2020年ACCA考试《财务会计》备考考点(1)
发布时间:2020-10-18
今日51题库考试学习网为大家带来“2020年ACCA考试《财务会计》备考考点(1)”的相关知识点,各位辛勤备考的小伙伴一起来看看吧。
THE CONTROL ENVIRONMENT OF A COMPANY (五)
Five Organizational structure
ISA 315 describes a company’s organizational
structure as being ‘the framework within which an entity’s activities for
achieving its objectives are planned, executed, controlled and reviewed’. The
appendix to the ISA then explains ‘that the appropriateness of an entity’s organizational
structure depends, in part, on its size and the nature of its activities’. It
follows from this that an international consulting company with offices and
operations in several countries has different priorities in terms of organizational
structure to a national car sales company with several offices and a number of
sales branches in a single country. Similarly, the organizational structure
deemed suitable for such a car sales company would not be appropriate for a
single site manufacturing company. Generally, an auditor may reasonably expect
there to be a positive correlation between the level of inherent risk and the
size and complexity of a company’s operations. In assessing, the level of the
risk of material misstatement the auditor should consider as to whether the
company’s organizational structure in terms of authority, responsibility and
lines of reporting meet desired objectives.
Six Assignment of authority and
responsibility
Normally, the larger as companies scale of
operations, then the larger the size of the workforce and, inevitably, the
larger the amount of assignment of authority and responsibility that is
required. Consequently, companies need to deal with not only ensuring that
appropriate levels of authority and responsibility are assigned to
appropriately qualify and experienced individuals. They also need to ensure
that adequate reporting relationships and authorization hierarchies are in
place.
Additionally, individuals need to be
properly resourced and made fully aware of their responsibilities and of how
their actions interrelate with the actions of others and contribute to the
objectives of the company. If a company is not successful in meeting each of
these needs, then there is an increased probability of ineffective decisions,
errors and oversights by employees leading to an increased risk of material
misstatement in its financial statements. For example, where a wages clerk is authorized
to process the wages payroll and is then assigned the (inappropriate!)
authority to enter new employee details into the wages master file.
以上就是51题库考试学习网带给大家的全部内容,相信小伙伴们都了解清楚。预祝大家在ACCA考试中取得满意的成绩,如果想要了解更多关于ACCA考试的资讯,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
On 1 April 2009 Pandar purchased 80% of the equity shares in Salva. The acquisition was through a share exchange of three shares in Pandar for every five shares in Salva. The market prices of Pandar’s and Salva’s shares at 1 April
2009 were $6 per share and $3.20 respectively.
On the same date Pandar acquired 40% of the equity shares in Ambra paying $2 per share.
The summarised income statements for the three companies for the year ended 30 September 2009 are:
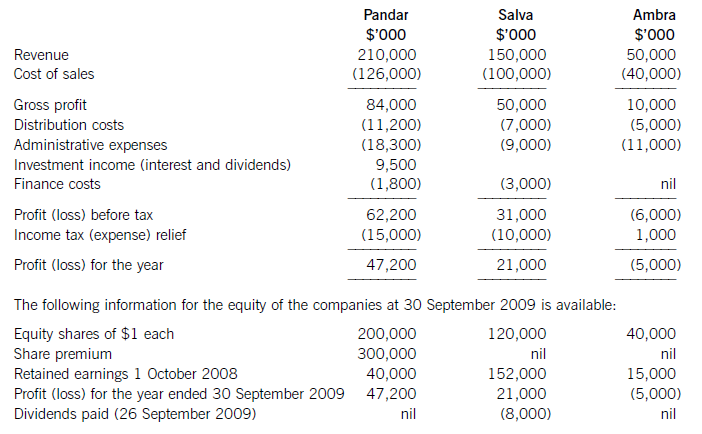
The following information is relevant:
(i) The fair values of the net assets of Salva at the date of acquisition were equal to their carrying amounts with the exception of an item of plant which had a carrying amount of $12 million and a fair value of $17 million. This plant had a remaining life of five years (straight-line depreciation) at the date of acquisition of Salva. All depreciation is charged to cost of sales.
In addition Salva owns the registration of a popular internet domain name. The registration, which had a
negligible cost, has a five year remaining life (at the date of acquisition); however, it is renewable indefinitely at a nominal cost. At the date of acquisition the domain name was valued by a specialist company at $20 million.
The fair values of the plant and the domain name have not been reflected in Salva’s financial statements.
No fair value adjustments were required on the acquisition of the investment in Ambra.
(ii) Immediately after its acquisition of Salva, Pandar invested $50 million in an 8% loan note from Salva. All interest accruing to 30 September 2009 had been accounted for by both companies. Salva also has other loans in issue at 30 September 2009.
(iii) Pandar has credited the whole of the dividend it received from Salva to investment income.
(iv) After the acquisition, Pandar sold goods to Salva for $15 million on which Pandar made a gross profit of 20%. Salva had one third of these goods still in its inventory at 30 September 2009. There are no intra-group current account balances at 30 September 2009.
(v) The non-controlling interest in Salva is to be valued at its (full) fair value at the date of acquisition. For this
purpose Salva’s share price at that date can be taken to be indicative of the fair value of the shareholding of the non-controlling interest.
(vi) The goodwill of Salva has not suffered any impairment; however, due to its losses, the value of Pandar’s
investment in Ambra has been impaired by $3 million at 30 September 2009.
(vii) All items in the above income statements are deemed to accrue evenly over the year unless otherwise indicated.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Salva at 1 April 2009; (6 marks)
(ii) Calculate the carrying amount of the investment in Ambra to be included within the consolidated
statement of financial position as at 30 September 2009. (3 marks)
(b) Prepare the consolidated income statement for the Pandar Group for the year ended 30 September 2009.(16 marks)
Section B – TWO questions ONLY to be attempted
(a) Cate is an entity in the software industry. Cate had incurred substantial losses in the fi nancial years 31 May 2004 to 31 May 2009. In the fi nancial year to 31 May 2010 Cate made a small profi t before tax. This included signifi cant non-operating gains. In 2009, Cate recognised a material deferred tax asset in respect of carried forward losses, which will expire during 2012. Cate again recognised the deferred tax asset in 2010 on the basis of anticipated performance in the years from 2010 to 2012, based on budgets prepared in 2010. The budgets included high growth rates in profi tability. Cate argued that the budgets were realistic as there were positive indications from customers about future orders. Cate also had plans to expand sales to new markets and to sell new products whose development would be completed soon. Cate was taking measures to increase sales, implementing new programs to improve both productivity and profi tability. Deferred tax assets less deferred tax liabilities represent 25% of shareholders’ equity at 31 May 2010. There are no tax planning opportunities available to Cate that would create taxable profi t in the near future. (5 marks)
(b) At 31 May 2010 Cate held an investment in and had a signifi cant infl uence over Bates, a public limited company. Cate had carried out an impairment test in respect of its investment in accordance with the procedures prescribed in IAS 36, Impairment of assets. Cate argued that fair value was the only measure applicable in this case as value-in-use was not determinable as cash fl ow estimates had not been produced. Cate stated that there were no plans to dispose of the shareholding and hence there was no binding sale agreement. Cate also stated that the quoted share price was not an appropriate measure when considering the fair value of Cate’s signifi cant infl uence on Bates. Therefore, Cate estimated the fair value of its interest in Bates through application of two measurement techniques; one based on earnings multiples and the other based on an option–pricing model. Neither of these methods supported the existence of an impairment loss as of 31 May 2010. (5 marks)
(c) At 1 April 2009 Cate had a direct holding of shares giving 70% of the voting rights in Date. In May 2010, Date issued new shares, which were wholly subscribed for by a new investor. After the increase in capital, Cate retained an interest of 35% of the voting rights in its former subsidiary Date. At the same time, the shareholders of Date signed an agreement providing new governance rules for Date. Based on this new agreement, Cate was no longer to be represented on Date’s board or participate in its management. As a consequence Cate considered that its decision not to subscribe to the issue of new shares was equivalent to a decision to disinvest in Date. Cate argued that the decision not to invest clearly showed its new intention not to recover the investment in Date principally through continuing use of the asset and was considering selling the investment. Due to the fact that Date is a separate line of business (with separate cash fl ows, management and customers), Cate considered that the results of Date for the period to 31 May 2010 should be presented based on principles provided by IFRS 5 Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations. (8 marks)
(d) In its 2010 fi nancial statements, Cate disclosed the existence of a voluntary fund established in order to provide a post-retirement benefi t plan (Plan) to employees. Cate considers its contributions to the Plan to be voluntary, and has not recorded any related liability in its consolidated fi nancial statements. Cate has a history of paying benefi ts to its former employees, even increasing them to keep pace with infl ation since the commencement of the Plan. The main characteristics of the Plan are as follows:
(i) the Plan is totally funded by Cate;
(ii) the contributions for the Plan are made periodically;
(iii) the post retirement benefi t is calculated based on a percentage of the fi nal salaries of Plan participants dependent on the years of service;
(iv) the annual contributions to the Plan are determined as a function of the fair value of the assets less the liability arising from past services.
Cate argues that it should not have to recognise the Plan because, according to the underlying contract, it can terminate its contributions to the Plan, if and when it wishes. The termination clauses of the contract establish that Cate must immediately purchase lifetime annuities from an insurance company for all the retired employees who are already receiving benefi t when the termination of the contribution is communicated. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss whether the accounting treatments proposed by the company are acceptable under International Financial Reporting Standards.
Professional marks will be awarded in this question for clarity and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
The mark allocation is shown against each of the four parts above.
(a) Deferred taxation
A deferred tax asset should be recognised for deductible temporary differences, unused tax losses and unused tax credits to the extent that it is probable that taxable profi t will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised. The recognition of deferred tax assets on losses carried forward does not seem to be in accordance with IAS 12 Income Taxes. Cate is not able to provide convincing evidence that suffi cient taxable profi ts will be generated against which the unused tax losses can be offset. According to IAS 12 the existence of unused tax losses is strong evidence that future taxable profi t may not be available against which to offset the losses. Therefore when an entity has a history of recent losses, the entity recognises deferred tax assets arising from unused tax losses only to the extent that the entity has suffi cient taxable temporary differences or there is convincing other evidence that suffi cient taxable profi t will be available. As Cate has a history of recent losses and as it does not have suffi cient taxable temporary differences, Cate needs to provide convincing other evidence that suffi cient taxable profi t would be available against which the unused tax losses could be offset. The unused tax losses in question did not result from identifi able causes, which were unlikely to recur (IAS 12) as the losses are due to ordinary business activities. Additionally there are no tax planning opportunities available to Cate that would create taxable profi t in the period in which the unused tax losses could be offset (IAS 12).
Thus at 31 May 2010 it is unlikely that the entity would generate taxable profi ts before the unused tax losses expired. The improved performance in 2010 would not be indicative of future good performance as Cate would have suffered a net loss before tax had it not been for the non-operating gains.
Cate’s anticipation of improved future trading could not alone be regarded as meeting the requirement for strong evidence of future profi ts. When assessing the use of carry-forward tax losses, weight should be given to revenues from existing orders or confi rmed contracts rather than those that are merely expected from improved trading. Estimates of future taxable profi ts can rarely be objectively verifi ed. Thus the recognition of deferred tax assets on losses carried forward is not in accordance with IAS 12 as Cate is not able to provide convincing evidence that suffi cient taxable profi ts would be generated against which the unused tax losses could be offset.
(b) Investment
Cate’s position for an investment where the investor has signifi cant infl uence and its method of calculating fair value can be challenged.
An asset’s recoverable amount represents its greatest value to the business in terms of its cash fl ows that it can generate i.e. the higher of fair value less costs to sell (which is what the asset can be sold for less direct selling expenses) and value in use (the cash fl ows that are expected to be generated from its continued use including those from its ultimate disposal). The asset’s recoverable amount is compared with its carrying value to indicate any impairment. Both net selling price (NSP) and value in use can be diffi cult to determine. However it is not always necessary to calculate both measures, as if the NSP or value in use is greater than the carrying amount, there is no need to estimate the other amount.
It should be possible in this case to calculate a fi gure for the recoverable amount. Cate’s view that market price cannot refl ect the fair value of signifi cant holdings of equity such as an investment in an associate is incorrect as IAS 36 prescribes the method of conducting the impairment test in such circumstances by stating that if there is no binding sale agreement but an asset is traded in an active market, fair value less costs to sell is the asset’s market price less the costs of disposal. Further, the appropriate market price is usually the current bid price.
Additionally the compliance with IAS 28, Investments in associates is in doubt in terms of the non-applicability of value in use when considering impairment. IAS 28 explains that in determining the value in use of the investments, an entity estimates:
(i) its share of the present value of the estimated future cash fl ows expected to be generated by the associate, including the cash fl ows from the operations of the associate and the proceeds on the ultimate disposal of the investment; or
(ii) the present value of the estimated future cash fl ows expected to arise from dividends to be received from the investment and from its ultimate disposal.
Estimates of future cash fl ows should be produced. These cash fl ows are then discounted to present value hence giving value in use.
It seems as though Cate wishes to avoid an impairment charge on the investment.
(c) Disposal group ‘held for sale’
IAS 27 Revised Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements moved IFRS to the use of the economic entity model. The economic entity approach treats all providers of equity capital as shareholders of the entity, even when they are not shareholders in the parent company. IFRS 5 has been amended such that if there is an intention to dispose of a controlling interest in a subsidiary which meets the defi nition of ‘held for sale’, then the net assets are classifi ed as ‘held for sale’, irrespective of whether the parent was expected to retain an interest after the disposal. A partial disposal of an interest in a subsidiary in which the parent company loses control but retains an interest as an associate or trade investment creates the recognition of a gain or loss on the entire interest. A gain or loss is recognised on the part that has been disposed of and a further holding gain or loss is recognised on the interest retained, being the difference between the fair value of the interest and the book value of the interest. The gains are recognised in the statement of comprehensive income. Any prior gains or loss recognised in other components of equity would now become realised in the statement of comprehensive income.
In this case, Cate should stop consolidating Date on a line-by-line basis from the date that control was lost. Further investigation is required into whether the holding is treated as an associate or trade investment. The agreement that Cate is no longer represented on the board or able to participate in management would suggest loss of signifi cant infl uence despite the 35% of voting rights retained. The retained interest would be recognised at fair value.
An entity classifi es a disposal group as held for sale if its carrying amount will be recovered mainly through selling the asset rather than through usage and intends to dispose of it in a single transaction.
The conditions for a non-current asset or disposal group to be classifi ed as held for sale are as follows:
(i) The assets must be available for immediate sale in their present condition and its sale must be highly probable.
(ii) The asset must be currently marketed actively at a price that is reasonable in relational to its current fair value.
(iii) The sale should be completed or expected to be so, within a year from the date of the classifi cation.
(iv) The actions required to complete the planned sale will have been made and it is unlikely that the plan will be signifi cantly changed or withdrawn.
(v) management is committed to a plan to sell.
Cate has not met all of the conditions of IFRS 5 but it could be argued that the best presentation in the fi nancial statements was that set out in IFRS 5 for the following reasons.
The issue of dilution is not addressed by IFRS and the decision not to subscribe to the issue of new shares of Date is clearly a change in the strategy of Cate. Further, by deciding not to subscribe to the issue of new shares of Date, Cate agreed to the dilution and the loss of control which could be argued is similar to a decision to sell shares while retaining a continuing interest in the entity. Also Date represents a separate line of business, which is a determining factor in IFRS 5, and information disclosed on IFRS 5 principles highlights the impact of Date on Cate’s fi nancial statements. Finally, the agreement between Date’s shareholders confi rms that Cate has lost control over its former subsidiary.
Therefore, in the absence of a specifi c Standard or Interpretation applying to this situation, IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors states that management should use its judgment and refer to other IFRS and the Framework.
Thus considering the requirements of IAS 27 (Para 32–37) and the above discussion, it could be concluded that the presentation based on IFRS 5 principles selected by the issuer was consistent with the accounting treatment required by IAS 27 when a parent company loses control of a subsidiary.
(d) Defi ned benefi t plan
The Plan is not a defi ned contribution plan because Cate has a legal or constructive obligation to pay further contributions if the fund does not have suffi cient assets to pay all employee benefi ts relating to employee service in the current and prior periods (IAS 19 Para 7). All other post-employment benefi t plans that do not qualify as a defi ned contribution plan are, by defi nition therefore defi ned benefi t plans. Defi ned benefi t plans may be unfunded, or they may be wholly or partly funded. Also IAS 19 (Para 26) indicates that Cate’s plan is a defi ned benefi t plan as IAS 19 provides examples where an entity’s obligation is not limited to the amount that it agrees to contribute to the fund. These examples include: (a) a plan benefi t formula that is not linked solely to the amount of contributions (which is the case in this instance); and (b) those informal practices that give rise to a constructive obligation. According to the terms of the Plan, if Cate opts to terminate, Cate is responsible for discharging the liability created by the plan. IAS 19 (Para 52) says that an entity should account not only for its legal obligation under the formal terms of a defi ned benefi t plan, but also for any constructive obligation that arises from the enterprise’s informal practices. Informal practices give rise to a constructive obligation where the enterprise has no realistic alternative but to pay employee benefi ts. Even if the Plan were not considered to be a defi ned benefi t plan under IAS 19, Cate would have a constructive obligation to provide the benefi t, having a history of paying benefi ts. The practice has created a valid expectation on the part of employees that the amounts will be paid in the future. Therefore Cate should account for the Plan as a defi ned benefi t plan in accordance with IAS 19. Cate has to recognise, at a minimum, its net present liability for the benefi ts to be paid under the Plan.
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Keffler Co, a private limited company engaged in the manufacture of
plastic products. The draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show revenue of $47·4 million
(2005 – $43·9 million), profit before taxation of $2 million (2005 – $2·4 million) and total assets of $33·8 million
(2005 – $25·7 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In April 2005, Keffler bought the right to use a landfill site for a period of 15 years for $1·1 million. Keffler
expects that the amount of waste that it will need to dump will increase annually and that the site will be
completely filled after just ten years. Keffler has charged the following amounts to the income statement for the
year to 31 March 2006:
– $20,000 licence amortisation calculated on a sum-of-digits basis to increase the charge over the useful life
of the site; and
– $100,000 annual provision for restoring the land in 15 years’ time. (9 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 KEFFLER CO
Tutorial note: None of the issues have any bearing on revenue. Therefore any materiality calculations assessed on revenue are
inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(a) Landfill site
(i) Matters
■ $1·1m cost of the right represents 3·3% of total assets and is therefore material.
■ The right should be amortised over its useful life, that is just 10 years, rather than the 15-year period for which
the right has been granted.
Tutorial note: Recalculation on the stated basis (see audit evidence) shows that a 10-year amortisation has been
correctly used.
■ The amortisation charge represents 1% of profit before tax (PBT) and is not material.
■ The amortisation method used should reflect the pattern in which the future economic benefits of the right are
expected to be consumed by Keffler. If that pattern cannot be determined reliably, the straight-line method must
be used (IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’).
■ Using an increasing sum-of-digits will ‘end-load’ the amortisation charge (i.e. least charge in the first year, highest
charge in the last year). However, according to IAS 38 there is rarely, if ever, persuasive evidence to support an
amortisation method that results in accumulated amortisation lower than that under the straight-line method.
Tutorial note: Over the first half of the asset’s life, depreciation will be lower than under the straight-line basis
(and higher over the second half of the asset’s life).
■ On a straight line basis the annual amortisation charge would be $0·11m, an increase of $90,000. Although this
difference is just below materiality (4·5% PBT) the cumulative effect (of undercharging amortisation) will become
material.
■ Also, when account is taken of the understatement of cost (see below), the undercharging of amortisation will be
material.
■ The sum-of-digits method might be suitable as an approximation to the unit-of-production method if Keffler has
evidence to show that use of the landfill site will increase annually.
■ However, in the absence of such evidence, the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement with the
amortisation method (resulting in intangible asset overstatement/amortisation expense understatement).
■ The annual restoration provision represents 5% of PBT and 0·3% of total assets. Although this is only borderline
material (in terms of profit), there will be a cumulative impact.
■ Annual provisioning is contrary to IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
■ The estimate of the future restoration cost is (presumably) $1·5m (i.e. $0·1 × 15). The present value of this
amount should have been provided in full in the current year and included in the cost of the right.
■ Thus the amortisation being charged on the cost of the right (including the restoration cost) is currently understated
(on any basis).
Tutorial note: A 15-year discount factor at 10% (say) is 0·239. $1·5m × 0·239 is approximately $0·36m. The
resulting present value (of the future cost) would be added to the cost of the right. Amortisation over 10 years
on a straight-line basis would then be increased by $36,000, increasing the difference between amortisation
charged and that which should be charged. The lower the discount rate, the greater the understatement of
amortisation expense.
Total amount expensed ($120k) is less than what should have been expensed (say $146k amortisation + $36k
unwinding of discount). However, this is not material.
■ Whether Keffler will wait until the right is about to expire before restoring the land or might restore earlier (if the
site is completely filled in 10 years).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Written agreement for purchase of right and contractual terms therein (e.g. to make restoration in 15 years’ time).
■ Cash book/bank statement entries in April 2005 for $1·1m payment.
■ Physical inspection of the landfill site to confirm Keffler’s use of it.
■ Annual dump budget/projection over next 10 years and comparison with sum-of-digits proportions.
■ Amount actually dumped in the year (per dump records) compared with budget and as a percentage/proportion of
the total available.
■ Recalculation of current year’s amortisation based on sum-of-digits. That is, $1·1m ÷ 55 = $20,000.
Tutorial note: The sum-of-digits from 1 to 10 may be calculated long-hand or using the formula n(n+1)/2 i.e.
(10 × 11)/2 = 55.
■ The basis of the calculation of the estimated restoration costs and principal assumptions made.
■ If estimated by a quantity surveyor/other expert then a copy of the expert’s report.
■ Written management representation confirming the planned timing of the restoration in 15 years (or sooner).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-10-15
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-10-15
- 2020-09-05
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-11
- 2021-04-08
- 2021-04-08
- 2020-10-15
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-11
- 2019-03-17
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-10-15
- 2020-10-11
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-04-04
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-10-15
- 2021-04-02