吉林省考生报名的缴费方式有哪些?应当注意什么问题?
发布时间:2020-01-10
ACCA考试是一个报名门槛较低但考试规定及其严格的考试,其证书的含金量和社会认可度吸引着众多的学子和公职人员不约而同地报考。在报考的时候不要忘了最重要的事情,就是缴费!那么缴费流程又是怎样的呢?且随51题库考试学习网一起去了解了解,建议收藏哦。
ACCA协会官方规定,即使申请免考通过,免考的几门科目要等同于需考试的科目,需要交与考试费相等的免考费。
在收到ACCA寄来的免试通知后尽快缴纳,若收到时间与考试报名时间比较接近,也可以与考试费一起缴纳。不用一次性交清的,注册报名时只需交注册费(按当年费用标准),以后收到ACCA寄来付费通知(如免试费、年费、考试费)时,再逐项交纳。如果只是免试费的话是不着急的,完全可以和你下次的考试费用一起缴纳,一般同一年度里就行。
缴费流程:
1.登录ACCA官网www.accaglobal.com点击My ACCA
2、输入自己的7位ACCA ID和密码,点击Sign in to MY ACCA
3、在左边菜单中点击ACCOUNT ADMINISTRATION并选择Fees,payments and Print Receipts 4、页面跳转后选择需要付款的选项(Annual Subscription Fee-Sub Fee)在前面小方框里打√最后点击上方的Pay键
若ACCOUNT BALANCE数值为0,即表示年费账单还未生成,可以过几天再登录账户查看
5、点击后生成缴款页确认需要缴款的数额是否正确然后再次点击Pay键
注意事项:现在ACCA官网已开通支付宝支付方式,但用支付宝会存在支付不成功的风险,如果支付不成功,款项会被退回到自己的账户中,需要重新支付,请大家不要慌!
6、交付后会生成以下页面如需ACCA考试缴费发票可点击下方Print Receipt按钮
7、点击下方Continue后回到TRANSACTIONS SUMMARY如看到Account Balance显示0.00即为缴费成功(如果显示为95,可以刷新一下试试;刷新无效的,等两天再查看自己的账户,如果还是95即缴费失败,请重新支付,第一次付款会原路退回自己的账户里)
温馨提示:如果过了最后缴费期限,那么当年算没有交年费,你将面临ACCA账户被冻结的影响,已经成为会员也无法再以ACCA会员作为对外称呼,也无法参加ACCA考试,会直接影响你的考试进度的,不过别担心,你只需要邮件联系官方,开通付费窗口,从付费窗口将之前没有交的年费重新支付,另外还要支付一定数额的罚金,罚金数目与未缴纳年费的年数有关,具体费用由官方界定。全部完成以后被冻结的会员将重新获得ACCA会员的头衔
每年的ACCA年费是在一月几号前要交掉呢?还是每年交年费之前会来信通知啊
答:“学员和会员一样都要交年费,每一年的年费都应该在前一年的12月31号前结清,当然晚一点也没关系,不过不交年费的话ACCA会除名,并且根本没资格参加下次考试”
看到这里,相信大家对ACCA考试的缴费也有了一定的了解,希望这些消息能对初次报考ACCA的同学有些许的帮助,51题库考试学习网提前预祝大家顺利通过考试!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
The following financial information relates to HGR Co:
Statement of financial position at the current date (extracts)
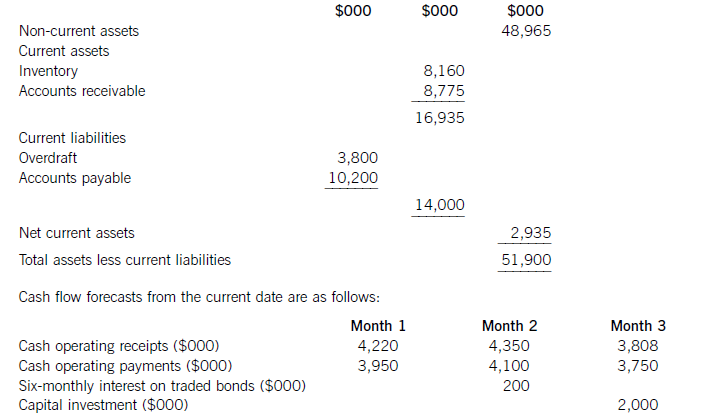
The finance director has completed a review of accounts receivable management and has proposed staff training and operating procedure improvements, which he believes will reduce accounts receivable days to the average sector value of 53 days. This reduction would take six months to achieve from the current date, with an equal reduction in each month. He has also proposed changes to inventory management methods, which he hopes will reduce inventory days by two days per month each month over a three-month period from the current date. He does not expect any change in the current level of accounts payable.
HGR Co has an overdraft limit of $4,000,000. Overdraft interest is payable at an annual rate of 6·17% per year, with payments being made each month based on the opening balance at the start of that month. Credit sales for the year to the current date were $49,275,000 and cost of sales was $37,230,000. These levels of credit sales and cost of sales are expected to be maintained in the coming year. Assume that there are 365 working days in each year.
Required:
(a) Discuss the working capital financing strategy of HGR Co. (7 marks)
(b) For HGR Co, calculate:
(i) the bank balance in three months’ time if no action is taken; and
(ii) the bank balance in three months’ time if the finance director’s proposals are implemented.
Comment on the forecast cash flow position of HGR Co and recommend a suitable course of action.
(10 marks)
(c) Discuss how risks arising from granting credit to foreign customers can be managed and reduced.
(8 marks)
(a)Whenconsideringthefinancingofworkingcapital,itisusefultodividecurrentassetsintofluctuatingcurrentassetsandpermanentcurrentassets.Fluctuatingcurrentassetsrepresentchangesinthelevelofcurrentassetsduetotheunpredictabilityofbusinessactivity.Permanentcurrentassetsrepresentthecorelevelofinvestmentincurrentassetsneededtosupportagivenlevelofturnoverorbusinessactivity.Asturnoverorlevelofbusinessactivityincreases,thelevelofpermanentcurrentassetswillalsoincrease.Thisrelationshipcanbemeasuredbytheratioofturnovertonetcurrentassets.Thefinancingchoiceasfarasworkingcapitalisconcernedisbetweenshort-termandlong-termfinance.Short-termfinanceismoreflexiblethanlong-termfinance:anoverdraft,forexample,isusedbyabusinessorganisationastheneedarisesandvariableinterestischargedontheoutstandingbalance.Short-termfinanceisalsomoreriskythanlong-termfinance:anoverdraftfacilitymaybewithdrawn,orashort-termloanmayberenewedonlessfavourableterms.Intermsofcost,thetermstructureofinterestratessuggeststhatshort-termdebtfinancehasalowercostthanlong-termdebtfinance.Thematchingprinciplesuggeststhatlong-termfinanceshouldbeusedforlong-terminvestment.Applyingthisprincipletoworkingcapitalfinancing,long-termfinanceshouldbematchedwithpermanentcurrentassetsandnon-currentassets.Afinancingpolicywiththisobjectiveiscalleda‘matchingpolicy’.HGRCoisnotusingthisfinancingpolicy,sinceofthe$16,935,000ofcurrentassets,$14,000,000or83%isfinancedfromshort-termsources(overdraftandtradepayables)andonly$2,935,000or17%isfinancedfromalong-termsource,inthiscaseequityfinance(shareholders’funds)ortradedbonds.ThefinancingpolicyorapproachtakenbyHGRCotowardsthefinancingofworkingcapital,whereshort-termfinanceispreferred,iscalledanaggressivepolicy.Relianceonshort-termfinancemakesthisriskierthanamatchingapproach,butalsomoreprofitableduetothelowercostofshort-termfinance.Followinganaggressiveapproachtofinancingcanleadtoovertrading(undercapitalisation)andthepossibilityofliquidityproblems.(b)Bankbalanceinthreemonths’timeifnoactionistaken:Workings:ReductioninaccountsreceivabledaysCurrentaccountsreceivabledays=(8,775/49,275)x365=65daysReductionindaysoversixmonths=65–53=12daysMonthlyreduction=12/6=2daysEachreceivablesdayisequivalentto8,775,000/65=$135,000(Alternatively,eachreceivablesdayisequivalentto49,275,000/365=$135,000)Monthlyreductioninaccountsreceivable=2x135,000=$270,000ReductionininventorydaysCurrentinventorydays=(8,160/37,230)x365=80daysEachinventorydayisequivalentto8,160,000/80=$102,000(Alternatively,eachinventoryday=37,230,000/365=$102,000)Monthlyreductionininventory=102,000x2=$204,000OverdraftinterestcalculationsMonthlyoverdraftinterestrate=1·06171/12=1·005or0·5%Ifnoactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0·005=$19,000Period2interest=3,549,000x0·005=$17,745or$18,000Period3interest=3,517,000x0·005=$17,585or$18,000Ifactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0.005=$19,000Period2interest=3,075,000x0.005=$15,375or$15,000Period3interest=2,566,000x0.005=$12,830or$13,000DiscussionIfnoactionistaken,thecashflowforecastshowsthatHGRCowillexceeditsoverdraftlimitof$4millionby$1·48millioninthreemonths’time.Ifthefinancedirector’sproposalsareimplemented,thereisapositiveeffectonthebankbalance,buttheoverdraftlimitisstillexceededinthreemonths’time,althoughonlyby$47,000ratherthanby$1·47million.Ineachofthethreemonthsfollowingthat,thecontinuingreductioninaccountsreceivabledayswillimprovethebankbalanceby$270,000permonth.Withoutfurtherinformationonoperatingreceiptsandpayments,itcannotbeforecastwhetherthebankbalancewillreturntolessthanthelimit,orevencontinuetoimprove.Themainreasonfortheproblemwiththebankbalanceisthe$2millioncapitalexpenditure.Purchaseofnon-currentassetsshouldnotbefinancedbyanoverdraft,butalong-termsourceoffinancesuchasequityorbonds.Ifthecapitalexpenditurewereremovedfromtheareaofworkingcapitalmanagement,theoverdraftbalanceattheendofthreemonthswouldbe$3·48millionifnoactionweretakenand$2·05millionifthefinancedirector’sproposalswereimplemented.GiventhatHGRCohasalmost$50millionofnon-currentassetsthatcouldpossiblybeusedassecurity,raisinglong-termdebtthrougheitherabankloanorabondissueappearstobesensible.Assumingabondinterestrateof10%peryear,currentlong-termdebtintheform.oftradedbondsisapproximately($200mx2)/0·1=$4m,whichismuchlessthantheamountofnoncurrentassets.AsuitablecourseofactionforHGRCotofollowwouldthereforebe,firstly,toimplementthefinancedirector’sproposalsand,secondly,tofinancethecapitalexpenditurefromalong-termsource.Considerationcouldalsobegiventousingsomelong-termdebtfinancetoreducetheoverdraftandtoreducethelevelofaccountspayable,currentlystandingat100days.(c)Whencreditisgrantedtoforeigncustomers,twoproblemsmaybecomeespeciallysignificant.First,thelongerdistancesoverwhichtradetakesplaceandthemorecomplexnatureoftradetransactionsandtheirelementsmeansforeignaccountsreceivableneedmoreinvestmentthantheirdomesticcounterparts.Longertransactiontimesincreaseaccountsreceivablebalancesandhencetheleveloffinancingandfinancingcosts.Second,theriskofbaddebtsishigherwithforeignaccountsreceivablethanwiththeirdomesticcounterparts.Inordertomanageandreducecreditrisks,therefore,exportersseektoreducetheriskofbaddebtandtoreducethelevelofinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivable.Manyforeigntransactionsareon‘openaccount’,whichisanagreementtosettletheamountoutstandingonapredetermineddate.Openaccountreflectsagoodbusinessrelationshipbetweenimporterandexporter.Italsocarriesthehighestriskofnon-payment.Onewaytoreduceinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableistoagreeearlypaymentwithanimporter,forexamplebypaymentinadvance,paymentonshipment,orcashondelivery.Thesetermsoftradeareunlikelytobecompetitive,however,anditismorelikelythatanexporterwillseektoreceivecashinadvanceofpaymentbeingmadebythecustomer.Onewaytoacceleratecashreceiptsistousebillfinance.Billsofexchangewithasignedagreementtopaytheexporteronanagreedfuturedate,supportedbyadocumentaryletterofcredit,canbediscountedbyabanktogiveimmediatefunds.Thisdiscountingiswithoutrecourseifbillsofexchangehavebeencountersignedbytheimporter’sbank.Documentarylettersofcreditareapaymentguaranteebackedbyoneormorebanks.Theycarryalmostnorisk,providedtheexportercomplieswiththetermsandconditionscontainedintheletterofcredit.Theexportermustpresentthedocumentsstatedintheletter,suchasbillsoflading,shippingdocuments,billsofexchange,andsoon,whenseekingpayment.Aseachsupportingdocumentrelatestoakeyaspectoftheoveralltransaction,lettersofcreditgivesecuritytotheimporteraswellastheexporter.Companiescanalsomanageandreduceriskbygatheringappropriateinformationwithwhichtoassessthecreditworthinessofnewcustomers,suchasbankreferencesandcreditreports.Insurancecanalsobeusedtocoversomeoftherisksassociatedwithgivingcredittoforeigncustomers.Thiswouldavoidthecostofseekingtorecovercashduefromforeignaccountsreceivablethroughaforeignlegalsystem,wheretheexportercouldbeatadisadvantageduetoalackoflocalorspecialistknowledge.Exportfactoringcanalsobeconsidered,wheretheexporterpaysforthespecialistexpertiseofthefactorasawayofreducinginvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableandreducingtheincidenceofbaddebts.
(b) Explain how the use of SWOT analysis may be of assistance to the management of Diverse Holdings Plc.
(3 marks)
(b) The use of SWOT analysis will focus management attention on current strengths and weaknesses of each subsidiary company
which will be of assistance in the formulating of the business strategy of Diverse Holdings Plc. It will also enable management
to monitor trends and developments in the constantly changing environments of their subsidiaries. Each trend or development
may be classified as an opportunity or a threat that will provide a stimulus for an appropriate management response.
Management can make an assessment of the feasibility of required actions in order that the company may capitalise upon
opportunities whilst considering how best to negate or minimise the effect of any threats.
A SWOT analysis should assist the management of Diverse Holdings Plc as they must identify their strengths, weaknesses,
opportunities and threats. These may be classified as follows:
Strengths which appear to include both OFL and HTL.
Weaknesses which must include PSL and its limited outlets, which generate little growth and could collapse overnight. KAL
is also a weakness due to its declining profitability.
Opportunities where OFT, HTL and OPL are operating in growth markets.
Threats from which KAL is suffering.
If these four categories are identified and analysed then the group should be strengthened.
You are the audit supervisor of Maple & Co and are currently planning the audit of an existing client, Sycamore Science Co (Sycamore), whose year end was 30 April 2015. Sycamore is a pharmaceutical company, which manufactures and supplies a wide range of medical supplies. The draft financial statements show revenue of $35·6 million and profit before tax of $5·9 million.
Sycamore’s previous finance director left the company in December 2014 after it was discovered that he had been claiming fraudulent expenses from the company for a significant period of time. A new finance director was appointed in January 2015 who was previously a financial controller of a bank, and she has expressed surprise that Maple & Co had not uncovered the fraud during last year’s audit.
During the year Sycamore has spent $1·8 million on developing several new products. These projects are at different stages of development and the draft financial statements show the full amount of $1·8 million within intangible assets. In order to fund this development, $2·0 million was borrowed from the bank and is due for repayment over a ten-year period. The bank has attached minimum profit targets as part of the loan covenants.
The new finance director has informed the audit partner that since the year end there has been an increased number of sales returns and that in the month of May over $0·5 million of goods sold in April were returned.
Maple & Co attended the year-end inventory count at Sycamore’s warehouse. The auditor present raised concerns that during the count there were movements of goods in and out the warehouse and this process did not seem well controlled.
During the year, a review of plant and equipment in the factory was undertaken and surplus plant was sold, resulting in a profit on disposal of $210,000.
Required:
(a) State Maples & Co’s responsibilities in relation to the prevention and detection of fraud and error. (4 marks)
(b) Describe SIX audit risks, and explain the auditor’s response to each risk, in planning the audit of Sycamore Science Co. (12 marks)
(c) Sycamore’s new finance director has read about review engagements and is interested in the possibility of Maple & Co undertaking these in the future. However, she is unsure how these engagements differ from an external audit and how much assurance would be gained from this type of engagement.
Required:
(i) Explain the purpose of review engagements and how these differ from external audits; and (2 marks)
(ii) Describe the level of assurance provided by external audits and review engagements. (2 marks)
(a) Fraud responsibility
Maple & Co must conduct an audit in accordance with ISA 240 The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements and are responsible for obtaining reasonable assurance that the financial statements taken as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether caused by fraud or error.
In order to fulfil this responsibility, Maple & Co is required to identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements due to fraud.
They need to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding the assessed risks of material misstatement due to fraud, through designing and implementing appropriate responses. In addition, Maple & Co must respond appropriately to fraud or suspected fraud identified during the audit.
When obtaining reasonable assurance, Maple & Co is responsible for maintaining professional scepticism throughout the audit, considering the potential for management override of controls and recognising the fact that audit procedures which are effective in detecting error may not be effective in detecting fraud.
To ensure that the whole engagement team is aware of the risks and responsibilities for fraud and error, ISAs require that a discussion is held within the team. For members not present at the meeting, Sycamore’s audit engagement partner should determine which matters are to be communicated to them.
(b) Audit risks and auditors’ responses



(c) (i) Review engagements
Review engagements are often undertaken as an alternative to an audit, and involve a practitioner reviewing financial data, such as six-monthly figures. This would involve the practitioner undertaking procedures to state whether anything has come to their attention which causes the practitioner to believe that the financial data is not in accordance with the financial reporting framework.
A review engagement differs to an external audit in that the procedures undertaken are not nearly as comprehensive as those in an audit, with procedures such as analytical review and enquiry used extensively. In addition, the practitioner does not need to comply with ISAs as these only relate to external audits.
(ii) Levels of assurance
The level of assurance provided by audit and review engagements is as follows:
External audit – A high but not absolute level of assurance is provided, this is known as reasonable assurance. This provides comfort that the financial statements present fairly in all material respects (or are true and fair) and are free of material misstatements.
Review engagements – where an opinion is being provided, the practitioner gathers sufficient evidence to be satisfied that the subject matter is plausible; in this case negative assurance is given whereby the practitioner confirms that nothing has come to their attention which indicates that the subject matter contains material misstatements.
(b) Explain and give examples of assertive behaviour. (7 marks)
(b) Assertive behaviour on the other hand is based on equality and co-operation. It involves standing up for one’s own rights and needs but also respects the rights and needs of others. It is not overbearing or aggressive but can be described as clear, honest and direct communication.
Assertive individuals defend their rights in a way that does not violate another individual’s rights. They express their needs,wants, opinions, feelings and beliefs in direct and appropriate ways.
Characteristics of assertive behaviour include statements that are short, clear and to the point, distinctions made between fact and opinion, suggestions weighted with advice and evidence. Constructive criticism is the norm and offered without blame or assumptions. Questions to establish the wishes, opinions and thoughts of others are used as ways of getting around problems. There are no ‘ought’ or ‘should’ conditions, the first statement is often held, the individual’s own feelings are expressed and not those of others. Assertive behaviour can be successful if it displays a willingness to deliver a mutual compromise as an aid to achieving a clear objective.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-02
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-02-11
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-01-16
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-02-27
- 2021-05-27
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-05-20
- 2021-01-13
- 2021-10-07