2019年ACCA考试《高级审计与认证(专业阶段)》每日一练(2019-03-22)
发布时间:2019-03-22
In the case of a
members' voluntary liquidation, which of the following is a responsibility of
the liquidator?
A.To call a formal
general meeting for members
B.To make a
statutory declaration of insolvency to the members
C.To request an
ordinary resolution to confirm the appointment
D.To convene a
meeting of the company's creditors
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Calculate her income tax (IT) and national insurance (NIC) payable for the year of assessment 2006/07.
(4 marks)
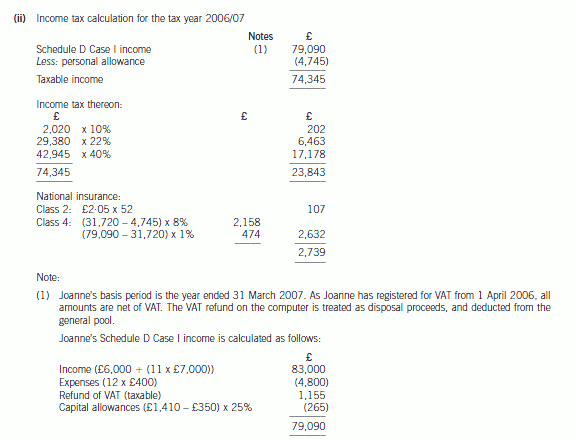
4 The transition to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) involves major change for companies as IFRSs
introduce significant changes in accounting practices that were often not required by national generally accepted
accounting practice. It is important that the interpretation and application of IFRSs is consistent from country to
country. IFRSs are partly based on rules, and partly on principles and management’s judgement. Judgement is more
likely to be better used when it is based on experience of IFRSs within a sound financial reporting infrastructure. It is
hoped that national differences in accounting will be eliminated and financial statements will be consistent and
comparable worldwide.
Required:
(a) Discuss how the changes in accounting practices on transition to IFRSs and choice in the application of
individual IFRSs could lead to inconsistency between the financial statements of companies. (17 marks)
(a) The transition to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) involves major change for companies as IFRS introduces
significant changes in accounting practices that often were not required by national GAAPs. For example financial instruments
and share-based payment plans in many instances have appeared on the statements of financial position of companies for
the first time. As a result IFRS financial statements are often significantly more complex than financial statements based on
national GAAP. This complexity is caused by the more extensive recognition and measurement rules in IFRS and a greater
number of disclosure requirements. Because of this complexity, it can be difficult for users of financial statements which have
been produced using IFRS to understand and interpret them, and thus can lead to inconsistency of interpretation of those
financial statements.
The form. and presentation of financial statements is dealt with by IAS1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’. This standard
sets out alternative forms or presentations of financial statements. Additionally local legislation often requires supplementary
information to be disclosed in financial statements, and best practice as to the form. or presentation of financial statements
has yet to emerge internationally. As a result companies moving to IFRS have tended to adopt IFRS in a way which minimises
the change in the form. of financial reporting that was applied under national GAAP. For example UK companies have tended
to present a statement of recognised income and expense, and a separate statement of changes in equity whilst French
companies tend to present a single statement of changes in equity.
It is possible to interpret standards in different ways and in some standards there is insufficient guidance. For example there
are different acceptable methods of classifying financial assets under IAS39 ‘Financial Instruments: Recognition and
Measurement’ in the statement of financial position as at fair value through profit or loss (subject to certain conditions) or
available for sale.
IFRSs are not based on a consistent set of principles, and there are conceptual inconsistencies within and between standards.
Certain standards allow alternative accounting treatments, and this is a further source of inconsistency amongst financial
statements. IAS31 ‘Interests in Joint Ventures’ allows interests in jointly controlled entities to be accounted for using the equity
method or proportionate consolidation. Companies may tend to use the method which was used under national GAAP.
Another example of choice in accounting methods under IFRS is IAS16 ‘Property, Plant and equipment’ where the cost or
revaluation model can be used for a class of property, plant and equipment. Also there is very little industry related accounting
guidance in IFRS. As a result judgement plays an important role in the selection of accounting policies. In certain specific
areas this can lead to a degree of inconsistency and lack of comparability.
IFRS1, ‘First time Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards’, allows companies to use a number of exemptions
from the requirements of IFRS. These exemptions can affect financial statements for several years. For example, companies
can elect to recognise all cumulative actuarial gains and losses relating to post-employment benefits at the date of transition
to IFRS but use the ‘corridor’ approach thereafter. Thus the effect of being able to use a ‘one off write off’ of any actuarial
losses could benefit future financial statements significantly, and affect comparability. Additionally after utilising the above
exemption, companies can elect to recognise subsequent gains and losses outside profit or loss in ‘other comprehensive
income’ in the period in which they occur and not use the ‘corridor’ approach thus affecting comparability further.
Additionally IAS18 ‘Revenue’ allows variations in the way revenue is recognised. There is no specific guidance in IFRS on
revenue arrangements with multiple deliverables. Transactions have to be analysed in accordance with their economic
substance but there is often no more guidance than this in IFRS. The identification of the functional currency under IAS21,
‘The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates’, can be subjective. For example the functional currency can be determined
by the currency in which the commodities that a company produces are commonly traded, or the currency which influences
its operating costs, and both can be different.
Another source of inconsistency is the adoption of new standards and interpretations earlier than the due date of application
of the standard. With the IASB currently preparing to issue standards with an adoption date of 1 January 2009, early adoption
or lack of it could affect comparability although IAS8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’
requires a company to disclose the possible impact of a new standard on its initial application. Many companies make very
little reference to the future impact of new standards.
Explain the grounds upon which a person may be disqualified under the Company Directors Disqualification Act 1986.(10 marks)
The Company Directors Disqualification Act (CDDA) 1986 was introduced to control individuals who persistently abused the various privileges that accompany incorporation, most particularly the privilege of limited liability. The Act applies to more than just directors and the court may make an order preventing any person (without leave of the court) from being:
(i) a director of a company;
(ii) a liquidator or administrator of a company;
(iii) a receiver or manager of a company’s property; or
(iv) in any way, whether directly or indirectly, concerned with or taking part in the promotion, formation or management of a company.
The CDDA 1986 identifies three distinct categories of conduct, which may, and in some circumstances must, lead the court to disqualify certain persons from being involved in the management of companies.
(a) General misconduct in connection with companies
This first category involves the following:
(i) A conviction for an indictable offence in connection with the promotion, formation, management or liquidation of a company or with the receivership or management of a company’s property (s.2 of the CDDA 1986). The maximum period for disqualification under s.2 is five years where the order is made by a court of summary jurisdiction, and 15 years in any other case.
(ii) Persistent breaches of companies legislation in relation to provisions which require any return, account or other document to be filed with, or notice of any matter to be given to, the registrar (s.3 of the CDDA 1986). Section 3 provides that a person is conclusively proved to be persistently in default where it is shown that, in the five years ending with the date of the application, he has been adjudged guilty of three or more defaults (s.3(2) of the CDDA 1986). This is without prejudice to proof of persistent default in any other manner. The maximum period of disqualification under this section is five years.
(iii) Fraud in connection with winding up (s.4 of the CDDA 1986). A court may make a disqualification order if, in the course of the winding up of a company, it appears that a person:
(1) has been guilty of an offence for which he is liable under s.993 of the CA 2006, that is, that he has knowingly been a party to the carrying on of the business of the company either with the intention of defrauding the company’s creditors or any other person or for any other fraudulent purpose; or
(2) has otherwise been guilty, while an officer or liquidator of the company or receiver or manager of the property of the company, of any fraud in relation to the company or of any breach of his duty as such officer, liquidator, receiver or manager (s.4(1)(b) of the CDDA 1986).
The maximum period of disqualification under this category is 15 years.(b) Disqualification for unfitness
The second category covers:
(i) disqualification of directors of companies which have become insolvent, who are found by the court to be unfit to be directors (s.6 of the CDDA 1986). Under s. 6, the minimum period of disqualification is two years, up to a maximum of 15 years;
(ii) disqualification after investigation of a company under Pt XIV of the CA 1985 (it should be noted that this part of the previous Act still sets out the procedures for company investigations) (s.8 of the CDDA 1986). Once again, the maximum period of disqualification is 15 years.
Schedule 1 to the CDDA 1986 sets out certain particulars to which the court is to have regard in deciding whether a person’s conduct as a director makes them unfit to be concerned in the management of a company. In addition, the courts have given indications as to what sort of behaviour will render a person liable to be considered unfit to act as a company director. Thus, in Re Lo-Line Electric Motors Ltd (1988), it was stated that:
‘Ordinary commercial misjudgment is in itself not sufficient to justify disqualification. In the normal case, the conduct complained of must display a lack of commercial probity, although . . . in an extreme case of gross negligence or total incompetence, disqualification could be appropriate.’
(c) Other cases for disqualification
This third category relates to:
(i) participation in fraudulent or wrongful trading under s.213 of the Insolvency Act (IA)1986 (s.10 of the CDDA 1986);
(ii) undischarged bankrupts acting as directors (s.11 of the CDDA 1986); and
(iii) failure to pay under a county court administration order (s.12 of the CDDA 1986).
For the purposes of most of the CDDA 1986, the court has discretion to make a disqualification order. Where, however, a person has been found to be an unfit director of an insolvent company, the court has a duty to make a disqualification order (s.6 of the CDDA 1986). Anyone who acts in contravention of a disqualification order is liable:
(i) to imprisonment for up to two years and/or a fine, on conviction on indictment; or
(ii) to imprisonment for up to six months and/or a fine not exceeding the statutory maximum, on conviction summarily (s.13 of the CDDA 1986).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-03-15
- 2019-03-22
- 2019-03-16
- 2019-03-16
- 2019-03-15
- 2019-03-22
- 2019-03-16
- 2019-03-22
- 2019-03-15