ACCA考试:会计师与企业基础经典习题(10)
发布时间:2022-01-09
各位参加ACCA考试的小伙伴们注意啦!今天51题库考试学习网给各位小伙伴分享ACCA考试:会计师与企业基础经典习题(10),感兴趣的小伙伴赶快来围观哦!
10.1 You have been asked to work on a majorinvestment decision that your company will be making, and discover that yourbrother-in-law is the managing directorof a firm that may benefit from theoutcome of the decision. You have no intention of allowing this to influencethe advice you give your firm, and you know that your brother-in-law will nottry to influence you in any way. What professional quality would make youconsider handing this task to a colleague, orotherwise raising questions withyour superiors?
A Scepticism
B Accountability
C Independence of mind
D Independence in appearance
答案:D
10.2 X plc is trying to get a tradingpermit, forwhich it qualifies. Unfortunately, there is a backlog at theissuing office, and X plc has been notified that there will be a delay in theprocessing of its permit. The divisional manager offers a donation to theissuing office//'s staff welfare fund, if the official concerned will expeditethe paperwork. Which of the following statements is true of this action?
A It is not unethical, because the money isoffered forpositive purposes.
B It is not unethical, because X plc islegally entitled to the benefit it is claiming.
C It constitutes bribery.
D It constitutes grease money.
答案:D
10.3 Which of the following is an approachto ethics which combines a concern forthe law with an emphasis on managerialresponsibility?
A Compliance based
B Integrity based
C Environmental based
D Economic based
答案:B
10.4 Farrah works in the sales tax sectionof the accounts department of BCD Co. When the finance directoris on holiday,Farrah notices that BCD Co has not been paying the correct quarterly amounts tothe authorities. Farrah had suspected this forsome time and decides to contactthe authorities to tell them about the fraud. This disclosure is known as _______What two words correctly complete the sentence?
A Confidentiality breach
B Corporate conscience
C Whistle blowing
答案:C
今天的试题分享到此结束,预祝各位小伙伴顺利通过接下来的ACCA考试,如需查看更多ACCA考试试题,记得关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
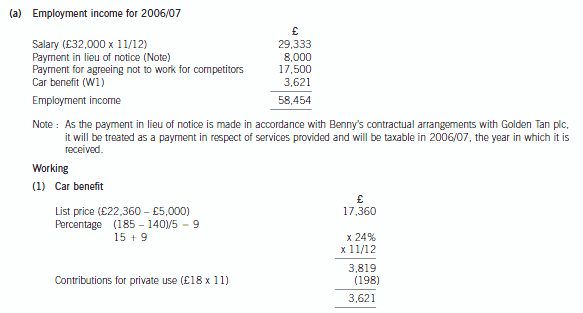
2 Benny Korere has been employed as the sales director of Golden Tan plc since 1994. He earns an annual salary of
£32,000 and is provided with a petrol-driven company car which has a CO2 emission rate of 187g/km and had a
list price when new of £22,360. In August 2003, when he was first provided with the car, Benny paid the company
£6,100 towards the capital cost of the car. Golden Tan plc does not pay for any of Benny’s private petrol and he is
also required to pay his employer £18 per month as a condition of being able to use the car for private purposes.
On 1 December 2006 Golden Tan plc notified Benny that he would be made redundant on 28 February 2007. On
that day the company will pay him his final month’s salary together with a payment of £8,000 in lieu of the three
remaining months of his six-month notice period in accordance with his employment contract. In addition the
company will pay him £17,500 in return for agreeing not to work for any of its competitors for the six-month period
ending 31 August 2007.
On receiving notification of his redundancy, Benny immediately contacted Joe Egmont, the managing director of
Summer Glow plc, who offered him a senior management position leading the company’s expansion into Eastern
Europe. Summer Glow plc is one of Golden Tan plc’s competitors and one of the most innovative companies in the
industry, although not all of its strategies have been successful.
Benny has agreed to join Summer Glow plc on 1 September 2007 for an annual salary of £39,000. On the day he
joins the company, Summer Glow plc will grant him an option to purchase 10,000 ordinary shares in the company
for £2·20 per share under an unapproved share option scheme. Benny can exercise the option once he has been
employed for six months but must hold the shares for at least a year before he sells them.
The new job will require Benny to spend a considerable amount of time in London. Summer Glow plc has offered
Benny the exclusive use of a flat that the company purchased on 1 June 2003 for £165,000; the flat is currently
rented out. The flat will be made available from 1 September 2007. The company will pay all of the utility bills
relating to the flat as well as furnishing and maintaining it. Summer Glow plc has also suggested that if Benny would
rather live in a more central part of the city, the company could sell the existing flat and buy a more centrally located
one, of the same value, with the proceeds.
On 15 March 2007 Benny intends to sell 5,800 shares in Mahana plc, a quoted company, for £24,608. His
transactions in the company’s shares have been as follows:
£
June 1988 Purchased 8,400 shares 6,744
February 1996 Sale of rights nil paid 610
January 2005 Purchased 1,300 shares 2,281
The sale of rights, nil paid, was not treated as a part disposal of Benny’s holding in Mahana plc.
Benny’s shareholding in Mahana plc represents less than 1% of the company’s issued ordinary share capital. He will
not make any other capital disposals in 2006/07.
In addition to his employment income, Benny receives rental income of £4,000 (net of deductible expenses) each
year. He normally submits his tax return in August but he has not yet prepared his return for 2005/06. He expects
to be very busy in December and January and is planning to prepare his tax return in late February 2007.
Required:
(a) Calculate Benny’s employment income for 2006/07. (4 marks)
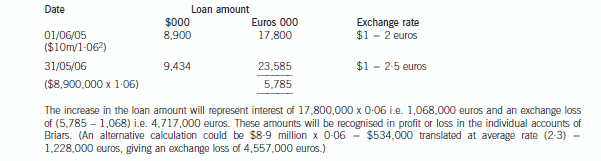
(b) Describe with suitable calculations how the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Briars will be dealt with in
the group financial statements and how the loan to Briars should be treated in the financial statements of
Briars for the year ended 31 May 2006. (9 marks)
(b) IAS21 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’ requires goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation
and fair value adjustments to acquired assets and liabilities to be treated as belonging to the foreign operation. They should
be expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate at each balance sheet date.
Effectively goodwill is treated as a foreign currency asset which is retranslated at the closing rate. In this case the goodwillarising on the acquisition of Briars would be treated as follows:

At 31 May 2006, the goodwill will be retranslated at 2·5 euros to the dollar to give a figure of $4·4 million. Therefore this
will be the figure for goodwill in the balance sheet and an exchange loss of $1·4 million recorded in equity (translation
reserve). The impairment of goodwill will be expensed in profit or loss to the value of $1·2 million. (The closing rate has been
used to translate the impairment; however, there may be an argument for using the average rate.)
The loan to Briars will effectively be classed as a financial liability measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for
financial liabilities that do not meet the definition of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. For most entities,
most financial liabilities will fall into this category. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the
liability is measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled, between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. In other words, fair value is an actual or estimated transaction price on the reporting
date for a transaction taking place between unrelated parties that have adequate information about the asset or liability being
measured.
Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value generally is assumed to equal the amount of
consideration paid or received for the financial asset or financial liability. Accordingly, IAS39 specifies that the best evidence
of the fair value of a financial instrument at initial recognition generally is the transaction price. However for longer-term
receivables or payables that do not pay interest or pay a below-market interest, IAS39 does require measurement initially at
the present value of the cash flows to be received or paid.
Thus in Briars financial statements the following entries will be made:
(c) mandatory continuing professional development (CPD) requirements. (5 marks)
(c) Continuing Professional Development (CPD)
CPD is defined5 as ‘the continuous maintenance, development and enhancement of the professional and personal knowledge
and skills which members of ACCA require throughout their working lives’.
All professional accountants need to maintain their competence and develop new skills to be effective in their current and
future employment. CPD helps keep accountants in practice employable and maintains their reputation with employers,
clients and the public. It also helps maintain the accounting profession’s reputation for producing and supporting high calibre
individuals. Therefore, CPD is something which professional accountants should take personal responsibility for, and be doing
as part of their everyday work.
Mandatory CPD for active members of IFAC member bodies (such as ACCA) was introduced with effect from 1 January 2005
onwards. ACCA has introduced CPD as a requirement for all active members, subject to the phasing-in dates (and waivers).
Tutorial note: IFAC issued International Education Standard (IES) 7, which requires the introduction of CPD for all active
members of IFAC member bodies.
ACCA practising certificate and insolvency licence holders are still required to participate in technical CPD training. All other
members will also be asked to state on their annual CPD return that they maintain competence in professional ethics.
The scheme is being introduced in phases:
■ phase 1 (2005) – members admitted since 1 January 2001, and all practising certificate and insolvency licence
holders;
■ phase 2 (2006) – members admitted between 1 January 1995 and 31 December 2000;
■ phase 3 (2007) – all remaining members.
Tutorial note: However, ACCA encouraged all members to adopt the scheme from 1 January 2005.
Affiliates join the CPD scheme on 1 January following their date of admittance to membership.
There are two routes to participation in ACCA’s CPD scheme:
(1) the unit scheme route (40 units approximate to 40 hours required each year); and
(2) the approved CPD employer route (i.e. where employers are recognised as effectively providing ACCA members with
CPD).
Tutorial note: Alternatively, if an ACCA member is also a member of another IFAC accounting body and that CPD scheme
is compliant with IFAC’s CPD IES 7, they may choose to follow that body’ s route.
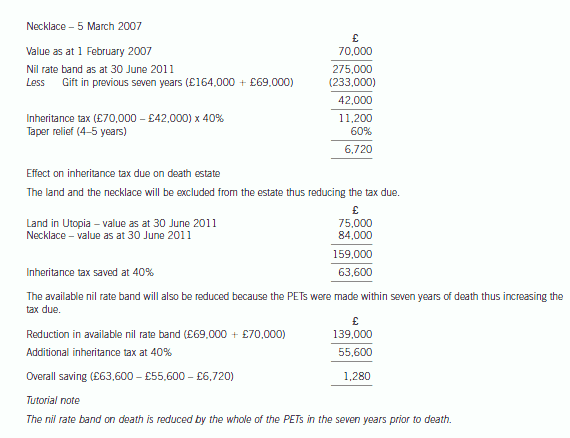
James died on 22 January 2015. He had made the following gifts during his lifetime:
(1) On 9 October 2007, a cash gift of £35,000 to a trust. No lifetime inheritance tax was payable in respect of this gift.
(2) On 14 May 2013, a cash gift of £420,000 to his daughter.
(3) On 2 August 2013, a gift of a property valued at £260,000 to a trust. No lifetime inheritance tax was payable in respect of this gift because it was covered by the nil rate band. By the time of James’ death on 22 January 2015, the property had increased in value to £310,000.
On 22 January 2015, James’ estate was valued at £870,000. Under the terms of his will, James left his entire estate to his children.
The nil rate band of James’ wife was fully utilised when she died ten years ago.
The nil rate band for the tax year 2007–08 is £300,000, and for the tax year 2013–14 it is £325,000.
Required:
(a) Calculate the inheritance tax which will be payable as a result of James’ death, and state who will be responsible for paying the tax. (6 marks)
(b) Explain why it might have been beneficial for inheritance tax purposes if James had left a portion of his estate to his grandchildren rather than to his children. (2 marks)
(c) Explain why it might be advantageous for inheritance tax purposes for a person to make lifetime gifts even when such gifts are made within seven years of death.
Notes:
1. Your answer should include a calculation of James’ inheritance tax saving from making the gift of property to the trust on 2 August 2013 rather than retaining the property until his death.
2. You are not expected to consider lifetime exemptions in this part of the question. (2 marks)
(a) James – Inheritance tax arising on death
Lifetime transfers within seven years of death
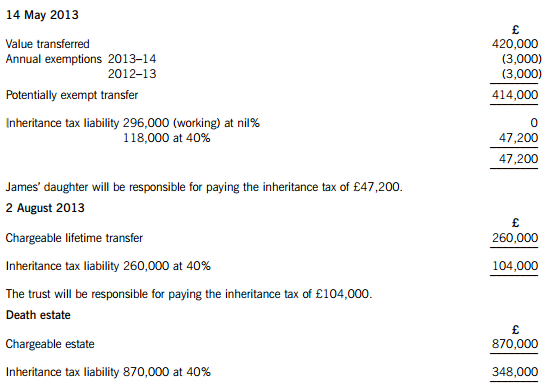
The personal representatives of James’ estate will be responsible for paying the inheritance tax of £348,000.
Working – Available nil rate band
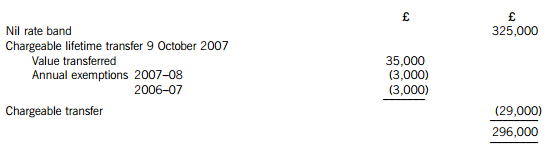
(b) Skipping a generation avoids a further charge to inheritance tax when the children die. Gifts will then only be taxed once before being inherited by the grandchildren, rather than twice.
(c) (1) Even if the donor does not survive for seven years, taper relief will reduce the amount of IHT payable after three years.
(2) The value of potentially exempt transfers and chargeable lifetime transfers are fixed at the time they are made.
(3) James therefore saved inheritance tax of £20,000 ((310,000 – 260,000) at 40%) by making the lifetime gift of property.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-08-16
- 2022-01-07
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-09-04
- 2022-01-09
- 2022-01-09
- 2022-01-08
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-10-14