河南省考生:2020年ACCA国际会计师几月份考试?
发布时间:2020-01-09
你是否因为自己错过2019年12月份的ACCA考试的报名时间而懊恼呢?自己呕心沥血准备几个月的考试就因为没有及时报名而前功尽弃了?那么,51题库考试学习网想告诉大家:好消息来啦!2020年ACCA国家会计师考试报名时间新鲜出炉啦~最近的一次考试就在两个月之后哟,有参加的同学可以开始备考啦!具体的时间如下所示:
首先是报名的时间节点,目前2020年3月份ACCA考试提前报名的时间已于2019年11月11日结束了,而常规报名时间仍在继续,持续时间到2020年1月27日,没有报名的同学赶紧去报名呀~不要到时候又遇到错过时间的尴尬局面:

以上是2020年ACCA四个考季的报名时间,有想报名的同学要随时关注时间哟~
了解完了报名时间,那么考试的具体时间又是什么时候呢?别担心,51题库考试学习网会为大家奉上2020年一整年的ACCA考试时间:


以上就是2020年ACCA考试的报名时间和考试时间的具体情况,51题库考试学习网提醒大家,在备考的同时千万不要忘记这些重要的时间节点哟~错过任何一个对大家来说都是一大损失。建议大家将自己考试的时间记录在一个明显且自己能够天天看到的位置,以免忘记。最后,大家还是需要根据自己实际的学习情况来报考,祝大家考试顺利通过~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
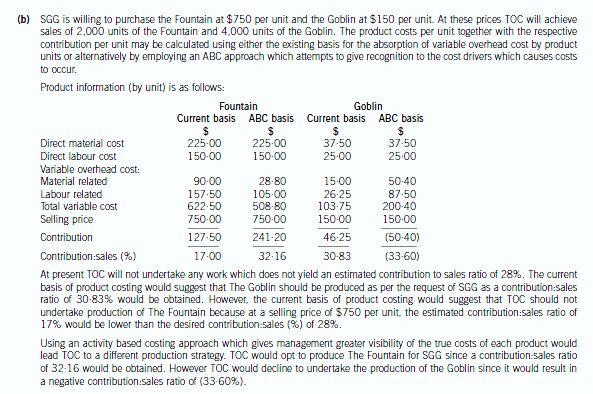
(b) Using the unit cost information available and your calculations in (a), prepare a financial analysis of the
decision strategy which TOC may implement with regard to the manufacture of each product. (6 marks)
Roy Crawford has argued for a reduction in both the product range and customer base to improve company
performance.
(b) Assess the operational advantages and disadvantages to Bonar Paint of choosing such a strategy.
(15 marks)
(b) Divestment of products or parts of the business is one of the most difficult strategic decisions. As apparent in Bonar Paint a
reduction in the products and customers served by the firm is likely to cause significant changes to the firm’s value chain and
system. Currently Bonar Paint supplies its customers, regardless of size, directly and this inevitably means that their
distribution costs are increased. The reduction in products and customers may allow a choice to be made about the costs of
supplying customers directly as against using distributors to handle the smaller customers.
In using the value chain one is looking to identify the significant cost activities and how those costs behave. Some costs may
be affected by the overall size of the firm e.g. advertising while others affected by the batch size being processed. The changeto fewer products will lead to a bigger batch size and a number of positive consequences for costs. The value chain’s major
benefit is in identifying and quantifying the links that exist between various activities within the firm and between the firm
and its customers and suppliers. In Bonar Paint’s case does a reduction in product range lead to less product failures and
consequent warranty claims? Does simplifying the product range lead to shorter lead times and better delivery time
performance for its customers? Above all, a good understanding of its value chain will let it know if it changes an activity what
are the consequences for other parts of the system.
In terms of reducing the product range, before such a decision is taken Bonar Paint must carry out a thorough analysis of the
pattern of customer demand for each paint type. In all probability it will find that 80% of its sales come from 20% of its
product range. Having given this qualification, reducing the product range can have a number of beneficial results on other
parts of the value chain. The immediate effect is likely to be that Bonar Paint produces fewer batches over a given time period
but produces them in larger quantities. This will bring cost savings but the impact on other parts of the value chain is equally
important. The beneficial effects are:
– With a smaller product range the control of raw materials and finished inventory will be simplified affecting inbound and
outbound logistics. This will improve the inventory turn and make for better product availability.
– With an improved inventory turn this will reduce the firm’s working capital needs and release significant amounts of
cash.
– A simpler operations process should facilitate staff savings and support more automation.
– Warranty claims and support costs could be reduced.
– Bonar Paint will be purchasing fewer raw materials but in greater volume and on a more regular basis. This will lead to
improved price and delivery terms from its suppliers.
– Bonar Paint can offer improved product reliability and better delivery to its customers and should improve its market
share.
In terms of operational disadvantages, these therefore are largely in terms of the impact on customer service levels seen in
terms of product range availability. Once again it is important to have accurate information on the sales and profitability of
each product so informed divestment decisions could be taken. Care must be taken to identify any paints, which though
ordered infrequently, and in small quantities are a pre-cursor for customers ordering other paints. Some important customers
may require that the full range of their paint needs are met in order to continue buying from Bonar Paint.
Reduction of the product range and customer base is an important strategic decision. Eliminating non-contributors or ‘dog’
products both in terms of paints and customers is a key part of managing the product portfolio. However, inertia both in terms
of products and customers is a real strategic weakness. In terms of the three tests of suitability, acceptability and feasibility
the analysis suggests that only acceptability is likely to be an issue. Tony Edmunds needs to be convinced that it is an
appropriate strategy to adopt. It is the lack of accurate sales analysis that lies at the heart of the problem and that is his areaof responsibility!
(c) On the assumption that the administrators of Noland’s estate will sell quoted shares in order to fund the
inheritance tax due as a result of his death, calculate the value of the quoted shares that will be available to
transfer to Avril. You should include brief notes of your treatment of the house and the shares in Kurb Ltd.
(9 marks)
Note: you should assume that the tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 apply throughout this
question.
(c) Value of quoted shares that can be transferred to Avril
The value of shares to be transferred to Avril will be equal to £370,000 less the inheritance tax due by the estate.
IHT is payable on transfers in the seven years prior to Noland’s death and on the death estate.
The only chargeable gift in the seven years prior to Noland’s death is the transfer to the discretionary trust. No tax is due in
respect of this gift as it is covered by the nil rate band.

(c) Critically evaluate Vincent Viola’s view that corporate governance provisions should vary by country.
(8 marks)
(c) Corporate governance provisions varying by country
There is a debate about the extent to which corporate governance provisions (in the form. of either written codes, laws or
general acceptances) should be global or whether they should vary to account for local differences. In this answer, Vincent
Viola’s view is critically evaluated.
In general terms, corporate governance provisions vary depending on such factors as local business culture, businesses’
capital structures, the extent of development of capital funding of businesses and the openness of stock markets. In Germany,
for example, companies have traditionally drawn much of their funding from banks thereby reducing their dependence on
shareholders’ equity. Stock markets in the Soviet Union are less open and less liquid than those in the West. In many
developing countries, business activity is concentrated among family-owned enterprises.
Against Vincent’s view
Although business cultures vary around the world, all business financed by private capital have private shareholders. Any
dilution of the robustness of provisions may ignore the needs of local investors to have their interests adequately represented.
This dilution, in turn, may allow bad practice, when present, to exist and proliferate.
Some countries suffer from a poor reputation in terms of endemic corruption and fraud and any reduction in the rigour with
which corporate governance provisions are implemented fail to address these shortcomings, notwithstanding the fact that they
might be culturally unexpected or difficult to implement.
In terms of the effects of macroeconomic systems, Vincent’s views ignore the need for sound governance systems to underpin
confidence in economic systems. This is especially important when inward investment needs are considered as the economic
wealth of affected countries are partly underpinned by the robustness, or not, of their corporate governance systems.
Supporting Vincent’s view
In favour of Vincent’s view are a number of arguments. Where local economies are driven more by small family businesses
and less by public companies, accountability relationships are quite different (perhaps the ‘family reasons’ referred to in the
case) and require a different type of accounting and governance.
There is a high compliance and monitoring cost to highly structured governance regimes that some developing countries may
deem unnecessary to incur.
There is, to some extent, a link between the stage of economic development and the adoption of formal governance codes.
It is generally accepted that developing countries need not necessarily observe the same levels of formality in governance as
more mature, developed economies.
Some countries’ governments may feel that they can use the laxity of their corporate governance regimes as a source of
international comparative advantage. In a ‘race to the bottom’, some international companies seeking to minimise the effects
of structured governance regimes on some parts of their operations may seek countries with less tight structures for some
operations.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-28
- 2020-03-01
- 2021-04-09
- 2020-03-22
- 2021-01-22
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-04-10
- 2020-01-13
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-01-13
- 2021-02-03
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-09-03
- 2021-01-02
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-02-23
- 2019-12-28
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-03-20