号外!号外!台湾2020年ACCA考试准考证可以打印啦!这些打印流程你知道吗?
发布时间:2020-01-08
2020年已经过去了一个多周了,除去周末节假日和春节假日,留给大家备考ACCA考试的时间也不多了,相信现在有很多ACCAer们已经开始埋头苦读、认真备考了,但是51题库考试学习网在这里提醒大家:认真备考的同时千万不要忘了一个最最最重要的事情:打印准考证!“新手”ACCAer不知道打印的流程也不用担心,51题库考试学习网会把大家想要知道的咨询都分享给大家:
ACCA考试准考证打印是什么时候?
首先,ACCAer们需要注意的第一件事情就是:ACCA各科目的准考证必须学员自行通过ACCA全球官网下载,原则上不允许从第三方网站上下载相关准考证。2020年3月ACCA考试准考证目前尚未开放下载,请大家等待,ACCA考试准考证一般来说会在考试前2-3周时间开放,请各位ACCAer们注意时间,以免错过打印的时间。打印的步骤如下所示:
1、在ACCA官网主页http://www.accaglobal.com/en.html点击MYACCA,进入登录页面:
2、进入MYACCA账户后点击左侧的EXAM
ENTRY:
3、进入个人页面后点击左侧的“DOCKET”;
4、点击下方红色的“Access your
docket”进入准考证界面;
5、点击“Access your
docket” ,在随后出现的页面中选择学习方式及培训机构,培训机构选择“Beijing Champion Hi-Tech Co. Ltd.Dist...”(2019年3月考季起,ACCA全球统考准考证将不会再有个人照片!)
6、 在弹出的页面或者提示栏中选择“保存”(或是“下载”) ,准考证会以 pdf 格式显示。(一个考季内,第一次进入准考证界面时会出现以下“调查”,按实际情况填写并保存即可。)
7.下载好以后,打开文件,仔细核对准考证上的个人信息及考试信息,准考证共2页。(建议:以正反面的形式,打印在一张纸上)准考证会以 pdf 格式显示,打印完成后,考试时带上您的准考证、身份证/护照参加考试即可。
准考证打印相关注意事项有哪些?
参加笔试的考生,记得要带黑色圆珠笔。
不能用水笔的,一定是黑色圆珠笔。准考证打印好后一定要与其他考试物品(如:黑色圆珠笔,计算器等)放在一起。考试那天,把这些一并带上,另外,不要忘了带身份证(或护照)!
准考证是每位ACCA学员参加考试时必须的进场证明,所以我们要注意的准考证数量要与我们参加的考试科数相同,此外,还要仔细核对报考科目和考试地点有无错误。
需要注意的是:准考证打印没有要求彩色的,所以可以选择黑白也可选择彩色的打印。同时,准考证的要求双面打印的,这两点要尤其重视一下,提前做好准备,预防出现不必要的麻烦。
看完以上的这些信息之后,ACCAer们是不是顿时觉得打印准考证不是很难呀?51题库考试学习网在这里由衷地告诉大家:“只有一条路不能选择——那就是放弃的路;只有一条路不能拒绝——那就是成长的路。”加油~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
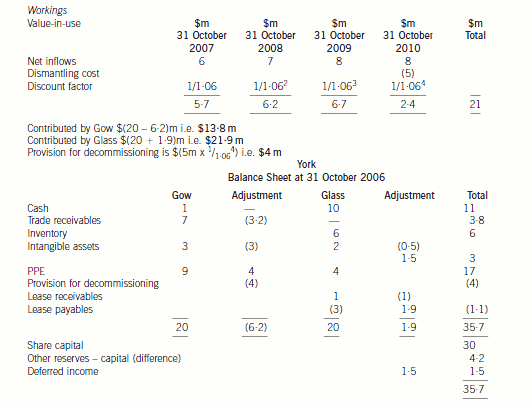
(b) Prepare the balance sheet of York at 31 October 2006, using International Financial Reporting Standards,
discussing the nature of the accounting treatments selected, the adjustments made and the values placed
on the items in the balance sheet. (20 marks)

Gow’s net assets
IAS36 ‘Impairment of Assets’, sets out the events that might indicate that an asset is impaired. These circumstances include
external events such as the decline in the market value of an asset and internal events such as a reduction in the cash flows
to be generated from an asset or cash generating unit. The loss of the only customer of a cash generating unit (power station)
would be an indication of the possible impairment of the cash generating unit. Therefore, the power station will have to be
impairment tested.
The recoverable amount will have to be determined and compared to the value given to the asset on the setting up of the
joint venture. The recoverable amount is the higher of the cash generating unit’s fair value less costs to sell, and its value-inuse.
The fair value less costs to sell will be $15 million which is the offer for the purchase of the power station ($16 million)
less the costs to sell ($1 million). The value-in-use is the discounted value of the future cash flows expected to arise from the
cash generating unit. The future dismantling costs should be provided for as it has been agreed with the government that it
will be dismantled. The cost should be included in the future cash flows for the purpose of calculating value-in-use and
provided for in the financial statements and the cost added to the property, plant and equipment ($4 million ($5m/1·064)).
The value-in-use based on a discount rate of 6 per cent is $21 million (working). Therefore, the recoverable amount is
$21 million which is higher than the carrying value of the cash generating unit ($20 million) and, therefore, the value of the
cash generating unit is not impaired when compared to the present carrying value of $20 million (value before impairment
test).
Additionally IAS39, ‘Financial Instruments: recognition and measurement’, says that an entity must assess at each balance
sheet date whether a financial asset is impaired. In this case the receivable of $7 million is likely to be impaired as Race is
going into administration. The present value of the estimated future cash flows will be calculated. Normally cash receipts from
trade receivables will not be discounted but because the amounts are not likely to be received for a year then the anticipated
cash payment is 80% of ($5 million × 1/1·06), i.e. $3·8 million. Thus a provision for the impairment of the trade receivables
of $3·2 million should be made. The intangible asset of $3 million would be valueless as the contract has been terminated.
Glass’s Net Assets
The leased property continues to be accounted for as property, plant and equipment and the carrying amount will not be
adjusted. However, the remaining useful life of the property will be revised to reflect the shorter term. Thus the property will
be depreciated at $2 million per annum over the next two years. The change to the depreciation period is applied prospectively
not retrospectively. The lease liability must be assessed under IAS39 in order to determine whether it constitutes a
de-recognition of a financial liability. As the change is a modification of the lease and not an extinguishment, the lease liability
would not be derecognised. The lease liability will be adjusted for the one off payment of $1 million and re-measured to the
present value of the revised future cash flows. That is $0·6 million/1·07 + $0·6 million/(1·07 × 1·07) i.e. $1·1 million. The
adjustment to the lease liability would normally be recognised in profit or loss but in this case it will affect the net capital
contributed by Glass.
The termination cost of the contract cannot be treated as an intangible asset. It is similar to redundancy costs paid to terminate
a contract of employment. It represents compensation for the loss of future income for the agency. Therefore it must be
removed from the balance sheet of York. The recognition criteria for an intangible asset require that there should be probable
future economic benefits flowing to York and the cost can be measured reliably. The latter criterion is met but the first criterion
is not. The cost of gaining future customers is not linked to this compensation.
IAS18 ‘Revenue’ contains a concept of a ‘multiple element’ arrangement. This is a contract which contains two or more
elements which are in substance separate and are separately identifiable. In other words, the two elements can operate
independently from each other. In this case, the contract with the overseas company has two distinct elements. There is a
contract not to supply gas to any other customer in the country and there is a contract to sell gas at fair value to the overseas
company. The contract has not been fulfilled as yet and therefore the payment of $1·5 million should not be taken to profit
or loss in its entirety at the first opportunity. The non supply of gas to customers in that country occurs over the four year
period of the contract and therefore the payment should be recognised over that period. Therefore the amount should be
shown as deferred income and not as a deduction from intangible assets. The revenue on the sale of gas will be recognised
as normal according to IAS18.
There may be an issue over the value of the net assets being contributed. The net assets contributed by Glass amount to
$21·9 million whereas those contributed by Gow only total $13·8 million after taking into account any adjustments required
by IFRS. The joint venturers have equal shareholding in York but no formal written agreements, thus problems may arise ifGlass feels that the contributions to the joint venture are unequal.
(ii) Explain the ethical tensions between these roles that Anne is now experiencing. (4 marks)
(ii) Tensions in roles
On one hand, Anne needs to cultivate and manage her relationship with her manager (Zachary) who seems convinced
that Van Buren, and Frank in particular, are incapable of bad practice. He shows evidence of poor judgment and
compromised independence. Anne must decide how to deal with Zachary’s poor judgment.
On the other hand, Anne has a duty to both the public interest and the shareholders of Van Buren to ensure that the
accounts do contain a ‘true and fair view’. Under a materiality test, she may ultimately decide that the payment in
question need not hold up the audit signoff but the poor client explanation (from Frank) is also a matter of concern to
Anne as a professional accountant.
(b) Historically, all owned premises have been measured at cost depreciated over 10 to 50 years. The management
board has decided to revalue these premises for the year ended 30 September 2005. At the balance sheet date
two properties had been revalued by a total of $1·7 million. Another 15 properties have since been revalued by
$5·4 million and there remain a further three properties which are expected to be revalued during 2006. A
revaluation surplus of $7·1 million has been credited to equity. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
(b) Revaluation of owned premises
(i) Matters
■ The revaluations are clearly material as $1·7 million, $5·4 million and $7·1 million represent 5·5% , 17·6% and
23·1% of total assets, respectively.
■ The change in accounting policy, from a cost model to a revaluation model, should be accounted for in accordance
with IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’ (i.e. as a revaluation).
Tutorial note: IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’ does not apply to the initial
application of a policy to revalue assets in accordance with IAS 16.
■ The basis on which the valuations have been carried out, for example, market-based fair value (IAS 16).
■ Independence, qualifications and expertise of valuer(s).
■ IAS 16 does not permit the selective revaluation of assets thus the whole class of premises should have been
revalued.
■ The valuations of properties after the year end are adjusting events (i.e. providing additional evidence of conditions
existing at the year end) per IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’.
Tutorial note: It is ‘now’ still less than three months after the year end so these valuations can reasonably be
expected to reflect year-end values.
■ If $5·4 million is a net amount of surpluses and deficits it should be grossed up so that the credit to equity reflects
the sum of the surpluses with any deficits being expensed through profit and loss (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ The revaluation exercise is incomplete. If the revaluations on the remaining three properties are expected to be
material and cannot be reasonably estimated for inclusion in the financial statements for the year ended
30 September 2005 perhaps the change in policy should be deferred for a year.
■ Depreciation for the year should have been calculated on cost as usual to establish carrying amount before
revaluation.
■ Any premises held under finance leases should be similarly revalued.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A schedule of depreciated cost of owned premises extracted from the non-current asset register.
■ Calculation of difference between valuation and depreciated cost by property. Separate summation of surpluses
and deficits.
■ Copy of valuation certificate for each property.
■ Physical inspection of properties with largest surpluses (including the two valued before the year end) to confirm
condition.
■ Extracts from local property guides/magazines indicating a range of values of similarly styled/sized properties.
■ Separate presentation of the revaluation surpluses (gross) in:
– the statement of changes in equity; and
– reconciliation of carrying amount at the beginning and end of the period.
■ IAS 16 disclosures in the notes to the financial statements including:
– the effective date of revaluation;
– whether an independent valuer was involved;
– the methods and significant assumptions applied in estimating fair values; and
– the carrying amount that would have been recognised under the cost model.
(c) Suggest ways in which each of the six problems chosen in (a) above may be overcome. (6 marks)
(c) Ways in which each of the problems might be overcome are as follows:
Meeting only the lowest targets
– To overcome the problem there must be some additional incentive. This could be through a change in the basis of bonus
payment which currently only provides an incentive to achieve the 100,000 tonnes of output.
Using more resources than necessary
– Overcoming the problem may require a change in the bonus system which currently does not provide benefit from any
output in excess of 100,000 tonnes. This may not be perceived as sufficiently focused in order to achieve action. It may
be that engendering a culture of continuous improvement would help ensure that employees actively sought ways of
reducing idle time levels.
Making the bonus – whatever it takes
– It is likely that efforts to change the ‘work ethos’ at all levels is required, while not necessarily removing the concept of
a bonus payable to all employees for achievement of targets. This may require the fostering of a culture for success within
the company. Dissemination of information to all staff relating to trends in performance, meeting targets, etc may help
to improve focus on continuous improvement.
Competing against other divisions, business units and departments
– The problem may need some input from the directors of TRG. For example, could a ‘dual-cost’ transfer pricing system
be explained to management at both the Bettamould division and also the Division with spare capacity in order to
overcome resistance to problems on transfer pricing and its impact on divisional budgets and reported results? In this
way it may be possible for the Bettamould division to source some of its input materials at a lower cost (particularly from
TRG’s viewpoint) and yet be acceptable to the management at the supplying division.
Ensuring that what is in the budget is spent
– In order to overcome the problem it may be necessary to educate management into acceptance of aspects of budgeting
such as the need to consider the committed, engineered and discretionary aspects of costs. For example, it may be
possible to reduce the number of salaried staff involved in the current quality checking of 25% of throughput on a daily
basis.
Providing inaccurate forecasts
– In order to overcome this problem there must be an integrated approach to the budget setting process. This may be
achieved to some extent through all aspects of the budget having to be agreed by all functions involved. For example,
engineers as well as production line management in reaching the agreed link between percentage process losses and
the falling efficiency of machinery due to age. In addition, TRC may insist an independent audit of aspects of budget
revisions by group staff.
Meeting the target but not beating it
– To overcome the problem may require that the bonus system should be altered to reflect any failure to control costs per
tonne at the budget level.
Avoiding risks
– In order to overcome such problems, TRC would have to provide some guarantees to Bettamould management that the
supply would be available during the budget period at the initially agreed price and that the quality would be maintained
at the required level. This would remove the risk element that the management of the Bettamould division may consider
currently exists.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-22
- 2021-01-01
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09