新疆考生:ACCA考试怎么样才算成功正确的打印了准考证呢?
发布时间:2020-01-10
ACCA资格考试是门槛相对较低的一个证书考试,比起只能毕业后报考的CPA证书来讲,报考条件显得低的很多。近期,有不少报考ACCA考试的萌新出现了困惑:这种国际性质的考试,准考证该怎么打印呢?下面是51题库考试学习网小编收集一些相关咨询,有兴趣的ACCAer可以收藏起来慢慢看哟
通常来说,在考前两周,可以登陆MYACCA里打印准考证。
打印准考证步骤:
(1) ACCA考试学员需登陆ACCA官网
(2) 点击MYACCA后登入您的学员号和密码进入
(3) 点击左侧栏里EXAM ENTRY & RESULTS进入
(4) 点击EXAM ATTENDANCE DOCKET生成页面打印即可
注意事项:
1、请仔细阅读准考证上EXAMINATION REGULATIONS和EXAMINATION GUIDELINES,务必严格遵守。ACCA考试学员请仔细核对的考试地点,仔细看准考证上的地址,以免大家走错考场。
2、ACCA准考证需双面打印,无需彩印,黑白打印即可。
3、准考证是学员考试必带的证明,请重视;打印准考证数量须和考试科数相同;
4、2017年3月考季起,ACCA全球统考准考证将不会再有个人照片。
5、因邮寄的准考证收到时间较晚,建议提前打印好准考证,仔细核对报考科目和考试地点有无错误。
6、准考证一定要提前打印,因为越往后官网可能出现各种崩溃状态,尽早打印。 ACCA何时打印准考证都是有ACCA官方统一安排公布时间,2016年实施每年4次考试之后,一般准考证会提前一个月左右就开放打印入口了,考生可自行打印。
ACCA准考证分为两种形式发放,一种是正式纸质版由ACCA英国方约在考前2-3周寄出,另一种是MY ACCA账户中的准考证。未收到ACCA官方邮寄准考证的考生可以在MY ACCA的账户中下载打印准考证,下载打印的准考证与英国邮寄的准考证作用相同。注:准考证必须有照片,准考证上面没有照片的学员请尽快与ACCA 英国方联系。
最后,51题库考试学习网想要在这里告诉大家,不要认为ACCA门槛较低,它的考试水准和难度就很容易。相反,考试难度也是很大的,毫不夸张地说ACCA是一个宽进严出的考试模式。因此,拿到证书的人是少之又少。
当然,51题库考试学习网也相信各位备考ACCA考试的同学们,一定会认真努力的学习和复习的,要相信只要努力就会有回报,哪怕是不能通过考试,也会收到比考试通过更宝贵的东西,大家共勉~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) With reference to CF Co, explain the ethical and other professional issues raised. (9 marks)
(b) There are several issues that must be addressed as a matter of urgency:
Extra work must be planned to discover the extent of the breakdown in internal controls that occurred during the year. It is
important to decide whether the errors were isolated, or continued through the accounting period and whether similar errors
have occurred in other areas e.g. cash receipts from existing customers or cash payments. A review of the working papers of
the internal audit team should be carried out as soon as possible. The materiality of the errors should be documented.
Errors discovered in the accounting systems will have serious implications for the planned audit approach of new customer
deposits. Nate & Co must plan to expand audit testing on this area as control risk is high. Cash deposits will represent a
significant class of transaction in CF Co. A more detailed substantive approach than used in prior year audits may be needed
in this material area if limited reliance can be placed on internal controls.
A combination of the time spent investigating the reasons for the errors, their materiality, and a detailed substantive audit on
this area means that the audit is likely to take longer than previously anticipated. This may have cost and recoverability
implications. Extra staff may need to be assigned to the audit team, and the deadline for completion of audit procedures may
need to be extended. This will need to be discussed with CF Co.
Due to the increased audit risk, Nate & Co should consider increasing review procedures throughout the audit. In addition CF
Co is likely to be a highly regulated company as it operates in financial services, increasing possible attention focused on the
audit opinion. These two factors indicate that a second partner review would be recommended.
A separate issue is that of Jin Sayed offering advice to the internal audit team. The first problem raised is that of quality control.
A new and junior member of the audit team should be subject to close direction and supervision which does not appear to
have been the case during this assignment.
Secondly, Jin Sayed should not have offered advice to the internal audit team. On being made aware of the errors, he should
have alerted a senior member of the audit team, who then would have decided the action to be taken. This implies that he
does not understand the limited extent of his responsibilities as a junior member of the audit team. Nate & Co may wish to
review the training provided to new members of staff, as it should be made clear when matters should be reported to a senior,
and when matters can be dealt with by the individual.
Thirdly, Jin Sayed must be questioned to discover what exactly he advised the internal audit team to do. Despite his academic
qualification, he has little practical experience in the financial information systems of CF Co. He may have given inappropriate
advice, and it will be crucial to confirm that no action has been taken by the internal audit team.
The audit partner should consider if Nate & Co are at risk because of the advice that has been provided by Jin Sayed. As he
is a member of the audit team, his advice would be considered by the client as advice offered by Nate & Co, and the partner
should ascertain by discussion with the client whether this advice has been acted upon.
Finally Nate & Co should consider whether as a firm they could provide the review of the financial information technology
system, as requested by CF Co. IFAC’s Code of Ethics, and ACCA’s Code of Ethics and Conduct places restrictions on the
provision of non-audit services. Nate & Co must be clear in what exactly the ‘review’ will involve.
Providing a summary of weaknesses in the system, with appropriate recommendations is considered part of normal audit
procedures. However, given the errors that have arisen in the year, CF Co may require Nate & Co to design and implement
changes to the system. This would constitute a self-review threat and should only be considered if significant safeguards are
put in place, for example, using a separate team to provide the non-audit service and/or having a second partner review of
the work.
For this part, assume today’s date is 15 August 2005.
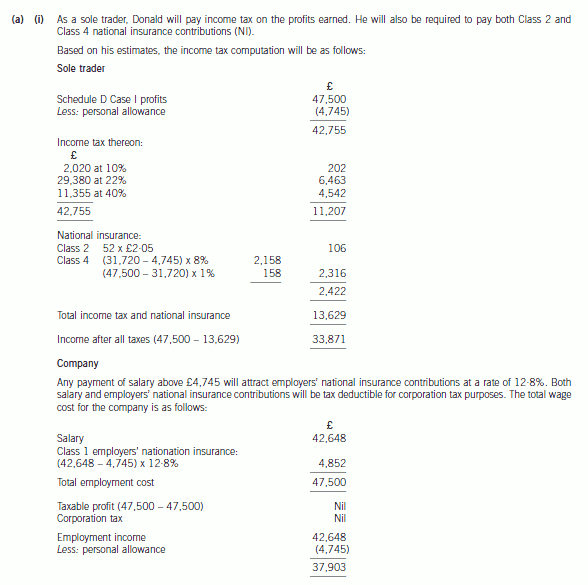
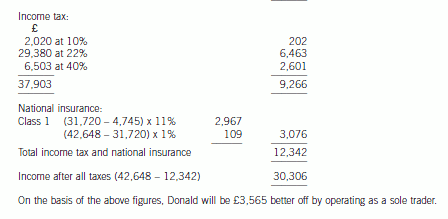
5 (a) Donald is aged 22, single, and about to finish his university education. He has plans to start up a business selling
computer games, and intends to start trading on 1 April 2006, making up accounts to 31 March annually.
He believes that his business will generate cash (equal to taxable profits) of £47,500 in the first year. He
originally intended to operate as a sole trader, but he has recently discovered that as an alternative, he could
operate through a company. He has been advised that if this is the case, he can take a maximum gross salary
of £42,648 out of the company.
Required:
(i) Advise Donald on the income tax (IT), national insurance (NIC) and corporation tax (CT) liabilities he
will incur for the year ended 31 March 2007 trading under each of the two alternative business
structures (sole trade/company). Your advice should be supported by calculations of disposable income
for both alternatives assuming that in the company case, he draws the maximum salary stated.
(7 marks)
3 Damian is the finance director of Linden Limited, a medium sized, unquoted, UK trading company, with a 31 July
year end. Damian personally owns 10% of the ordinary issued share capital of Linden Limited, for which he paid
£10,000 in June 1998. He estimates that the current market value of Linden Limited is £9 million and that the
company will make taxable profits of £1·4 million in the forthcoming year to 31 July 2007.
(a) Damian believes that Linden Limited should conduct its activities in a socially responsible manner and to this
end has proposed that in future all cars purchased by the company should be low emission vehicles. The sales
director has stated that several of his staff, who are the main recipients of company cars, other than the directors,
are extremely unhappy with this proposal, perceiving it as downgrading their value and status.
The cars currently provided to the sales staff have a list price of £19,600, on which Linden Limited receives a
bulk purchase discount of 6% from the dealer, and a CO2 emission rate of 168 grams/kilometre. The company
pays for up to £400 of accessories, of the salesmen’s own choice to be fitted to the cars and all of the running
costs, including private petrol. The cars are replaced every three years and the ‘old’ cars are sold at auction,
because they are high mileage vehicles.
The low emission cars it is proposed to purchase will have the same list price as the current cars, but the dealer
is only prepared to offer a bulk discount of 5% on these vehicles. Damian does not propose to make any other
changes to Linden Limited’s company car policy or practice.
Required:
(i) Explain the tax consequences of the proposed move to low emission vehicles for both the individual
salesmen and Linden Limited, illustrating your answer by means of relevant calculations of the tax and
national insurance (NIC) savings arising. (9 marks)
(a) (i) Individual salesmen
The taxable benefit is determined by the list price of the vehicle plus the cost of the accessories (£20,000) and the CO2
emission rate. The current vehicles have a CO2 emission rate of 168 grams/kilometre, so the benefit will be calculated
at the rate of 20% ((168 – 140)/5 + 15), resulting in a total annual car and car fuel benefit charge of £6,880 (20,000
x 20% + 14,400 x 20%). The low emission vehicles will be chargeable at the basic percentage rate of 15% resulting
in a total annual car and fuel benefit charge of £5,160 (20,000 x 15% + 14,400 x 15%). The salesmen will thus
make an annual income tax saving at their marginal rate of tax, i.e. £378 (1,720 x 22%) if they are basic rate taxpayers
and £688 (1,720 x 40%) if they are higher rate taxpayers.
Linden Limited
The current vehicles will be classed as ‘expensive’ cars based on the discounted list price plus the cost of the accessories
of £18,824 (19,600 x 94% + 400). The annual writing down allowances will thus be restricted to £3,000 throughout
the period of ownership, but there will be no restriction of the balancing allowance available on disposal. The low
emission vehicles will be eligible for a 100% first year allowance of £19,020 (19,600 x 95% + 400), but there will
also be a balancing charge on disposal equivalent to the sales proceeds. Therefore, the total of the allowances available
over the life of the cars will be effectively the same in both cases. As a single company with taxable profits of
£1·4 million, Linden Limited will pay corporation tax at the small companies marginal rate of 32·75% in the year to
31 July 2007, giving a tax benefit in that year of £5,247 for each low emission car purchased ((19,020 – 3,000) x
32·75%).
The company will also make an annual saving in terms of the Class 1A national insurance contributions payable on the
salesmen’s benefits of £220 ((6,880 – 5,160) x 12·8%). But, as these Class 1A contributions are deductible for
corporation tax, the net saving will only be £205 (220 x (100 – 32·75)%).
As the VAT liability payable on the provision of private fuel is based on engine capacity (not the CO2 emission rate) this
will not necessarily be affected.
5 (a) Compare and contrast the responsibilities of management, and of auditors, in relation to the assessment of
going concern. You should include a description of the procedures used in this assessment where relevant.
(7 marks)
5 Dexter Co
(a) Responsibilities of management and auditors
Responsibilities
ISA 570 Going Concern provides a clear framework for the assessment of the going concern status of an entity, and
differentiates between the responsibilities of management and of auditors. Management should assess going concern in order
to decide on the most appropriate basis for the preparation of the financial statements. IAS 1 Presentation of Financial
Statements (revised) requires that where there is significant doubt over an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern, the
uncertainties should be disclosed in a note to the financial statements. Where the directors intend to cease trading, or have
no realistic alternative but to do so, the financial statements should be prepared on a ‘break up’ basis.
Thus the main focus of the management’s assessment of going concern is to ensure that relevant disclosures are made where
necessary, and that the correct basis of preparation is used.
The auditor’s responsibility is to consider the appropriateness of the management’s use of the going concern assumption in
the preparation of the financial statements and to consider whether there are material uncertainties about the entity’s ability
to continue as a going concern that need to be disclosed in a note.
The auditor should also consider the length of the time period that management have looked at in their assessment of going
concern.
The auditor will therefore need to come to an opinion as to the going concern status of an entity but the focus of the auditor’s
evaluation of going concern is to see whether they agree with the assessment made by the management. Therefore whether
they agree with the basis of preparation of the financial statements, or the inclusion in a note to the financial statements, as
required by IAS 1, of any material uncertainty.
Evaluation techniques
In carrying out the going concern assessment, management will evaluate a wide variety of indicators, including operational
and financial. An entity employing good principles of corporate governance should be carrying out such an assessment as
part of the on-going management of the business.
Auditors will use a similar assessment technique in order to come to their own opinion as to the going concern status of an
entity. They will carry out an operational review of the business in order to confirm business understanding, and will conduct
a financial review as part of analytical procedures. Thus both management and auditors will use similar business risk
assessment techniques to discover any threats to the going concern status of the business.
Auditors should not see going concern as a ‘completion issue’, but be alert to issues affecting going concern throughout the
audit. In the same way that management should continually be managing risk (therefore minimising going concern risk),
auditors should be continually be alert to going concern problems throughout the duration of the audit.
However, one difference is that when going concern problems are discovered, the auditor is required by IAS 570 to carry out
additional procedures. Examples of such procedures would include:
– Analysing and discussing cash flow, profit and other relevant forecasts with management
– Analysing and discussing the entity’s latest available interim financial statements
– Reviewing events after the period end to identify those that either mitigate or otherwise affect the entity’s ability to
continue as a going concern, and
– Reading minutes of meetings of shareholders, those charged with governance and relevant committees for reference to
financing difficulties.
Management are not explicitly required to gather specific evidence about going concern, but as part of good governance would
be likely to investigate and react to problems discovered.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-08-15
- 2021-01-01
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-04-17
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09