Consequently, this means that Perkin must change its plans frequently to be able to compete effectively with other component manufacturers and therefore will need to move away from annual incremental budgeting to introducing regular rolling forecasts. This process will need supporting by KPIs which will have a longer term focus. The impact of this will be that Perkin will need to develop a coherent set of strategies which supports its corporate objective, which will then need to be translated into targets and appropriate KPIs selected and developed. It will also mean that performance measures at the operational level will need to be revised from annual budgetary targets to these longer term objectives. Management at all levels will require training on the production of rolling forecasts and Perkin will need to assess if additional resources will also be required to run this new system.
Beyond budgeting focuses on the long-term success of the business by division managers working towards targets which may be non-financial. The use of external benchmarks and non-financial information will mean Perkin will need to put processes in place to collect this information and analyse it to assess performance. This will be a learning process as Perkin does not currently do this. The status of preferred supplier with key customers, for example, would be important to the long-term success of the business and this could be an objective which Perkin sets for its divisional managers.
Beyond budgeting allows authority to be delegated to suitably trained and supported managers to take decisions in the long-term interests of the business. It allows managers to respond quickly and effectively to changes in the external environment, and encourages them to develop innovative solutions to external change. In Perkin, budgets proposed by divisional managers are changed by the board to reflect its overall plans for the business. This means that a change in the approach to communication between the board and the divisions will be necessary as Perkin would need to switch from the top down process currently adopted to a more devolved decision-making structure. This will again require training for management to enable them to be ready to deal with this delegated authority as it will be very different from their existing approach.
Traditional budgeting may constrain managers who are not allowed to fail to meet the approved budget. This can be seen when P Division did not adapt its components because it did not want to incur the costs of doing so, which had not been budgeted for. Similarly, prices of raw materials are known to be volatile. Beyond budgeting makes resources available for managers to take advantage of opportunities in the market, such as the smartphone designed for playing games. Managers would also be able to react to changes in the price of materials or changes in foreign currency exchange rates, for example, by having the authority to purchase silver for inventory at times when the price of silver is low. This will mean that as a result there will be fewer budgetary constraints; however, these resources and targets will still need to be effectively managed. This management will mean that strategic initiatives invested in will need monitoring rather than closely scrutinising departmental budgets, which will be a significant change in Perkin.
In Perkin, the two divisions share some manufacturing facilities and are likely to compete for other resources, for example, when setting budgets. When manufacturing facilities are in short supply, each division will prioritise its own requirements rather than those of the business as a whole. Beyond budgeting encourages managers to work together for the good of the business and to share knowledge and resources. This is important in a business such as Perkin where product innovation is key and where the activities and products of the two divisions are similar. This coordinated approach will be new to Perkin so there will be a culture change. Also, the customer-oriented element of beyond budgeting is key here and will require the setup of customer focused teams which will require more harmonised actions in the divisions.
Each division currently has its own IT systems. In order to effectively share knowledge and to be able to respond to the external environment, which are key elements of beyond budgeting, it would be preferable for them to have shared IT facilities. This will mean that Perkin may have to invest in new technology capable of sharing information across the organisation in a rapid and open fashion but also be able to collect all relevant comparative data to allow for continuous monitoring of performance. This will facilitate better planning and control across all levels of Perkin.
With appropriate training of managers and investment in information systems, it would be relevant for Perkin to adopt beyond budgeting because of the rapid changes in the external environment in which it operates.
(b) The directors of Carver Ltd are aware that some of the company’s shareholders want to realise the value in their
shares immediately. Accordingly, instead of investing in the office building or the share portfolio they are
considering two alternative strategies whereby, following the sale of the company’s business, a payment will be
made to the company’s shareholders.
(i) Liquidate the company. The payment by the liquidator would be £126 per share.
(ii) The payment of a dividend of £125 per share following which a liquidator will be appointed. The payment
by the liquidator to the shareholders would then be £1 per share.
The company originally issued 20,000 £1 ordinary shares at par value to 19 members of the Cutler family.
Following a number of gifts and inheritances there are now 41 shareholders, all of whom are family members.
The directors have asked you to attend a meeting to set out the tax implications of these two alternative strategies
for each of the two main groups of shareholders: adults with shareholdings of more than 500 shares and children
with shareholdings of 200 shares or less.
Required:
Prepare notes explaining:
– the amount chargeable to tax; and
– the rates of tax that will apply
in respect of each of the two strategies for each of the two groups of shareholders ready for your meeting
with the directors of Carver Ltd. You should assume that none of the shareholders will have any capital
losses either in the tax year 2007/08 or brought forward as at 5 April 2007. (10 marks)
Note:
You should assume that the rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 will continue to apply for the
foreseeable future.



For this part, assume today’s date is 15 August 2005.
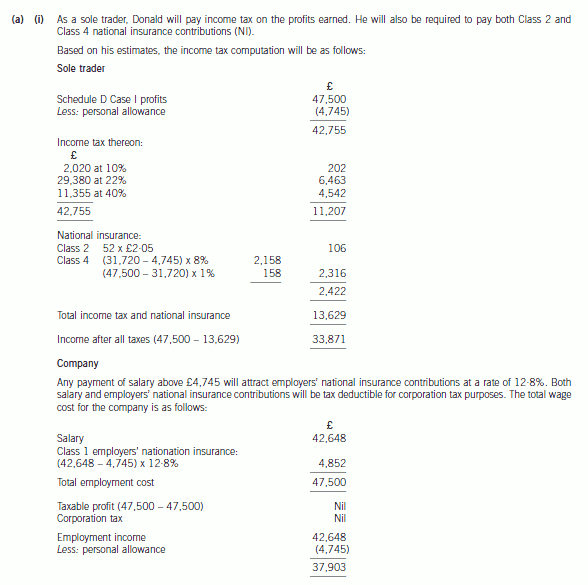
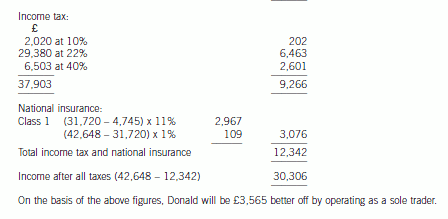
5 (a) Donald is aged 22, single, and about to finish his university education. He has plans to start up a business selling
computer games, and intends to start trading on 1 April 2006, making up accounts to 31 March annually.
He believes that his business will generate cash (equal to taxable profits) of £47,500 in the first year. He
originally intended to operate as a sole trader, but he has recently discovered that as an alternative, he could
operate through a company. He has been advised that if this is the case, he can take a maximum gross salary
of £42,648 out of the company.
Required:
(i) Advise Donald on the income tax (IT), national insurance (NIC) and corporation tax (CT) liabilities he
will incur for the year ended 31 March 2007 trading under each of the two alternative business
structures (sole trade/company). Your advice should be supported by calculations of disposable income
for both alternatives assuming that in the company case, he draws the maximum salary stated.
(7 marks)
(b) Assess the likely strategic impact of the new customer delivery system on Supaserve’s activities and its ability
to differentiate itself from its competitors. (10 marks)
(b) Supaserve, through its electronic point of sale system (EPOS), is already likely to have useful information on the overall
patterns of buying behaviour in terms of products bought frequently, peak periods, etc. It is less likely to have detailed
information on individual customer purchase patterns, though it may be monitoring where its customers are living, travel
patterns, etc. The introduction of the new online system has the potential to have a major strategic impact on the company
and its relationship with its customers. Impact can be measured by assessing the significance of the change on the company’s
operations and the likelihood of its occurrence. In Michael Porter’s words, ‘the basic tool for understanding the influence of
information technology on companies is the value chain . . . and how it affects both a company’s cost and the value delivered
to buyers’.
Clearly the investment in Internet based technology will affect both the cost and revenue sides of the business. In terms of
operations the company will need to decide the way in which to integrate the new method of customer buying with its
traditional methods. Does it create a separate ‘dedicated’ warehouse operation solely involved with the online business or does
it integrate it within its existing operations? The customer will have immediate access to information on whether goods are in
stock or not, and this may have a significant impact on the procurement systems Supaserve has with its suppliers and the
inbound logistics which get the products to where they are needed for dispatch to the customers.
Online shopping will have a major impact on outbound logistics in that a totally new distribution process will have to be
created. The extent to which this new service is provided in-house by setting up a new activity within Supaserve, or
alternatively is outsourced to specialist distributors is a key decision affecting costs and efficiency. Supaserve’s delivery
performance will be both measurable and potentially available to competitors and a real source of competitive advantage or
disadvantage.
The new online system will have an immediate impact on marketing and sales. Can customers pay over the Internet?
Opportunities for direct marketing to individual customers are opened up and customisation becomes a real possibility.
Customers can link into after-sales services and provide insights into customer satisfaction. On the support side of the value
chain the impact on human resources may be profound and technology lies at the heart of the change. Above all there is a
key need to link the new strategy to the operational systems needed to deliver it.
Clearly, the introduction of the online shopping system offers an opportunity for Supaserve to differentiate itself from its
aggressive competitors. The online service, as suggested above, is likely to appeal to a limited but growing segment of its
customers. In strategic terms it is a focus differentiation strategy enabling Supaserve to provide an improved level of service
to its customers. For this customers are willing to pay a small premium. Perhaps the more significant impact on its profit
margins will be derived from improved levels of customer retention and the attraction of customers who formerly shopped
with its competitors. The ability to sustain its competitive advantage will be measured by the impact on its competitors and
their ability to introduce a similar service.
There are a number of useful models for assessing the impact of an IT related change. These could include the five forces
model and the frameworks developed by Michael Earl assessing the strategic impact of IT. Michael Earl argues persuasively
for the correct alignment between business strategy and IT strategy. Indeed he sees a need for a ‘binary approach’ with the
alignment of IT investment activities in existing ways of doing business as having to be accommodated with the IT investments
associated with more radical change to the ways business is conducted.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04