海南省考生注意:2020年ACCA国际会计师考试准考证打印预计时间
发布时间:2020-01-09
目前,距离2020年3月份的ACCA考试已经仅剩下2个月左右的时间了,近期不少萌新ACCAer来咨询51题库考试学习网,想知道ACCA考试今年3月份准考证打印的时间以及打印的步骤是什么?那么接下来,51题库考试学习网就这一问题为大家解答相关的困惑,“老手”ACCAer也可以看一下,看看是否和记忆中的打印流程是一样的呢?
目前2020年3月份的ACCA考试打印的通道暂未开通,但近些年,准考证的打印流程变化其实不大的,因此大家可以借鉴一下2019年12月份的打印流程,差别不算很大的。
ACCA考试准考证打印流程:
1.打开ACCA英国官网:http://www.uk.accaglobal.com/,点击右上角的MY
ACCA

2.在登录界面,Username处输入ACCA学员号、Password处输入密码,进行登录

3.登录后点击左侧的Docket。

4.点击 Access you docket。

5.这时会弹出一个调查页面,请按上课情况进行选择:(主要是以学员的学习方式来进行选择的)
(1)周末/寒暑假上面授的学员:请在Part time -face to face后面的Other-Provider填写Beijing ZBCT International
Financial Education co. , Ltd-guangzhou,点击SAVE & CONFIRM后会自动跳转下载准考证;
(2)方向班(周一到周五在学校上课)的学员请在Full time -face to face后面的Learning Provider 选择你学校的名字;如果选项里没有你的学校,请在后面的Other-Provider 填写学校的英文名,点击 SAVE & CONFIRM后会自动跳转下载准考证;
(3)网课的学员请在Distance/Online learning后面的Other-Provider填写Beijing ZBCT International Financial Education co. , Ltd-guangzhou,点击 SAVE & CONFIRM后会自动跳转下载准考证;


以上历年来ACCA准考证打印的流程,若与上面描述的内容有误差,建议参考ACCA官网,一切以官网发布的消息为主。
准考证是考试必备的验证自己身份的东西,因此考生要重视准考证的打印,不要等到临近考试的时候才发现准考证没有打印而导致没有成功参加考试,这样就得不偿失了。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
1 The Great Western Cake Company (GWCC) is a well-established manufacturer of specialist flour confectionery
products, including cakes. GWCC sells its products to national supermarket chains. The company’s success during
recent years is largely attributable to its ability to develop innovative products which appeal to the food selectors within
national supermarket chains.
The marketing department of Superstores plc, a national supermarket chain has asked GWCC to manufacture a cake
known as the ‘Mighty Ben’. Mighty Ben is a character who has recently appeared in a film which was broadcast
around the world. The cake is expected to have a minimum market life of one year although the marketing department
consider that this might extend to eighteen months.
The management accountant of GWCC has collated the following estimated information in respect of the Mighty Ben
cake:
(1) Superstores plc has decided on a launch price of £20·25 for the Mighty Ben cake and it is expected that this
price will be maintained for the duration of the product’s life. Superstores plc will apply a 35% mark-up on the
purchase price of each cake from GWCC.
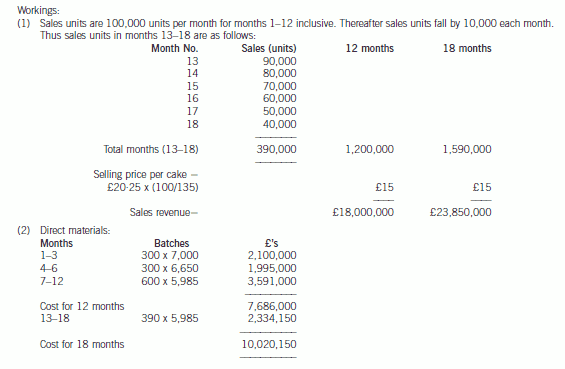
(2) Sales of the Mighty Ben cake are expected to be 100,000 units per month during the first twelve months.
Thereafter sales of the Mighty Ben cake are expected to decrease by 10,000 units in each subsequent month.
(3) Due to the relatively short shelf-life of the Mighty Ben cake, management has decided to manufacture the cakes
on a ‘just-in-time’ basis for delivery in accordance with agreed schedules. The cakes will be manufactured in
batches of 1,000. Direct materials input into the baking process will cost £7,000 per batch for each of the first
three months’ production. The material cost of the next three months’ production is expected to be 95% of the
cost of the first three months’ production. All batches manufactured thereafter will cost 90% of the cost of the
second three months’ production.
(4) Packaging costs will amount to £0·75 per cake. The original costs of the artwork and design of the packaging
will amount to £24,000. Superstores plc will reimburse GWCC £8,000 in the event that the product is
withdrawn from sale after twelve months.
(5) The design of the Mighty Ben cake is such that it is required to be hand-finished. A 75% learning curve will
apply to the total labour time requirement until the end of month five. Thereafter a steady state will apply with
labour time required per batch stabilising at that of the final batch in month five. The labour requirement for the
first batch of Mighty Ben cakes to be manufactured is expected to be 6,000 hours at £10 per hour.
(6) A royalty of 5% of sales revenue (subject to a maximum royalty of £1·1 million) will be payable by GWCC to the
owners of the Mighty Ben copyright.
(7) Variable overheads are estimated at £3·50 per direct labour hour.
(8) The manufacture of the Mighty Ben cake will increase fixed overheads by £75,000 per month.
(9) In order to provide a production facility dedicated to the Mighty Ben cake, an investment of £1,900,000 will be
required and this will be fully depreciated over twelve months.
(10) The directors of GWCC require an average annual return of 35% on their investment over 12 months and
18 months.
(11) Ignore taxation and the present value of cash flows.
Note: Learning curve formula:
y = axb
where y = average cost per batch
a = the cost of the initial batch
x = the total number of batches
b = learning index (= –0·415 for 75% learning rate)
Required:
(a) Prepare detailed calculations to show whether the manufacture of Mighty Ben cakes will provide the required
rate of return for GWCC over periods of twelve months and eighteen months. (20 marks)


15 Which of the following statements about intangible assets are correct?
1 If certain criteria are met, research expenditure must be recognised as an intangible asset.
2 Goodwill may not be revalued upwards.
3 Internally generated goodwill should not be capitalised.
A 2 and 3 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 1 and 2 only
D All three statements are correct
Susan is aware of benchmarking as a useful input into performance measurement and strategic change.
(b) Assess the contribution benchmarking could make to improving the position of the Marlow Fashion Group
and any limitations to its usefulness. (8 marks)
(b) Benchmarking at Marlow Fashion will not be an easy exercise. Marlow Fashion has developed a distinctive way of reaching
its markets that means direct comparisons will be hard to make. Certainly, it can carry out historical benchmarking in
comparing how its own processes and activities have improved, or otherwise, over a relevant period of time. Unfortunately,
this is likely to simply confirm worsening performance. It can compare its own key operations against the ‘best in class’;
regardless of which industry the excellent performer comes from. It could and should have been carrying out competitive
benchmarking on the retail side of the business where information should be more easily available. There may be an
opportunity to benchmark itself against firms that have gone through a similar crisis and achieved a successful turnaround.
In terms of the advantages and disadvantages, the willingness of managers responsible for a key area of performance to
compare themselves against relevant external performance measures should make them take responsibility for any changes
necessary. In Marlow Fashion, the acceptance that things have to be done differently will be the first stage in the turnaround.
Getting managers face-to-face with the problems, accepting responsibility for change and recognising that the necessary
changes are ‘doable’ is an important stage in creating a willingness to change. The disadvantages are that every organisation
and situation is different and there is no one best way. Marlow Fashion thought it had discovered the best way and this created
an unwillingness to change. There is also the danger that you are solving today’s problems with yesterday’s solutions. A good
competitor will be trying to maintain its competitive advantage through constantly improving its processes. It also has a vested
interest in trying to prevent its improvements from being revealed to its competitors. Also, many of the ‘softer’ processes –
typically involving people – are difficult if not impossible to replicate in another organisation. These advantages are to do with
culture and leadership and not easily transferable to another organisation and the context in which it is operating.
(ii) Analyse why moving to a ‘no frills’ low-cost strategy would be inappropriate for ONA.
Note: requirement (b) (ii) includes 3 professional marks (16 marks)
(ii) ‘No frills’ low-cost budget airlines are usually associated with the following characteristics. Each of these characteristics
is considered in the context of Oceania National Airlines (ONA).
– Operational economies of scale
Increased flight frequency brings operational economies and is attractive to both business and leisure travellers. In
the international sector where ONA is currently experiencing competition from established ‘no frills’ low-cost budget
airlines ONA has, on average, one flight per day to each city. It would have to greatly extend its flight network, flight
frequency and the size of its aircraft fleet if it planned to become a ‘no frills’ carrier in this sector. This fleet
expansion appears counter to the culture of an organisation that has expanded very gradually since its formation.
Table 1 shows only three aircraft added to the fleet in the period 2004–2006. It is likely that the fleet size would
have to double for ONA to become a serious ‘no frills’ operator in the international sector. In the regional sector, the
flight density, an average of three flights per day, is more characteristic of a ‘no frills’ airline. However, ONA would
have to address the relatively low utilisation of its aircraft (see Tables 1 and 2) and the cost of maintenance
associated with a relatively old fleet of aircraft.
– Reduced costs through direct sales
On-line booking is primarily aimed at eliminating commission sales (usually made through travel agents). ‘No frills’
low-cost budget airlines typically achieve over 80% of their sales on-line. The comparative figure for ONA (see
Table 2) is 40% for regional sales and 60% for international sales, compared with an average of 84% for their
competitors. Clearly a major change in selling channels would have to take place for ONA to become a ‘no frills’
low-cost budget airline. It is difficult to know whether this is possible. The low percentage of regional on-line sales
seems to suggest that the citizens of Oceania may be more comfortable buying through third parties such as travel
agents.
– Reduced customer service
‘No frills’ low-cost budget airlines usually do not offer customer services such as free meals, free drinks and the
allocation of passengers to specific seats. ONA prides itself on its in-flight customer service and this was one of the
major factors that led to its accolade as Regional Airline of the Year. To move to a ‘no frills’ strategy, ONA would
have to abandon a long held tradition of excellent customer service. This would require a major cultural change
within the organisation. It would also probably lead to disbanding the award winning (Golden Bowl) catering
department and the redundancies of catering staff could prove difficult to implement in a heavily unionised
organisation.
Johnson, Scholes and Whittington have suggested that if an organisation is to ‘achieve competitive advantage through
a low price strategy then it has two basic choices. The first is to try and identify a market segment which is unattractive
(or inaccessible) to competitors and in this way avoid competitive pressures to erode price.’ It is not possible for ONA to
pursue this policy in the international sector because of significant competition from established continental ‘no frills’
low-cost budget airlines. It may be a candidate strategy for the regional sector, but the emergence of small ‘no frills’ lowcost
budget airlines in these countries threaten this. Many of these airlines enter the market with very low overheads
and use the ‘no frills’ approach as a strategy to gain market share before progressing to alternative strategies.
Secondly, a ‘no frills’ strategy depends for its success on margin. Johnson, Scholes and Whittington suggest that ‘in the
long run, a low price strategy cannot be pursued without a low-cost base’. Evidence from the scenario suggests that ONA
does not have a low cost base. It continues to maintain overheads (such as a catering department) that its competitors
have either disbanded or outsourced. More fundamentally (from Table 2), its flight crew enjoy above average wages and
the whole company is heavily unionised. The scenario acknowledges that the company pays above industry salaries and
offers excellent benefits such as a generous non-contributory pension. Aircraft utilisation and aircraft age also suggest a
relatively high cost base. The aircraft are older than their competitors and presumably incur greater maintenance costs.
ONA’s utilisation of its aircraft is also lower than its competitors. It seems highly unlikely that ONA can achieve the
changes required in culture, cost base and operations required for it to become a ‘no frills’ low-cost budget airline. Other
factors serve to reinforce this. For example:
– Many ‘no frills’ low-cost budget airlines fly into airports that offer cheaper taking off and landing fees. Many of these
airports are relatively remote from the cities they serve. This may be acceptable to leisure travellers, but not to
business travellers – ONA’s primary market in the regional sector.
– Most ‘no frills’ low-cost budget airlines have a standardised fleet leading to commonality and familiarity in
maintenance. Although ONA has a relatively small fleet it is split between three aircraft types. This is due to
historical reasons. The Boeing 737s and Airbus A320s appear to be very similar aircraft. However, the Boeings
were inherited from OceaniaAir and the Airbuses from Transport Oceania.
In conclusion, the CEO’s decision to reject a ‘no frills’ strategy for ONA appears to be justifiable. It would require major
changes in structure, cost and culture that would be difficult to justify given ONA’s current position. Revolution is the
term used by Baligan and Hope to describe a major rapid strategic change. It is associated with a sudden transformation
required to react to extreme pressures on the organisation. Such an approach is often required when the company is
facing a crisis and needs to quickly change direction. There is no evidence to support the need for a radical
transformation. This is why the CEO brands the change to a ‘no frills’ low-cost budget airline as ‘unnecessary’. The
financial situation (Table 3) is still relatively healthy and there is no evidence of corporate predators. It can be argued
that a more incremental approach to change would be beneficial, building on the strengths of the organisation and the
competencies of its employees. Moving ONA to a ‘no frills’ model would require seismic changes in cost and culture. If
ONA really wanted to move into this sector then they would be better advised to start afresh with a separate brand andairline and to concentrate on the regional sector where it has a head start over many of its competitors.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-01-01
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-12-24
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-01-01
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-12-24
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-01-01
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-04-11
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-09-04