本文告诉你答案!普通大专学历可不可以报考ACCA
发布时间:2020-01-07
最近有人问51题库考试学习网:自己学历太低,只是普通大专学历可不可以报考ACCA,就这个问题51题库考试学习网今天来为大家讲解一下ACCA的报考政策。
报名注册ACCA条件,具备以下3条中的1条即可:
1、教育部认可的高等院校在校生(本科在校),顺利完成大一的课程考试,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
2、凡具有教育部承认的大专以上学历,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
3、未符合1、2项报名资格的申请者,可以先申请参加FIA(Foundations in
Accountancy)基础财务资格考试。在完成FAB(基础商业会计)、FMA(基础管理会计)、FFA(基础财务会计)3门课程后,可以豁免ACCA AB-FA三门课程的考试,直接进入ACCA技能课程的考试。
综上可知,大专在校期间是不能直接报考ACCA的,不过可以通过第三个方式进行报考。如果需要使用大专学历的话,就要等到毕业后方能报考ACCA。
为什么那么多大学生都要报考ACCA?
报考门槛较低、含金量高
在国内很多会计证书都是要大学本科学历,且只能毕业后才能报考的,例如中高级会计职称、国内注册会计师资格等等,而ACCA是为数不多可以大学期间就能考的含金量高的证书,而且每年有4次考试机会,各位同学可以根据自身情况合理规划时间,安排考试。
人才缺口大,机遇多
当代经济发展新形势下,ACCA采用英式教育方式授课,注重学习中的应用和理解,其专业知识和能力受到业界广泛认同,人才需求量大。此外,中国遵照WTO约定全面开放银行、保险、投资等金融业务后,国内外涉及的金融人才缺口三百多万,机遇多。
职位高,薪资待遇优
世界500强一致青睐,ACCA会员多在世界各地大公司担任高级职位,财务经理、财务总监CFO,甚至总裁CEO。根据官方统计,ACCA会员收入在50万至200万之间的比例高达29.7%。
快速获得海外名校学士学位,不出国门“留学”海外
学习ACCA将有机会获得英国牛津·布鲁克斯大学提供的会计学理学士、甚至MBA学位。不出国门,留学海外,费用大为节省。
签证通过率高,留学移民获技术加分
ACCA证书持有者,留学签证通过率高,优先获得海外奖学金,海外就业认同率高,海外移民更可获技术加分。
想要参加考试的小伙伴们赶快准备起来吧!希望51题库考试学习网为大家分享的内容能给大家带来帮助,也祝各位考生都能取得优异成绩!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
This scenario summarises the development of a company called Rock Bottom through three phases, from its founding in 1965 to 2008 when it ceased trading.
Phase 1 (1965–1988)
In 1965 customers usually purchased branded electrical goods, largely produced by well-established domestic companies, from general stores that stocked a wide range of household products. However, in that year, a recent university graduate, Rick Hein, established his first shop specialising solely in the sale of electrical goods. In contrast to the general stores, Rick Hein’s shop predominantly sold imported Japanese products which were smaller, more reliable and more sophisticated than the products of domestic competitors. Rick Hein quickly established a chain of shops, staffed by young people who understood the capabilities of the products they were selling. He backed this up with national advertising in the press, an innovation at the time for such a specialist shop. He branded his shops as ‘Rock Bottom’, a name which specifically referred to his cheap prices, but also alluded to the growing importance of
rock music and its influence on product sales. In 1969, 80% of sales were of music centres, turntables, amplifiers and speakers, bought by the newly affluent young. Rock Bottom began increasingly to specialise in selling audio equipment.
Hein also developed a high public profile. He dressed unconventionally and performed a number of outrageous stunts that publicised his company. He also encouraged the managers of his stores to be equally outrageous. He rewarded their individuality with high salaries, generous bonus schemes and autonomy. Many of the shops were extremely successful, making their managers (and some of their staff) relatively wealthy people.
However, by 1980 the profitability of the Rock Bottom shops began to decline significantly. Direct competitors using a similar approach had emerged, including specialist sections in the large general stores that had initially failed to react to the challenge of Rock Bottom. The buying public now expected its electrical products to be cheap and reliable.
Hein himself became less flamboyant and toned down his appearance and actions to satisfy the banks who were becoming an increasingly important source of the finance required to expand and support his chain of shops.
Phase 2 (1989–2002)
In 1988 Hein considered changing the Rock Bottom shops into a franchise, inviting managers to buy their own shops (which at this time were still profitable) and pursuing expansion though opening new shops with franchisees from outside the company. However, instead, he floated the company on the country’s stock exchange. He used some of the capital raised to expand the business. However, he also sold shares to help him throw the ‘party of a lifetime’ and to purchase expensive goods and gifts for his family. Hein became Chairman and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the newly quoted company, but over the next thirteen years his relationship with his board and shareholders became increasingly difficult. Gradually new financial controls and reporting systems were put in place. Most of the established managers left as controls became more centralised and formal. The company’s performance was solid but unspectacular. Hein complained that ‘business was not fun any more’. The company was legally required to publish directors’ salaries in its annual report and the generous salary package enjoyed by the Chairman and CEO increasingly became an issue and it dominated the 2002 Annual General Meeting (AGM). Hein was embarrassed by its publication and the discussion it led to in the national media. He felt that it was an infringement of his privacy and
civil liberties.
Phase 3 (2003–2008)
In 2003 Hein found the substantial private equity investment necessary to take Rock Bottom private again. He also used all of his personal fortune to help re-acquire the company from the shareholders. He celebrated ‘freeing Rock Bottom from its shackles’ by throwing a large celebration party. Celebrities were flown in from all over the world to attend. However, most of the new generation of store managers found Hein’s style. to be too loose and unfocused. He became rude and angry about their lack of entrepreneurial spirit. Furthermore, changes in products and how they were purchased meant that fewer people bought conventional audio products from specialist shops. The reliability of these products now meant that they were replaced relatively infrequently. Hein, belatedly, started to consider selling via an Internet site. Turnover and profitability plummeted. In 2007 Hein again considered franchising the company,but he realised that this was unlikely to be successful. In early 2008 the company ceased trading and Hein himself,now increasingly vilified and attacked by the press, filed for personal bankruptcy.
Required:
(a) Analyse the reasons for Rock Bottom’s success or failure in each of the three phases identified in the
scenario. Evaluate how Rick Hein’s leadership style. contributed to the success or failure of each phase.
(18 marks)
(b) Rick Hein considered franchising the Rock Bottom brand at two points in its history – 1988 and 2007.
Explain the key factors that would have made franchising Rock Bottom feasible in 1988, but would have
made it ‘unlikely to be successful’ in 2007. (7 marks)
(a) The product life cycle model suggests that a product passes through six stages: introduction, development, growth, shakeout,
maturity and decline. The first Rock Bottom phase appears to coincide with the introduction, development and growth periods
of the products offered by the company. These highly specified, high quality products were new to the country and were
quickly adopted by a certain consumer segment (see below). The life cycle concept also applies to services, and the innovative
way in which Rock Bottom sold and marketed the products distinguished the company from potential competitors. Not only
were these competitors still selling inferior and older products but their retail methods looked outdated compared with Rock Bottom’s bright, specialist shops. Rock Bottom’s entry into the market-place also exploited two important changes in the
external environment. The first was the technological advance of the Japanese consumer electronics industry. The second
was the growing economic power of young people, who wished to spend their increasing disposable income on products that
allowed them to enjoy popular music. Early entrants into an industry gain experience of that industry sooner than others. This
may not only be translated into cost advantages but also into customer loyalty that helps them through subsequent stages of
the product’s life cycle. Rock Bottom enjoyed the advantages of a first mover in this industry.
Hein’s leadership style. appears to have been consistent with contemporary society and more than acceptable to his young
target market. As an entrepreneur, his charismatic leadership was concerned with building a vision for the organisation and
then energising people to achieve it. The latter he achieved through appointing branch managers who reflected, to some
degree, his own style. and approach. His willingness to delegate considerable responsibility to these leaders, and to reward
them well, was also relatively innovative. The shops were also staffed by young people who understood the capabilities of the
products they were selling. It was an early recognition that intangible resources of skills and knowledge were important to the
organisation.
In summary, in the first phase Rock Bottom’s organisation and Hein’s leadership style. appear to have been aligned with
contemporary society, the customer base, employees and Rock Bottom’s position in the product/service life cycle.
The second phase of the Rock Bottom story appears to reflect the shakeout and maturity phases of the product life cycle. The
entry of competitors into the market is a feature of the growth stage. However, it is in the shakeout stage that the market
becomes saturated with competitors. The Rock Bottom product and service approach is easily imitated. Hein initially reacted
to these new challenges by a growing maturity, recognising that outrageous behaviour might deter the banks from lending to
him. However, the need to raise money to fund expansion and a latent need to realise (and enjoy) his investment led to the
company being floated on the country’s stock exchange. This, eventually, created two problems.
The first was the need for the company to provide acceptable returns to shareholders. This would have been a new challenge
for Hein. He would have to not only maintain dividends to external shareholders, but he would also have to monitor and
improve the publicly quoted share price. In an attempt to establish an organisation that could deliver such value, changes
were made in the organisational structure and style. Most of the phase 1 entrepreneur-style. managers left. This may have
been inevitable anyway as Rock Bottom would have had problems continuing with such high individual reward packages in
a maturing market. However, the new public limited organisation also demanded managers who were more transactional
leaders, focusing on designing systems and controlling performance. This style. of management was alien to Rick’s approach.
The second problem was the need for the organisation to become more transparent. The publishing of Hein’s financial details
was embarrassing, particularly as his income fuelled a life-style. that was becoming less acceptable to society. What had once
appeared innovative and amusing now looked like an indulgence. The challenge now was for Hein to change his leadership
style. to suit the new situation. However, he ultimately failed to do this. Like many leaders who have risen to their position
through entrepreneurial ability and a dominant spirit, the concept of serving stakeholders rather than ordering them around
proved too difficult to grasp. The sensible thing would have been to leave Rock Bottom and start afresh. However, like many
entrepreneurs he was emotionally attached to the company and so he persuaded a group of private equity financiers to help
him buy it back. Combining the roles of Chairman and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) is also controversial and likely to attract
criticism concerning corporate governance.
In summary, in the second phase of Hein’s leadership he failed to change his approach to reflect changing social values, a
maturing product/service market-place and the need to serve new and important stakeholders in the organisation. He clearly
saw the public limited company as a ‘shackle’ on his ambition and its obligations an infringement of his personal privacy.
It can be argued that Hein took Rock Bottom back into private ownership just as the product life cycle moved into its decline
stage. The product life cycle is a timely reminder that any product or service has a finite life. Forty years earlier, as a young
man, Hein was in touch with the technological and social changes that created a demand for his product and service.
However, he had now lost touch with the forces shaping the external environment. Products have now moved on. Music is
increasingly delivered through downloaded files that are then played through computers (for home use) or MP3s (for portable
use). Even where consumers use traditional electronic equipment, the reliability of this equipment means that it is seldom
replaced. The delivery method, through specialised shops, which once seemed so innovative is now widely imitated and
increasingly, due to the Internet, less cost-effective. Consumers of these products are knowledgeable buyers and are only
willing to purchase, after careful cost and delivery comparisons, through the Internet. Hence, Hein is in a situation where he
faces more competition to supply products which are used and replaced less frequently, using a sales channel that is
increasingly uncompetitive. Consequently, Hein’s attempt to re-vitalise the shops by using the approach he adopted in phase
1 of the company was always doomed to failure. This failure was also guaranteed by the continued presence of the managers
appointed in phase 2 of the company. These were managers used to tight controls and targets set by centralised management.
To suddenly be let loose was not what they wanted and Hein appears to have reacted to their inability to act entrepreneurially
with anger and abuse. Hein’s final acts of reinvention concerned the return to a hedonistic, conspicuous life style. that he had
enjoyed in the early days of the company. He probably felt that this was possible now that he did not have the reporting
requirements of the public limited company. However, he had failed to recognise significant changes in society. He celebrated
the freeing of ‘Rock Bottom from its shackles’ by throwing a large celebration party. Celebrities were flown in from all over the
world to attend. It seems inevitable that the cost and carbon footprint of such an event would now attract criticism.
Finally, in summary, Hein’s approach and leadership style. in phase 3 became increasingly out of step with society’s
expectations, customers’ requirements and employees’ expectations. However, unlike phase 2, Hein was now free of the
responsibilities and controls of professional management in a public limited company. This led him to conspicuous activities
that further devalued the brand, meaning that its demise was inevitable.
(b) At the end of the first phase Hein still had managers who were entrepreneurial in their outlook. It might have been attractive
for them to become franchisees, particularly as this might be a way of protecting their income through the more challenging
stages of the product and service life cycle that lay ahead. However, by the time Hein came to look at franchising again (phase
3), the managers were unlikely to be of the type that would take up the challenge of running a franchise. These were
managers used to meeting targets within the context of centrally determined policies and budgets within a public limited
company. Hein would have to make these employees redundant (at significant cost) and with no certainty that he could find
franchisees to replace them.
At the end of phase 1, Rock Bottom was a strong brand, associated with youth and innovation. First movers often retain
customer loyalty even when their products and approach have been imitated by new aggressive entrants to the market. A
strong brand is essential for a successful franchise as it is a significant part of what the franchisee is buying. However, by the
time Hein came to look at franchising again in phase 3, the brand was devalued by his behaviour and incongruent with
customer expectations and sales channels. For example, it had no Internet sales channel. If Hein had developed Rock Bottom
as a franchise it would have given him the opportunity to focus on building the brand, rather than financing the expansion
of the business through the issue of shares.
At the end of phase 1, Rock Bottom was still a financially successful company. If it had been franchised at this point, then
Hein could have realised some of his investment (through franchise fees) and used some of this to reward himself, and the
rest of the money could have been used to consolidate the brand. Much of the future financial risk would have been passed
to the franchisees. There would have been no need to take Rock Bottom public and so suffer the scrutiny associated with a
public limited company. However, by the time Hein came to look at franchising again in phase 3, most of the shops were
trading at a loss. He saw franchising as a way of disposing of the company in what he hoped was a sufficiently well-structured
way. In effect, it was to minimise losses. It seems highly unlikely that franchisees would have been attracted by investing in
something that was actually making a loss. Even if they were, it is unlikely that the franchise fees (and hence the money
immediately realised) would be very high.
(iii) Whether or not you agree with the statement of the marketing director in note (9) above. (5 marks)
Professional marks for appropriateness of format, style. and structure of the report. (4 marks)
(iii) The marketing director is certainly correct in recognising that success is dependent on levels of service quality provided
by HFG to its clients. However, whilst the number of complaints is an important performance measure, it needs to be
used with caution. The nature of a complaint is, very often, far more indicative of the absence, or a lack, of service
quality. For example, the fact that 50 clients complained about having to wait for a longer time than they expected to
access gymnasium equipment is insignificant when compared to an accident arising from failure to maintain properly a
piece of gymnasium equipment. Moreover, the marketing director ought to be aware that the absolute number of
complaints may be misleading as much depends on the number of clients serviced during any given period. Thus, in
comparing the number of complaints received by the three centres then a relative measure of complaints received per
1,000 client days would be far more useful than the absolute number of complaints received.
The marketing director should also be advised that the number of complaints can give a misleading picture of the quality
of service provision since individuals have different levels of willingness to complain in similar situations.
The marketing director seems to accept the current level of complaints but is unwilling to accept any increase above this
level. This is not indicative of a quality-oriented organisation which would seek to reduce the number of complaints over
time via a programme of ‘continuous improvement’.
From the foregoing comments one can conclude that it would be myopic to focus on the number of client complaints
as being the only performance measure necessary to measure the quality of service provision. Other performance
measures which may indicate the level of service quality provided to clients by HFG are as follows:
– Staff responsiveness assumes critical significance in service industries. Hence the time taken to resolve client
queries by health centre staff is an important indicator of the level of service quality provided to clients.
– Staff appearance may be viewed as reflecting the image of the centres.
– The comfort of bedrooms and public rooms including facilities such as air-conditioning, tea/coffee-making and cold
drinks facilities, and office facilities such as e-mail, facsimile and photocopying.
– The availability of services such as the time taken to gain an appointment with a dietician or fitness consultant.
– The cleanliness of all areas within the centres will enhance the reputation of HFG. Conversely, unclean areas will
potentially deter clients from making repeat visits and/or recommendations to friends, colleagues etc.
– The presence of safety measures and the frequency of inspections made regarding gymnasium equipment within
the centres and compliance with legislation are of paramount importance in businesses like that of HFG.
– The achievement of target reductions in weight that have been agreed between centre consultants and clients.
(Other relevant measures would be acceptable.)

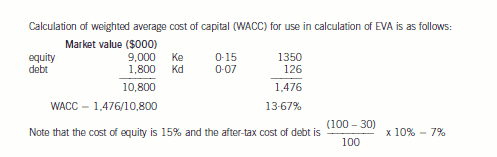
(ii) Calculate the chargeable gain arising as a consequence of Jan accepting Jumper’s offer. (4 marks)
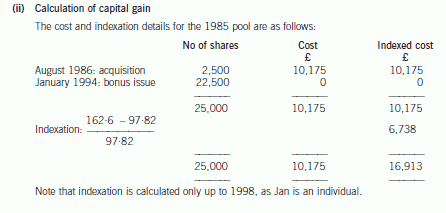

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-01-03
- 2019-01-06
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-06
- 2019-01-06
- 2020-02-28
- 2019-01-17
- 2020-07-31
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-03
- 2019-01-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-01-06
- 2021-04-04
- 2020-02-23