ACCA考试F7模拟测试题:Analysing and interpreting financial statement
发布时间:2019-01-04
Question:Which two of the following are valid reasons why the inventory turnover period of a company increases from one year to the next?
A.Slow down in trading.
B.Obsolete goods
C.Seasonal fluctuations in orders.
D.A marketing decision to reduce selling
prices.
The correct answers are: Obsolete goods and
slow down in trading
A slow down in trade increases the
inventory turnover period. Assuming that inventory is still being ordered at
the same rate this can lead to a build up in inventory.
Inventory increases may occur where there
is no longer a demand for the product due, for example, to technical
obsolescence.
Seasonal fluctuations in orders will affect
the amount of inventory held at any one time but they will not affect inventory
turnover period year on year.
A decision to reduce sales price would not
directly affect either purchase price or level of inventory. If anything, it
would be likely to reduce inventory holding period as the company moves to a
low margin, fast turnover approach.
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.
Summarised statements of financial position as at:
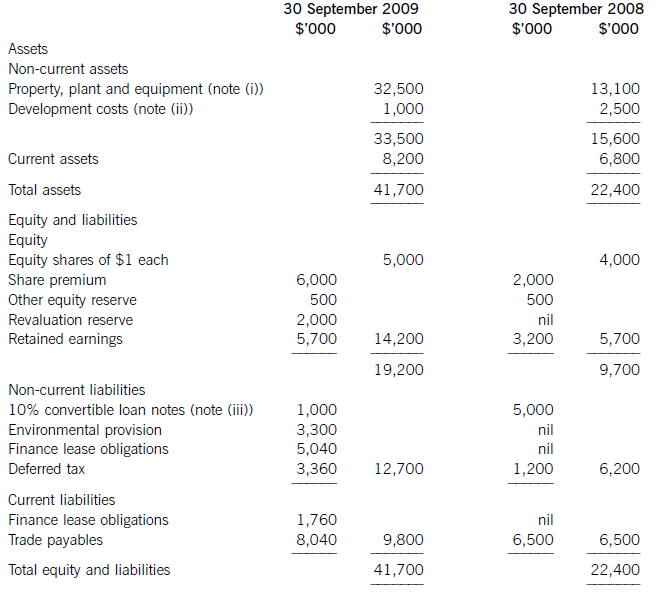
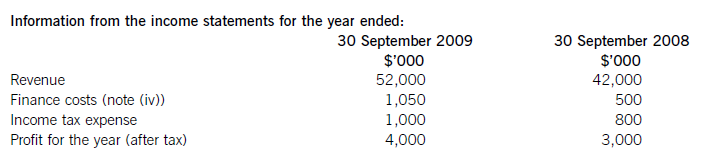
The following information is available:
(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansion programme for its non-current assets. The details of this programme are:
On 1 October 2008 Crosswire acquired a platinum mine at a cost of $5 million. A condition of mining the
platinum is a requirement to landscape the mining site at the end of its estimated life of ten years. The
present value of this cost at the date of the purchase was calculated at $3 million (in addition to the
purchase price of the mine of $5 million).
Also on 1 October 2008 Crosswire revalued its freehold land for the first time. The credit in the revaluation
reserve is the net amount of the revaluation after a transfer to deferred tax on the gain. The tax rate applicable to Crosswire for deferred tax is 20% per annum.
On 1 April 2009 Crosswire took out a finance lease for some new plant. The fair value of the plant was
$10 million. The lease agreement provided for an initial payment on 1 April 2009 of $2·4 million followed
by eight six-monthly payments of $1·2 million commencing 30 September 2009.
Plant disposed of during the year had a carrying amount of $500,000 and was sold for $1·2 million. The
remaining movement on the property, plant and equipment, after charging depreciation of $3 million, was
the cost of replacing plant.
(ii) From 1 October 2008 to 31 March 2009 a further $500,000 was spent completing the development
project at which date marketing and production started. The sales of the new product proved disappointing
and on 30 September 2009 the development costs were written down to $1 million via an impairment
charge.
(iii) During the year ended 30 September 2009, $4 million of the 10% convertible loan notes matured. The
loan note holders had the option of redemption at par in cash or to exchange them for equity shares on the
basis of 20 new shares for each $100 of loan notes. 75% of the loan-note holders chose the equity option.
Ignore any effect of this on the other equity reserve.
All the above items have been treated correctly according to International Financial Reporting Standards.
(iv) The finance costs are made up of:
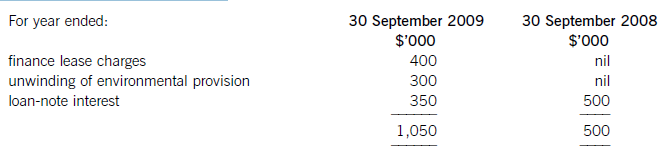
Required:
(i) Prepare a statement of the movements in the carrying amount of Crosswire’s non-current assets for the
year ended 30 September 2009; (9 marks)
(ii) Calculate the amounts that would appear under the headings of ‘cash flows from investing activities’
and ‘cash flows from financing activities’ in the statement of cash flows for Crosswire for the year ended
30 September 2009.
Note: Crosswire includes finance costs paid as a financing activity. (8 marks)
(b) A substantial shareholder has written to the directors of Crosswire expressing particular concern over the
deterioration of the company’s return on capital employed (ROCE)
Required:
Calculate Crosswire’s ROCE for the two years ended 30 September 2008 and 2009 and comment on the
apparent cause of its deterioration.
Note: ROCE should be taken as profit before interest on long-term borrowings and tax as a percentage of equity plus loan notes and finance lease obligations (at the year end). (8 marks)
(i)Thecashelementsoftheincreaseinproperty,plantandequipmentare$5millionforthemine(thecapitalisedenvironmentalprovisionisnotacashflow)and$2·4millionforthereplacementplantmakingatotalof$7·4million.(ii)Ofthe$4millionconvertibleloannotes(5,000–1,000)thatwereredeemedduringtheyear,75%($3million)ofthesewereexchangedforequitysharesonthebasisof20newsharesforeach$100inloannotes.Thiswouldcreate600,000(3,000/100x20)newsharesof$1eachandsharepremiumof$2·4million(3,000–600).As1million(5,000–4,000)newshareswereissuedintotal,400,000musthavebeenforcash.Theremainingincrease(aftertheeffectoftheconversion)inthesharepremiumof$1·6million(6,000–2,000b/f–2,400conversion)mustrelatetothecashissueofshares,thuscashproceedsfromtheissueofsharesis$2million(400nominalvalue+1,600premium).(iii)Theinitialleaseobligationis$10million(thefairvalueoftheplant).At30September2009totalleaseobligationsare$6·8million(5,040+1,760),thusrepaymentsintheyearwere$3·2million(10,000–6,800).(b)TakingthedefinitionofROCEfromthequestion:Fromtheaboveitcanbeclearlyseenthatthe2009operatingmarginhasimprovedbynearly1%point,despitethe$2millionimpairmentchargeonthewritedownofthedevelopmentproject.ThismeansthedeteriorationintheROCEisduetopoorerassetturnover.Thisimpliestherehasbeenadecreaseintheefficiencyintheuseofthecompany’sassetsthisyearcomparedtolastyear.Lookingatthemovementinthenon-currentassetsduringtheyearrevealssomemitigatingpoints:Thelandrevaluationhasincreasedthecarryingamountofproperty,plantandequipmentwithoutanyphysicalincreaseincapacity.Thisunfavourablydistortsthecurrentyear’sassetturnoverandROCEfigures.TheacquisitionoftheplatinummineappearstobeanewareaofoperationforCrosswirewhichmayhaveadifferent(perhapslower)ROCEtootherpreviousactivitiesoritmaybethatitwilltakesometimefortheminetocometofullproductioncapacity.Thesubstantialacquisitionoftheleasedplantwashalf-waythroughtheyearandcanonlyhavecontributedtotheyear’sresultsforsixmonthsatbest.Infutureperiodsafullyear’scontributioncanbeexpectedfromthisnewinvestmentinplantandthisshouldimprovebothassetturnoverandROCE.Insummary,thefallintheROCEmaybeduelargelytotheabovefactors(effectivelythereplacementandexpansionprogramme),ratherthantopooroperatingperformance,andinfutureperiodsthismaybereversed.ItshouldalsobenotedthathadtheROCEbeencalculatedontheaveragecapitalemployedduringtheyear(ratherthantheyearendcapitalemployed),whichisarguablymorecorrect,thenthedeteriorationintheROCEwouldnothavebeenaspronounced.
(b) Describe the potential benefits for Hugh Co in choosing to have a financial statement audit. (4 marks)
(b) There are several benefits for Hugh Co in choosing a voluntary financial statement audit.
An annual audit will ensure that any material mistakes made by the part-qualified accountant in preparing the year end
financial statements will be detected. This is important as the directors will be using the year end accounts to review their
progress in the first year of trading and will need reliable figures to assess performance. An audit will give the directors comfort
that the financial statements are a sound basis for making business decisions.
Accurate first year figures will also enable more effective budgeting and forecasting, which will be crucial if rapid growth is to
be achieved.
The auditors are likely to use the quarterly management accounts as part of normal audit procedures. The auditors will be
able to advise Monty Parkes of any improvements that could be made to the management accounts, for example, increased
level of detail, more frequent reporting. Better quality management accounts will help the day-to-day running of the business
and enable a speedier response to any problems arising during the year.
As a by-product of the audit, a management letter (report to those charged with governance) will be produced, identifying
weaknesses and making recommendations on areas such as systems and controls which will improve the smooth running of
the business.
It is likely that Hugh Co will require more bank funding in order to expand, and it is likely that the bank would like to see
audited figures for review, before deciding on further finance. It will be easier and potentially cheaper to raise finance from
other providers with an audited set of financial statements.
As the business deals in cash sales, and retails small, luxury items there is a high risk of theft of assets. The external audit
can act as both a deterrent and a detective control, thus reducing the risk of fraud and resultant detrimental impact on the
financial statements.
Accurate financial statements will be the best basis for tax assessment and tax planning. An audit opinion will enhance the
credibility of the figures.
If the business grows rapidly, then it is likely that at some point in the future, the audit exemption limit will be exceeded and
thus an audit will become mandatory.
Choosing to have an audit from the first year of incorporation will reduce potential errors carried down to subsequent periods
and thus avoid qualifications of opening balances.
(c) With specific reference to Hugh Co, discuss the objective of a review engagement and contrast the level of
assurance provided with that provided in an audit of financial statements. (6 marks)
(c) The objective of a review engagement is to enable the auditor to obtain moderate assurance as to whether the financial
statements have been prepared in accordance with an identified financial reporting framework. This is defined in ISRE 2400
Engagements to Review Financial Statements.
In order to obtain this assurance, it is necessary to gather evidence using analytical procedures and enquiries with
management. Detailed substantive procedures will not be performed unless the auditor has reason to believe that the
information may be materially misstated.
The auditor should approach the engagement with a high degree of professional scepticism, looking for circumstances that
may cause the financial statements to be misstated. For example, in Hugh Co, the fact that the preparer of the financial
statements is part-qualified may lead the auditor to believe that there is a high inherent risk that the figures are misstated.
As a result of procedures performed, the auditor’s objective is to provide a clear written expression of negative assurance on
the financial statements. In a review engagement the auditor would state that ‘we are not aware of any material modifications
that should be made to the financial statements….’
This is normally referred to as an opinion of ‘negative assurance’.
Negative assurance means that the auditor has performed limited procedures and has concluded that the financial statements
appear reasonable. The user of the financial statements gains some comfort that the figures have been subject to review, but
only a moderate level of assurance is provided. The user may need to carry out additional procedures of their own if they
want to rely on the financial statements. For example, if Hugh Co were to use the financial statements as a means to raise
further bank finance, the bank would presumably perform, or require Hugh Co to perform, additional procedures to provide
a higher level of assurance as to the validity of the figures contained in the financial statements.
In comparison, in an audit, a high level of assurance is provided. The auditors provide an opinion of positive, but not absolute
assurance. The user is assured that the figures are free from material misstatement and that the auditor has based the opinion
on detailed procedures.
(b) Describe the principal audit procedures to be carried out in respect of the following:
(i) The measurement of the share-based payment expense; (6 marks)
(b) (i) Principal audit procedures – measurement of share-based payment expense
– Obtain management calculation of the expense and agree the following from the calculation to the contractual
terms of the scheme:
– Number of employees and executives granted options
– Number of options granted per employee
– The official grant date of the share options
– Vesting period for the scheme
– Required performance conditions attached to the options.
– Recalculate the expense and check that the fair value has been correctly spread over the stated vesting period.
– Agree fair value of share options to specialist’s report and calculation, and evaluate whether the specialist report is
a reliable source of evidence.
– Agree that the fair value calculated is at the grant date.
Tutorial note: A specialist such as a chartered financial analyst would commonly be used to calculate the fair value
of non-traded share options at the grant date, using models such as the Black-Scholes Model.
– Obtain and review a forecast of staffing levels or employee turnover rates for the duration of the vesting period, and
scrutinise the assumptions used to predict level of staff turnover.
– Discuss previous levels of staff turnover with a representative of the human resources department and query why
0% staff turnover has been predicted for the next three years.
– Check the sensitivity of the calculations to a change in the assumptions used in the valuation, focusing on the
assumption of 0% staff turnover.
– Obtain written representation from management confirming that the assumptions used in measuring the expense
are reasonable.
Tutorial note: A high degree of scepticism must be used by the auditor when conducting the final three procedures
due to the management assumption of 0% staff turnover during the vesting period.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-08-19
- 2020-08-19