2019年山东ACCA报名条件
发布时间:2019-01-06
2019年山东ACCA报名条件:
a.具有教育部认可的大专以上学历,既可以报名成为ACCA的正式学员。
b.教育部认可的高等院校在校生,且顺利通过第一学年的所有课程考试,既可报名成为ACCA正式学员。
c.未符合以上报名资格的申请者,而年龄在21岁以上,可以遵循成年考生(MSER)途径申请入会。该途径允许学生作为ACCA校外进修生学习,只须在前两年的四次考试中通过1.1和1.2两门课程,便能以正式学员身份继续参加其它课程考试。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
2 The Rubber Group (TRG) manufactures and sells a number of rubber-based products. Its strategic focus is channelled
through profit centres which sell products transferred from production divisions that are operated as cost centres. The
profit centres are the primary value-adding part of the business, where commercial profit centre managers are
responsible for the generation of a contribution margin sufficient to earn the target return of TRG. The target return is
calculated after allowing for the sum of the agreed budgeted cost of production at production divisions, plus the cost
of marketing, selling and distribution costs and central services costs.
The Bettamould Division is part of TRG and manufactures moulded products that it transfers to profit centres at an
agreed cost per tonne. The agreed cost per tonne is set following discussion between management of the Bettamould
Division and senior management of TRG.
The following information relates to the agreed budget for the Bettamould Division for the year ending 30 June 2009:
(1) The budgeted output of moulded products to be transferred to profit centres is 100,000 tonnes. The budgeted
transfer cost has been agreed on a two-part basis as follows:
(i) A standard variable cost of $200 per tonne of moulded products;
(ii) A lump sum annual charge of $50,000,000 in respect of fixed costs, which is charged to profit centres, at
$500 per tonne of moulded products.
(2) Budgeted standard variable costs (as quoted in 1 above) have been set after incorporating each of the following:
(i) A provision in respect of processing losses amounting to 15% of material inputs. Materials are sourced on
a JIT basis from chosen suppliers who have been used for some years. It is felt that the 15% level of losses
is necessary because the ageing of the machinery will lead to a reduction in the efficiency of output levels.
(ii) A provision in respect of machine idle time amounting to 5%. This is incorporated into variable machine
costs. The idle time allowance is held at the 5% level partly through elements of ‘real-time’ maintenance
undertaken by the machine operating teams as part of their job specification.
(3) Quality checks are carried out on a daily basis on 25% of throughput tonnes of moulded products.
(4) All employees and management have contracts based on fixed annual salary agreements. In addition, a bonus
of 5% of salary is payable as long as the budgeted output of 100,000 tonnes has been achieved;
(5) Additional information relating to the points in (2) above (but NOT included in the budget for the year ending
30 June 2009) is as follows:
(i) There is evidence that materials of an equivalent specification could be sourced for 40% of the annual
requirement at the Bettamould Division, from another division within TRG which has spare capacity.
(ii) There is evidence that a move to machine maintenance being outsourced from a specialist company could
help reduce machine idle time and hence allow the possibility of annual output in excess of 100,000 tonnes
of moulded products.
(iii) It is thought that the current level of quality checks (25% of throughput on a daily basis) is vital, although
current evidence shows that some competitor companies are able to achieve consistent acceptable quality
with a quality check level of only 10% of throughput on a daily basis.
The directors of TRG have decided to investigate claims relating to the use of budgeting within organisations which
have featured in recent literature. A summary of relevant points from the literature is contained in the following
statement:
‘The use of budgets as part of a ‘performance contract’ between an organisation and its managers may be seen as a
practice that causes management action which might lead to the following problems:
(a) Meeting only the lowest targets
(b) Using more resources than necessary
(c) Making the bonus – whatever it takes
(d) Competing against other divisions, business units and departments
(e) Ensuring that what is in the budget is spent
(f) Providing inaccurate forecasts
(g) Meeting the target, but not beating it
(h) Avoiding risks.’
Required:
(a) Explain the nature of any SIX of the eight problems listed above relating to the use of budgeting;
(12 marks)
2 Suggested answer content for each of the eight problems contained within the scenario is as follows:
(a) The nature of each of the problems relating to the use of budgeting is as follows:
Meeting only the lowest targets
– infers that once a budget has been negotiated, the budget holder will be satisfied with this level of performance unless
there is good reason to achieve a higher standard.
Using more resources than necessary
– Once the budget has been agreed the focus will be to ensure that the budgeted utilisation of resources has been adhered
to. Indeed the current system does not provide a specific incentive not to exceed the budget level. It may be, however,
that failure to achieve budget targets would reflect badly on factors such as future promotion prospects or job security.
Making the bonus – whatever it takes
– A bonus system is linked to the budget setting and achievement process might lead to actions by employees and
management which they regard as ‘fair game’. This is because they view the maximisation of bonuses as the main
priority in any aspect of budget setting or work output.
Competing against other divisions, business units and departments
– Competition may manifest itself through the attitudes adopted in relation to transfer pricing of goods/services between
divisions, lack of willingness to co-operate on sharing information relating to methods, sources of supply, expertise, etc.
Ensuring that what is in the budget is spent
– Management may see the budget setting process as a competition for resources. Irrespective of the budgeting method
used, there will be a tendency to feel that unless the budget allowance for one year is spent, there will be imposed
reductions in the following year. This will be particularly relevant in the case of fixed cost areas where expenditure is
viewed as discretionary to some extent.
Providing inaccurate forecasts
– This infers that some aspects of budgeting problems such as ‘Gaming’ and ‘misrepresentation’ may be employed by the
budget holder in order to gain some advantage. Gaming may be seen as a deliberate distortion of the measure in order
to secure some strategic advantage. Misrepresentation refers to creative planning in order to suggest that the measure
is acceptable.
Meeting the target but not beating it
– There may be a view held by those involved in the achievement of the budget target that there is no incentive for them
to exceed that level of effectiveness.
Avoiding risks
– There may be a prevailing view by those involved in the achievement of the budget target that wherever possible
strategies incorporated into the achievement of the budget objective should be left unchanged if they have been shown
to be acceptable in the past. Change may be viewed as increasing the level of uncertainty that the proposed budget
target will be achievable.
(b) Explain Mintzberg’s five organisational components. (10 marks)
(b) The strategic apex is the highest level of the organisation and is therefore the highest level of management. This part ensures that the organisation’s mission is followed and manages the relationship with the environment.
The operating core is the part that represents the productive activity of the organisation, gathering inputs and, through conversion, turns them into outputs.
The middle line represents that part of the organisation where the middle managers operate. The role of this part is to turn the instructions of the strategic apex into activities for the operating core.
The technostructure includes the staff who provide a technical or supportive activity but which are not a part of the core activities. This part of the organisation includes the engineering, accounting and human resource departments.
The support staff carry out the ancillary activities that are neither part of the core nor the technostructure. Support staff have no role in the direct activities of the organisation: these activities include catering and public relations.(Students may draw the appropriate diagram)
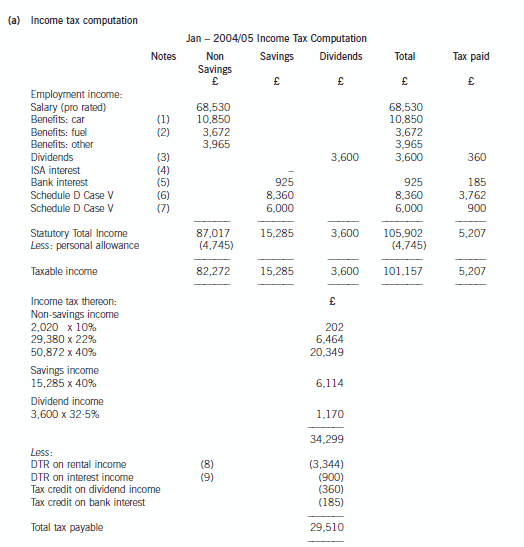
2 Assume that today’s date is 1 July 2005.
Jan is aged 45 and single. He is of Danish domicile but has been working in the United Kingdom since 1 May 2004
and intends to remain in the UK for the medium to long term. Although Jan worked briefly in the UK in 1986, he
has forgotten how UK taxation works and needs some assistance before preparing his UK income tax return.
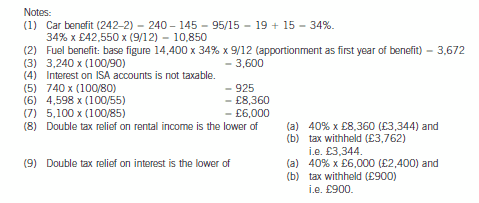
Jan’s salary from 1 May 2004 was £74,760 per annum. Jan also has a company car – a Jaguar XJ8 with a list price
of £42,550 including extras, and CO2 emissions of 242g/km. The car was available to him from 1 July 2004. Free
petrol is provided by the company. Jan has other taxable benefits amounting to £3,965.
Jan’s other 2004/05 income comprises:
£
Dividend income from UK companies (cash received) 3,240
Interest received on an ISA account 230
Interest received on a UK bank account 740
Interest remitted from an offshore account (net of 15% withholding tax) 5,100
Income remitted from a villa in Portugal (net of 45% withholding tax) 4,598
The total interest arising on the offshore account was £9,000 (gross). In addition, Jan has not remitted other
Portuguese rental income arising in the year, totalling a further £1,500 (gross).
Jan informs you that his employer is thinking of providing him with rented accommodation while he looks for a house
to buy. The accommodation would be a two bedroom flat, valued at £155,000 with an annual value of £6,000. It
would be made available from 6 August 2005. The company will pay the rent of £600 per month for the first six
months. All other bills will be paid by Jan.
Jan also informs you that he has 25,000 ordinary shares in Gilet Ltd (‘Gilet’), an unquoted UK trading company. He
has held these shares since August 1986 when he bought 2,500 shares at £4.07 per share. In January 1994, a
bonus issue gave each shareholder nine shares for each ordinary share held. In the last week all Gilet’s shareholders
have received an offer from Jumper plc (‘Jumper’) who wishes to acquire the shares. Jumper has offered the following:
– 3 shares in Jumper (currently trading at £3.55 per share) for every 5 shares in Gilet, and
– 25p cash per share
Required:
(a) Calculate Jan’s 2004/05 income tax (IT) payable. (11 marks)
15 A trader who fixes her prices by adding 50% to cost actually achieved a mark-up of 45%.
Which of the following factors could account for the shortfall?
1 Sales were lower than expected.
2 The opening inventories had been overstated.
3 The closing inventories of the business were higher than the opening inventories.
4 Goods taken from inventories by the proprietor were recorded by debiting drawings and crediting purchases with
the cost of the goods.
A All four factors
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2 only
D 3 and 4 only
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-05
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-05
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-12-27