ACCA考试F2基础模拟题:Sources of data
发布时间:2019-01-04
Question:A company wishes to carry out a
national survey of adults' reading habits. To reduce travelling costs, the
country was divided into constituencies. A sample of 50 constituencies was
selected at random. With each of these constituencies, 5 polling districts were
selected, again using random techniques. Interviewers will visit a random
selection of 30 people on the electoral register of each district selected.
What sampling method
is the company using?
A.Stratified
B.Systematic
C.Multi-stage
D.Simple random
The correct answer
is: C
The sample is
selected in stages, at first selecting not individuals but constituencies.
Multi-stage sampling
is the correct answer as this method involves dividing the population into a
number of sub-populations and then selecting a small sample of these
sub-populations at random. Each sub-population is then divided further.
Stratified sampling
involves dividing the population into strata and then taking a random sample
from each stratum.
Random sampling is
where every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected and
systematic where every nth item after a random start is selected.
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Explain THREE strategies that might be adopted in order to improve the future prospects of Diverse
Holdings Plc. (6 marks)
(ii) The forecast situation of Diverse Holdings Plc is not without its problems. KAL and OPL require the immediate attention
of management. The position of KAL is precarious to say the least. There is a choice of strategies for it:
(i) Outsource the manufacture of appliances
(ii) Set up a manufacturing operation overseas
(ii) Withdraw from the market.
Each alternative must be assessed. Whatever decision is taken it is unlikely to affect the other four subsidiaries.
PSL is also independent of the other subsidiaries. A strategic decision to widen its range of products and outlets must
surely help. Hence management should endeavour to find new markets for its products, which are separate and distinct
from those markets served by its appointed distributors.
21
In order to improve the prospects of OPL management need to adopt appropriate strategies since at the present time the
company appears to be in a high growth market but is unable to capture a reasonable market share. Perhaps the answer
lies in increased or more effective advertising of the endorsement of the product range by health and safety experts.
Management should endeavour to develop a strategy to integrate further its subsidiaries so that they can benefit from
each other and also derive as much synergy as possible from the acquisition of HTL.
It is of paramount importance that management ensure that sufficient funds are channelled into growing OFL and HTL,
which are both showing a rising trend in profitability. The group has depleted cash reserves which must to some extent
be attributable to the purchase of HTL. It is possible that the divestment of KAL would provide some much needed
funding.
(b) Describe the advantages of external recruitment. (5 marks)
(b) External recruitment describes the situation where the organisation decides to fill a staff vacancy and recruit from outside the organisation.
It may be essential if particular skills or expertise are not already available within the organisation and is necessary to restore depleted staffing levels or when for some reason the organisation urgently needs new employees. New staff members bring new ideas and novel approaches to the organisation and to the specific task, often providing experience and work methods from other employers.
(c) Discuss the practical problems that may be encountered in the implementation of an activity-based system
of product cost management. (5 marks)
(c) The benefits of an activity-based system as the basis for product cost/profit estimation may not be straightforward. A number
of problems may be identified.
The selection of relevant activities and cost drivers may be complicated where there are many activities and cost drivers in
complex business situations.
There may be difficulty in the collection of data to enable accurate cost driver rates to be calculated. This is also likely to
require an extensive data collection and analysis system.
The problem of ‘cost driver denominator level’ may also prove difficult. This is similar to the problem in a traditional volume
related system. This is linked to the problem of fixed/variable cost analysis. For example the cost per batch may be fixed. Its
impact may be reduced, however, where the batch size can be increased without a proportionate increase in cost.
The achievement of the required level of management skill and commitment to change may also detract from the
implementation of the new system. Management may feel that the activity based approach contains too many assumptions
and estimates about activities and cost drivers. There may be doubt as to the degree of increased accuracy which it provides.
(alternative relevant examples and discussion would be acceptable)
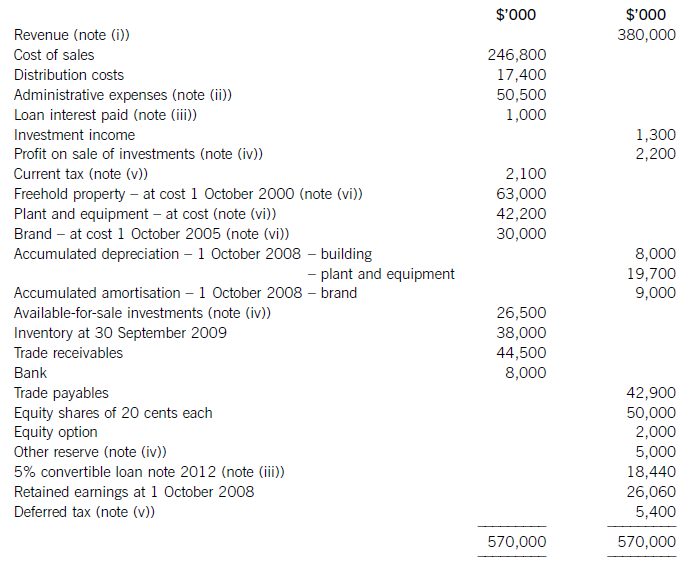
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04