想问一下ACCA下半年9月份12月份的F3F5...
发布时间:2021-01-04
想问一下ACCA下半年9月份12月份的F3F5F6F7考纲变化
最佳答案
财萃回答,仁兄好厉害啊,都考虑2019年ACCA的知识点了,果然高瞻远瞩啊,说真的,ACCA每年的知识点变化不会很大,某些科目会有一些细微的调整,详情还得依据考季最新考纲为主,建议多关注ACCA官方最新动态,掌握最新的考试信息。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
22 Which of the following items may appear in a company’s statement of changes in equity, according to IAS 1 Presentation of financial statements?
1 Unrealised revaluation gains.
2 Dividends paid.
3 Proceeds of equity share issue.
4 Profit for the period.
A 2, 3 and 4 only
B 1, 3 and 4 only
C All four items
D 1, 2 and 4 only
6 Discuss how developments in each of the following areas has affected the scope of the audit and the audit work
undertaken:
(a) fair value accounting; (6 marks)
6 DEVELOPMENTS
General comments
Tutorial note: The following comments, that could be made in respect of any of the three areas of development, will be given
credit only once.
■ Audit scope – the scope of a statutory audit should be as necessary to form. an audit opinion (i.e. unlimited).
■ Audit work undertaken – the nature, timing and extent of audit procedures should be as necessary to implement the overall
audit plan.
(a) Fair value accounting
■ Different definitions of fair value exist (among financial reporting frameworks or for different assets and liabilities within
a particular framework). For example, under IFRS it is ‘the amount for which an asset could be exchanged (or a liability
settled) between knowledgeable, willing parties in an arm’s length transaction’.
■ The term ‘fair value accounting’ is used to describe the measurement and disclosure of assets and/or liabilities at fair
value and the charging to profit and loss (or directly to equity) of any changes in fair value measurements.
■ Fair value accounting concerns measurements and disclosures but not initial recognition of assets and liabilities in
financial statements. It does not then, for example, affect the nature, timing and extent of audit procedures to confirm
the existence and completeness of rights and obligations.
■ Fair value may be determined with varying degrees of subjectivity. For example, there will be little (if any) subjectivity
for assets bought and sold in active and open markets that readily provide reliable information on the prices at which
exchange transactions occur. However, the valuation of assets with unique characteristics (or entity-specific assets) often
requires the projection and discounting of future cash flows.
■ The audit of estimates of fair values based on valuation models/techniques can be approached like other accounting
estimates (in accordance with ISA 540 ‘Audit of Accounting Estimates’). However, although the auditor should be able
to review and test the process used by management to develop the estimate, there may be:
? a much greater need for an independent estimate (and hence greater reliance on the work of experts in accordance
with ISA 620);
? no suitable subsequent events to confirm the estimate made (e.g. for assets that are held for use and not for
trading).
Tutorial note: Consider, for example, how the audit of ‘in-process research and development’ might compare with that
for an allowance for slow-moving inventory.
■ Different financial reporting frameworks require or permit a variety of fair value measures and disclosures in financial
statements. They also vary in the level of guidance provided (to preparers of the financial statements – and hence their
auditors). Under IFRS, certain fair values are based on management intent and ‘reasonable supportable assumptions’.
■ The audit of management intent potentially increases the auditor’s reliance on management representations. The auditor
must obtain such representations from the highest level of management and exercise an appropriate degree of
professional scepticism, being particularly alert to the implications of any conflicting evidence.
■ A significant development in international financial reporting is that it is no longer sufficient to report transactions and
past and future events that may only be possible. IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ (Revised) requires that
key assumptions (and other key sources of estimation uncertainty) be disclosed. This requirement gives rise to yet
another area on which auditors may qualify their audit opinion, on grounds of disagreement, where such disclosure is
incorrect or inadequate.
■ Perhaps one of the most significant impacts of fair value accounting on audit work is that it necessarily increases it.
Consider for example, that even where the fair value of an asset is as easily vouched as original cost, fair value is
determined at least annually whereas historic cost is unchanged (and not re-vouched to original purchase
documentation).
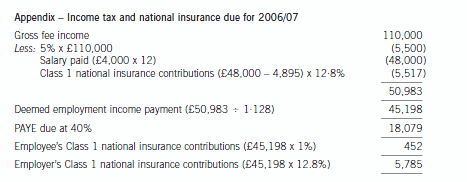
6 Charles and Jane Miro, aged 31 and 34 years respectively, have been married for ten years and have two children
aged six and eight years. Charles is a teacher but for the last five years he has stayed at home to look after their
children. Jane works as a translator for Speak Write Ltd.
Speak Write Ltd was formed and began trading on 6 April 2006. It provides translation services to universities. Jane,
who ceased employment with Barnham University to found the company, owns 100% of its ordinary share capital
and is its only employee.
Speak Write Ltd has translated documents for four different universities since it began trading. Its biggest client is
Barnham University which represents 70% of the company’s gross income. It is estimated that the company’s gross
fee income for its first 12 months of trading will be £110,000. Speak Write Ltd usually agrees fixed fees in advance
with its clients although it charges for some projects by reference to the number of days taken to do the work. None
of the universities makes any payment to Speak Write Ltd in respect of Jane being on holiday or sick.
All of the universities insist that Jane does the work herself. Jane carries out the work for three of the universities in
her office at home using a computer and specialised software owned by Speak Write Ltd. The work she does for
Barnham University is done in the university’s library on one of its computers as the documents concerned are too
delicate to move.
The first set of accounts for Speak Write Ltd will be drawn up for the year ending 5 April 2007. It is estimated that
the company’s tax adjusted trading profit for this period will be £52,500. This figure is after deducting Jane’s salary
of £4,000 per month and the related national insurance contributions but before any adjustments required by the
application of the personal service companies (IR 35) legislation. The company has no other sources of income or
capital gains.
Jane has not entered into any communication with HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) with respect to the company
and wants to know:
– When the corporation tax computation should be submitted and when the tax is due.
– When the corporation tax computation can be regarded as having been agreed by HMRC.
Charles and Jane have requested a meeting to discuss the family’s finances. In particular, they wish to consider the
shortfall in the family’s annual income and any other related issues if Jane were to die. Their mortgage is covered
by a term assurance policy but neither of them have made any pension contributions or carried out any other long
term financial planning.
Jane has estimated that her annual after tax income from Speak Write Ltd, on the assumption that she extracts all of
the company’s profits, will be £58,000. Charles owns two investment properties that together generate after tax
income of £8,500. He estimates that he could earn £28,000 after tax if he were to return to work.
The couple’s annual surplus income, after payment of all household expenditure including mortgage payments of
£900 per month, is £21,000. Charles and Jane have no other sources of income.
Required:
(a) Write a letter to Jane setting out:
(i) the arguments that HMRC could put forward, based only on the facts set out above, in support of
applying the IR 35 legislation to Speak Write Ltd; and
(ii) the additional income tax and national insurance contributions that would be payable, together with
their due date of payment, if HMRC applied the IR 35 legislation to all of the company’s income in
2006/07. (11 marks)

(c) (i) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended
30 September 2005 should be submitted, and advise the company of the penalties that will be due if
the return is not submitted until 31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(ii) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005
should be paid, and advise the company of the interest that will be due if the liability is not paid until
31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(c) Self-assessment tax return
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be submitted by
30 September 2006.
(2) If the company does not submit its self-assessment tax return until 31 May 2007, then there will be an automatic fixed
penalty of £200 since the return is more than three months late.
(3) There will also be an additional corporation tax related penalty of £4,415 (44,150 × 10%) being 10% of the tax unpaid,
since the self-assessment tax return is more than six months late.
Corporation tax liability
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be paid by 1 July 2006.
(2) If the company does not pay its corporation tax until 31 May 2007, then interest of £3,035 (44,150 at 7·5% = 3,311
× 11/12) will be charged by HM Revenue & Customs for the period 1 July 2006 to 31 May 2007.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-05-25
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-06-09
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-06-27
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-06-15
- 2021-03-13
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-06-23
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-02-16
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-07-27
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-11