ACCA考试考完之后在哪里查询成绩呢?
发布时间:2021-05-09
ACCA考试考完之后在哪里查询成绩呢?
最佳答案
ACCA随时机考的成绩是当场就能够知道的,而ACCA分季机考和ACCA笔试的成绩一般在考试以后一个月左右时间才能够知道。 在报名的网址可以查询到的
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
6 Certain practices have developed that threaten to damage the integrity and objectivity of professional accountants and
the reputation of the accounting profession.
Required:
Explain the following practices and associated ethical risks and discuss whether current ethical guidance is
sufficient:
(a) ‘lowballing’; (5 marks)
6 CERTAIN PRACTICES
Tutorial note: The answer which follows is indicative of the range of points which might be made. Other relevant material will
be given suitable credit.
(a) ‘Lowballing’
Explanation of term
‘Lowballing’ is the ‘loss-leading’ practice in which auditors compete for clients by reducing their fees for statutory audits.
Lower audit fees are then compensated by the auditor carrying out more lucrative non-audit work (e.g. consultancy and tax
advice). Audits may even be offered for free.
Such ‘predatory pricing’ may undercut an incumbent auditor to secure an appointment into which higher price consultancy
services may be sold.
Ethical risks
There is a risk of incompetence if the non-audit work does not materialise and the lowballing firm comes under pressure to
cut corners or resort to irregular practices (e.g. the falsification of audit working papers) in order to ‘keep within budget’.
However, a lack of audit quality may only be discovered if the situation arises that the company collapses and the auditors
are charged with negligence.
If, rather than comprise the quality of the audit, an audit firm substantially increases audit fees, a fee dispute could arise. In
this case the client might refuse to pay the higher fee. It could be difficult then for the firm to take the matter to arbitration
if the client was misled. Thus an advocacy threat may arise.
Financial dependence is a direct incentive that threatens independence. A self-interest threat therefore arises when, having
secured the audit, the audit firm needs the client to retain its services in order to recoup any losses initially incurred.
The provision of many other services gives rise to a self-review threat (as well as a self-interest threat).
Sufficiency of current ethical guidance
In current ethical guidance, the fact that an accountancy firm quotes a lower fee than other tendering firms is not improper,
providing that the prospective client is not misled about:
– the precise range of services that the quoted fee is intended to cover; and
– the likely level of fees for any other work undertaken.
This is clearly insufficient to prevent the practice of lowballing.
Legal prohibitions on the provision of many non-audit services (e.g. bookkeeping, financial information systems design and
implementation, valuation services, actuarial services, internal audit (outsourced), human resource services for executive
positions, investment and legal services) should make lowballing a riskier pricing strategy. This may curb the tendency to
lowball.
Lowballing could be eliminated if, for example, auditors were required to act ‘exclusively as auditors’. Although regulatory
environments have moved towards this there is not a total prohibition on non-audit services.
(c) Describe the purposes for which a person specification might be used. (4 marks)
Part (c):
The person specification might be used for a number of purposes:
In recruitment, to provide an illustration of the type of candidate sought prior to the selection stage.
In selection, the most obvious and popular use of this document, is to assess whether an individual’s personality, abilities and
experience match the organisation’s requirements.
For promotion, to evaluate whether an individual has the necessary ability and personality to move within the organisation.
In evaluation of performance to assess whether the person has demonstrated the necessary skills to do the job effectively.
In disciplinary procedures through demonstrating that the person specification required to do a particular job for which some one
was appointed are not evident or being applied. For example, where an employee required to be discrete is discovered to have
disclosed confidential information to third parties.
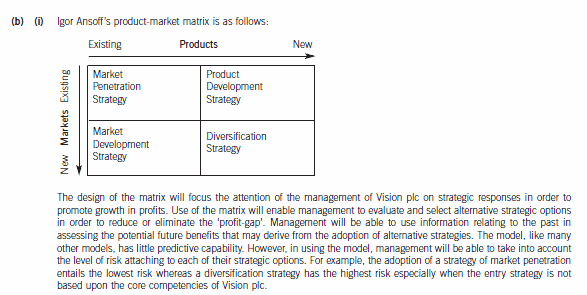
(b) (i) Explain how the use of Ansoff’s product-market matrix might assist the management of Vision plc to
reduce the profit-gap that is forecast to exist at 30 November 2009. (3 marks)
3 The directors of The Healthy Eating Group (HEG), a successful restaurant chain, which commenced trading in 1998,
have decided to enter the sandwich market in Homeland, its country of operation. It has set up a separate operation
under the name of Healthy Sandwiches Co (HSC). A management team for HSC has been recruited via a recruitment
consultancy which specialises in food sector appointments. Homeland has very high unemployment and the vast
majority of its workforce has no experience in a food manufacturing environment. HSC will commence trading on
1 January 2008.
The following information is available:
(1) HSC has agreed to make and supply sandwiches to agreed recipes for the Superior Food Group (SFG) which
owns a chain of supermarkets in all towns and cities within Homeland. SFG insists that it selects the suppliers
of the ingredients that are used in making the sandwiches it sells and therefore HSC would be unable to reduce
the costs of the ingredients used in the sandwiches. HSC will be the sole supplier for SFG.
(2) The number of sandwiches sold per year in Homeland is 625 million. SFG has a market share of 4%.
(3) The average selling price of all sandwiches sold by SFG is $2·40. SFG wishes to make a mark-up of 331/3% on
all sandwiches sold. 90% of all sandwiches sold by SFG are sold before 2 pm each day. The majority of the
remaining 10% are sold after 8 pm. It is the intention that all sandwiches are sold on the day that they are
delivered into SFG’s supermarkets.
(4) The finance director of HSC has estimated that the average cost of ingredients per sandwich is $0·70. All
sandwiches are made by hand.
(5) Packaging and labelling costs amount to $0·15 per sandwich.
(6) Fixed overheads have been estimated to amount to $5,401,000 per annum. Note that fixed overheads include
all wages and salaries costs as all employees are subject to fixed term employment contracts.
(7) Distribution costs are expected to amount to 8% of HSC’s revenue.
(8) The finance director of HSC has stated that he believes the target sales margin of 32% can be achieved, although
he is concerned about the effect that an increase in the cost of all ingredients would have on the forecast profits
(assuming that all other revenue/cost data remains unchanged).
(9) The existing management information system of HEG was purchased at the time that HEG commenced trading.
The directors are now considering investing in an enterprise resource planning system (ERPS).
Required:
(a) Using only the above information, show how the finance director of HSC reached his conclusion regarding
the expected sales margin and also state whether he was correct to be concerned about an increase in the
price of ingredients. (5 marks)

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-06-03
- 2021-06-04
- 2021-06-18
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-12-31
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-04-21
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-05-09
- 2021-01-05
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-05-19
- 2021-06-10
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-05-13
- 2021-05-29
- 2021-05-07
- 2021-06-05
- 2021-04-15
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-01-03
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12