看过来:上海市2020年9月ACCA考试报名截止时间
发布时间:2020-07-04
各位小伙伴注意了,上海市2020年9月ACCA考试报名正在火热进行中,本次考试常规报名的截止日期是:7月27日。
以下是9月份ACCA考试报名的具体费用详情。

ACCA考试报名步骤
第一步:登录MYACCA
第二步:在左侧导航栏中找到“EXAM ENTRY”,点击进入。
第三步:点击页面右下角的“Enter for Exams”
第四步:在下拉框中选择考试时间。
第五步:选择考试时间后,点击右下角的“Apply for Exam Session”
第六步:选择考试科目,在相应的方框中打勾。
第七步:在左侧选择考试国家,在右侧选择考试地点,然后点击“Next”
第八步:不要勾选,请直接点击“Next”
第九步:如果需要选择版本,弄清楚之后,在这里选择版本。
第十步:最后检查所有考试报名信息是否正确,在确保无误后,在“Terms and
Conditions”后面的方格内打钩,然后点击右下角的“Proceed to payment”进行网上付费。
第十一步:进行网上交费。
以上就是今天分享的全部内容了,上海的小伙伴可要记得在规定时间完成报名,预祝各位在9月的考试顺顺利利,如需了解更多考试相关内容,请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) (i) Discusses the principles involved in accounting for claims made under the above warranty provision.
(6 marks)
(ii) Shows the accounting treatment for the above warranty provision under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’ for the year ended 31 October 2007. (3 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and communication of advice. (2 marks)
(b) Provisions – IAS37
An entity must recognise a provision under IAS37 if, and only if:
(a) a present obligation (legal or constructive) has arisen as a result of a past event (the obligating event)
(b) it is probable (‘more likely than not’), that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle
the obligation
(c) the amount can be estimated reliably
An obligating event is an event that creates a legal or constructive obligation and, therefore, results in an enterprise having
no realistic alternative but to settle the obligation. A constructive obligation arises if past practice creates a valid expectation
on the part of a third party. If it is more likely than not that no present obligation exists, the enterprise should disclose a
contingent liability, unless the possibility of an outflow of resources is remote.
The amount recognised as a provision should be the best estimate of the expenditure required to settle the present obligation
at the balance sheet date, that is, the amount that an enterprise would rationally pay to settle the obligation at the balance
sheet date or to transfer it to a third party. This means provisions for large populations of events such as warranties, are
measured at a probability weighted expected value. In reaching its best estimate, the entity should take into account the risks
and uncertainties that surround the underlying events.
Expected cash outflows should be discounted to their present values, where the effect of the time value of money is material
using a risk adjusted rate (it should not reflect risks for which future cash flows have been adjusted). If some or all of the
expenditure required to settle a provision is expected to be reimbursed by another party, the reimbursement should be
recognised as a separate asset when, and only when, it is virtually certain that reimbursement will be received if the entity
settles the obligation. The amount recognised should not exceed the amount of the provision. In measuring a provision future
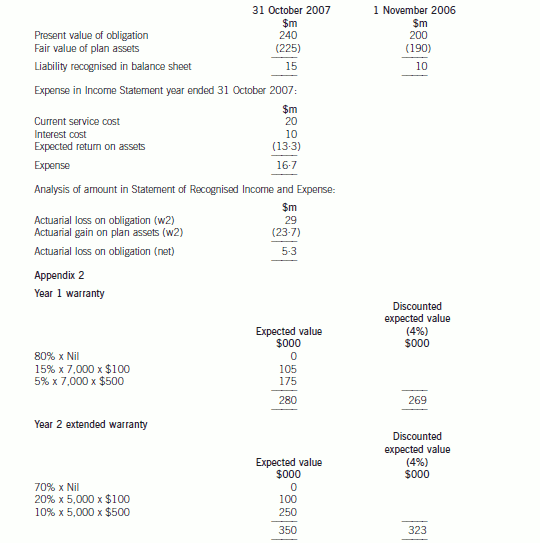
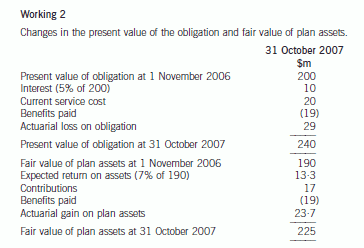
events should be considered. The provision for the warranty claim will be determined by using the expected value method.
The past event which causes the obligation is the initial sale of the product with the warranty given at that time. It would be
appropriate for the company to make a provision for the Year 1 warranty of $280,000 and Year 2 warranty of $350,000,
which represents the best estimate of the obligation (see Appendix 2). Only if the insurance company have validated the
counter claim will Macaljoy be able to recognise the asset and income. Recovery has to be virtually certain. If it is virtually
certain, then Macaljoy may be able to recognise the asset. Generally contingent assets are never recognised, but disclosed
where an inflow of economic benefits is probable.
The company could discount the provision if it was considered that the time value of money was material. The majority of
provisions will reverse in the short term (within two years) and, therefore, the effects of discounting are likely to be immaterial.
In this case, using the risk adjusted rate (IAS37), the provision would be reduced to $269,000 in Year 1 and $323,000 in
Year 2. The company will have to determine whether this is material.
Appendix 1
The accounting for the defined benefit plan is as follows:

(ii) Discuss TWO problems that may be faced in implementing quality control procedures in a small firm of
Chartered Certified Accountants, and recommend how these problems may be overcome. (4 marks)
(ii) Consultation – it may not be possible to hold extensive consultations on specialist issues within a small firm, due to a
lack of specialist professionals. There may be a lack of suitably experienced peers to discuss issues arising on client
engagements. Arrangements with other practices for consultation may be necessary.
Training/Continuing Professional Development (CPD) – resources may not be available, and it is expensive to establish
an in-house training function. External training consortia can be used to provide training/CPD for qualified staff, and
training on non-exam related issues for non-qualified staff.
Review procedures – it may not be possible to hold an independent review of an engagement within the firm due to the
small number of senior and experienced auditors. In this case an external review service may be purchased.
Lack of specialist experience – where special skills are needed within an engagement; the skills may be bought in, for
example, by seconding staff from another practice. Alternatively if work is too specialised for the firm, the work could be
sub-contracted to another practice.
Working papers – the firm may lack resources to establish an in-house set of audit manuals or standard working papers.
In this case documentation can be provided by external firms or professional bodies.
(c) Explain the benefits of performance-related pay in rewarding directors and critically evaluate the implications
of the package offered to Choo Wang. (8 marks)
(c) Choo Wang’s remuneration package
Benefits of PRP
In general terms, performance-related pay serves to align directors’ and shareholders’ interests in that the performancerelated
element can be made to reflect those things held to be important to shareholders (such as financial targets). This, in
turn, serves to motivate directors, especially if they are directly responsible for a cost or revenue/profit budget or centre. The
possibility of additional income serves to motivate directors towards higher performance and this, in turn, can assist in
recruitment and retention. Finally, performance-related pay can increase the board’s control over strategic planning and
implementation by aligning rewards against strategic objectives.
Critical evaluation of Choo Wang’s package
Choo Wang’s package appears to have a number of advantages and shortcomings. It was strategically correct to include some
element of pay linked specifically to Southland success. This will increase Choo’s motivation to make it successful and indeed,
he has said as much – he appears to be highly motivated and aware that additional income rests upon its success. Against
these advantages, it appears that the performance-related component does not take account of, or discount in any way for,
the risk of the Southland investment. The bonus does not become payable on a sliding scale but only on a single payout basis
when the factory reaches an ‘ambitious’ level of output. Accordingly, Choo has more incentive to be accepting of risk with
decisions on the Southland investment than risk averse. This may be what was planned, but such a bias should be pointed
out. Clearly, the company should accept some risk but recklessness should be discouraged. In conclusion, Choo’s PRP
package could have been better designed, especially if the Southland investment is seen as strategically risky.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-04-07
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-12-31
- 2020-02-27
- 2021-10-09
- 2020-03-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-03-22
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-04-17
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-05-06