ACCA考试费用一般国内要多少呢?
发布时间:2021-03-10
ACCA考试费用一般国内要多少呢?
最佳答案
ACCA费用主要包括:注册费,年费,报名费,教材费,培训费。
1、注册费:79英镑
2、年费:105英镑,每年。
大部分ACCA学员学习ACCA一般都需要三到四年,就按照四年年费来计算
3、ACCA考试费用:(注:所有考试费用都以早期缴费为准。)79+99+(F1-F4费用)+103*5(F5-F9)+180(SBL)+129*3(SBR+2门选修课)=1260+(F1-F4费用,费用是每科70-80英镑),这样下来,你所缴纳的ACCA官方报名费用约在人民币一万四到两万左右。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) the factors that should be considered in the design of a reward scheme for BGL; (7 marks)
(ii) The factors that should be considered in the design of a reward scheme for BGL.
– Whether performance targets should be set with regard to results or effort. It is more difficult to set targets for
administrative and support staff since in many instances the results of their efforts are not easily quantifiable. For
example, sales administrators will improve levels of customer satisfaction but quantifying this is extremely difficult.
– Whether rewards should be monetary or non-monetary. Money means different things to different people. In many
instances people will prefer increased job security which results from improved organisational performance and
adopt a longer term-perspective. Thus the attractiveness of employee share option schemes will appeal to such
individuals. Well designed schemes will correlate the prosperity of the organisation with that of the individuals it
employs.
– Whether the reward promise should be implicit or explicit. Explicit reward promises are easy to understand but in
many respects management will have their hands tied. Implicit reward promises such as the ‘promise’ of promotion
for good performance is also problematic since not all organisations are large enough to offer a structured career
progression. Thus in situations where not everyone can be promoted there needs to be a range of alternative reward
systems in place to acknowledge good performance and encourage commitment from the workforce.
– The size and time span of the reward. This can be difficult to determine especially in businesses such as BGL
which are subject to seasonal variations. i.e. summerhouses will invariably be purchased prior to the summer
season! Hence activity levels may vary and there remains the potential problem of assessing performance when
an organisation operates with surplus capacity.
– Whether the reward should be individual or group based. This is potentially problematic for BGL since the assembly
operatives comprise some individuals who are responsible for their own output and others who work in groups.
Similarly with regard to the sales force then the setting of individual performance targets is problematic since sales
territories will vary in terms of geographical spread and customer concentration.
– Whether the reward scheme should involve equity participation? Such schemes invariably appeal to directors and
senior managers but should arguably be open to all individuals if ‘perceptions of inequity’ are to be avoided.
– Tax considerations need to be taken into account when designing a reward scheme.
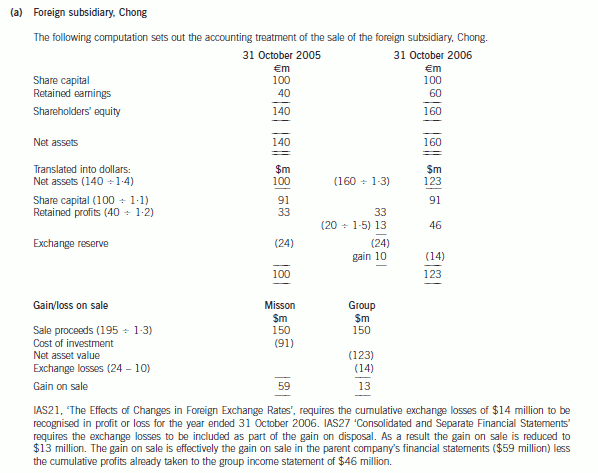
2 Misson, a public limited company, has carried out transactions denominated in foreign currency during the financial
year ended 31 October 2006 and has conducted foreign operations through a foreign entity. Its functional and
presentation currency is the dollar. A summary of the foreign currency activities is set out below:
(a) Misson has a 100% owned foreign subsidiary, Chong, which was formed on 1 November 2004 with a share
capital of 100 million euros which has been taken as the cost of the investment. The total shareholders’ equity
of the subsidiary as at 31 October 2005 and 31 October 2006 was 140 million euros and 160 million euros
respectively. Chong has not paid any dividends to Misson and has no other reserves than retained earnings in its
financial statements. The subsidiary was sold on 31 October 2006 for 195 million euros.
Misson would like to know how to treat the sale of the subsidiary in the parent and group accounts for the year
ended 31 October 2006. (8 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above transactions in accordance with the advice required by the
directors.
(Candidates should show detailed workings as well as a discussion of the accounting treatment used.)
2 Ramon Silva is a Spanish property developer, who has made a considerable fortune from the increasing numbers of
Europeans looking to buy new homes and apartments in the coastal regions of Mediterranean Spain. His frequent
contact with property buyers has made him aware of their need for low cost hotel accommodation during the lengthy
period between finding a property to buy and when they actually move into their new home. These would-be property
owners are looking for inexpensive hotels in the same locations as tourists looking for cheap holiday accommodation.
Closer investigation of the market for inexpensive or budget hotel accommodation has convinced Ramon of the
opportunity to offer something really different to his potential customers. He has the advantage of having no
preconceived idea of what his chain of hotels might look like. The overall picture for the budget hotel industry is not
encouraging with the industry suffering from low growth and consequent overcapacity. There are two distinct market
segments in the budget hotel industry; firstly, no-star and one-star hotels, whose average price per room is between
30 and 45 euros. Customers are simply attracted by the low price. The second segment is the service provided by
two-star hotels with an average price of 100 euros a night. These more expensive hotels attract customers by offering
a better sleeping environment than the no-star and one-star hotels. Customers therefore have to choose between low
prices and getting a poor night’s sleep owing to noise and inferior beds or paying more for an untroubled night’s sleep.
Ramon quickly deduced that a hotel chain that can offer a better price/quality combination could be a winner.
The two-star hotels typically offer a full range of services including restaurants, bars and lounges, all of which are
costly to operate. The low price budget hotels offer simple overnight accommodation with cheaply furnished rooms
and staffed by part-time receptionists. Ramon is convinced that considerable cost savings are available through better
room design, construction and furniture and a more effective use of hotel staff. He feels that through offering hotel
franchises under the ‘La Familia Amable’ (‘The Friendly Family’) group name, he could recruit husband and wife teams
to own and operate them. The couples, with suitable training, could offer most of the services provided in a two-star
hotel, and create a friendly, family atmosphere – hence the company name. He is sure he can offer the customer twostar
hotel value at budget prices. He is confident that the value-for-money option he offers would need little marketing
promotion to launch it and achieve rapid growth.
Required:
(a) Provide Ramon with a brief report, using strategic models where appropriate, showing where his proposed
hotel service can add value to the customer’s experience. (12 marks)
(a) To: Ramon Silva
From:
Value innovation in La Familia Amable hotel chain
In strategic terms you are looking to create a competitive advantage over existing hotels based on a cost focus strategy. The
success of this niche marketing strategy will depend on your ability to attract customers from the existing providers but there
does seem a gap to exploit. In many ways you have an advantage in that you are not constrained by previous experience in
the hotel industry and this has enabled you to look to deliver a significantly different value proposition to your customers and
not simply look to marginally improve on what currently is on offer. One particular study on innovation drew attention to five
dimensions of strategy where innovators can significantly outperform. existing companies. This is important, as the industry
does not look particularly attractive with low growth and overcapacity – a recipe for low profitability.
Industry assumptions – here existing companies take the competitive conditions as given whereas innovators are looking to
influence and change those conditions.
Strategic focus – simply benchmarking against the current hotel providers may not create any real advantage, innovators are
seeking to provide a step change in the experience given to the customer.
Customers – the route to success may not be through ever increasing segmentation and customisation but by actually looking
to focus on the shared attributes of the service that customers value – a good night’s sleep for a low price being a prime
example.
Assets and capabilities – rather than looking to leverage existing assets and capabilities the innovator looks to ask what would
we do if we were starting a new business.
Product and service offering – existing competitors may again be constrained in their thinking by the existing boundaries of
the industry and the innovator by identifying new customers and services that take them outside this boundary may offer a
‘total solution’ that transforms the industry. The ‘no frills’, low cost budget airlines are a good example of such thinking.
In the hotel business ‘location, location, location’ is argued to be at the heart of a successful strategy. Clearly this will be your
choice and is affected by the customer groups you are looking to attract. Establishing a brand name and reputation is an
important marketing strategy and this will be facilitated by growing the chain rapidly and giving customers easy access to
your hotels. In value chain terms the company infrastructure looks to be lean with a reliance on trained husband and wife
teams to deliver the service. Franchising would also seem to be a route to grow the business that will place reduced strain
on company headquarters. The creation of a chain should lend itself to significant buying and procurement advantages, right
from the design of the hotels which will focus on the core value you are providing – namely quiet and cost. One French hotel
chain was able to cut in half the average cost of building a room, its ‘no frills’ service cut staff costs from between 25% and
35% of sales – the industry average – to between 20% and 23%.
Good design will therefore affect the quality of service that the operations side of the value chain delivers to the customer.
This may be a simpler service to that provided by its competitors – simpler, more basic rooms, no expensive restaurants or
lounge areas all impact on the cost of operations and consequently the price charged. Marketing, as previously referred to
above, is much more effectively done through satisfied customers’ recommendations than by expensive advertising. Many
hotel chains have used technology to create customer loyalty schemes of questionable benefit to the customer. You will
certainly have to seriously consider the value of such an after sales service. The established competitors often make
assumptions as to what a customer wants and typically this is offering more and more services that are expensive to provide.
Your entry into a ‘mature’ industry such as this, allows you to really challenge these assumptions and deliver a price/value
combination that is hard to beat.
Yours,
(ii) Describe the basis for the calculation of the provision for deferred taxation on first time adoption of IFRS
including the provision in the opening IFRS balance sheet. (4 marks)
(ii) A company has to apply IAS12 to the temporary differences between the carrying amount of the assets and liabilities in
its opening IFRS balance sheet (1 November 2003) and their tax bases (IFRS1 ‘First time adoption of IFRS’). The
deferred tax provision will be calculated using tax rates that have been enacted or substantially enacted by the balance
sheet date. The carrying values of the assets and liabilities at the opening balance sheet date will be determined by
reference to IFRS1 and will use the applicable IFRS in the first IFRS financial statements. Any adjustments required to
the deferred tax balance will be recognised directly in retained earnings.
Subsequent balance sheets (at 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005) will be drawn up using the IFRS used in the
financial statements to 31 October 2005. The deferred tax provision will be adjusted as at 31 October 2004 and thenas at 31 October 2005 to reflect the temporary differences arising at those dates.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-01-03
- 2021-02-16
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-06-09
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-06-02
- 2021-05-20
- 2021-06-09
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-05-13
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-05-11
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-12-30
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-01-02
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-02-23
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-12-30
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-04-21