2020年第二考试季ACCA考试时间:6月1日-6日
发布时间:2020-03-07
ACCA考试科目较多,考试方式也不同。前四门科目随约随考,剩下的科目则需要在官网上进行报名,并在规定时间内参加考试。由于2020年第一考试季的ACCA考试已经取消,因此第二考试季的ACCA考试报名人数明显上升。同时,网上也增加了有关考试时间的询问。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来2020年ACCA考试时间的相关信息,以供参考。
根据ACCA官网之前公布的消息,2020年第二考试季的ACCA考试将在6月1日至5日举行,各科目的具体考试时间还请各位考生在ACCA官网上查询。
一般来说,ACCA考试每年举行四次,分别在每年的3月、6月、9月、12月。不同年份的具体考试时间略有差异,请考生注意ACCA官网发布的消息。每次考试报名时间都分为三个阶段:提前报名、常规报名、后期报名。不同年份的具体时间略有不同,通常而言,3月份考试的报名截止时间分别为上一年的11月、1月、2月;6月份考试的报名截止时间分别为当年的2月、4月以及5月;9月份考试的报名截止时间分别为当年的5月、7月、8月;12月份报名截止时间分别在当年的8月、10月、11月。注意,以上的报名时间均为截止日期。
以上就是关于2020年ACCA考试报名时间及考试时间的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:ACCA考试报名后可以在ACCA账户上修改,但是修改时间仅限于常规报名时间结束之前,请各位考生注意。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
2 Your audit client, Prescott Co, is a national hotel group with substantial cash resources. Its accounting functions are
well managed and the group accounting policies are rigorously applied. The company’s financial year end is
31 December.
Prescott has been seeking to acquire a construction company for some time in order to bring in-house the building
and refurbishment of hotels and related leisure facilities (e.g. swimming pools, squash courts and restaurants).
Prescott’s management has recently identified Robson Construction Co as a potential target and has urgently requested
that you undertake a limited due diligence review lasting two days next week.
Further to their preliminary talks with Robson’s management, Prescott has provided you with the following brief on
Robson Construction Co:
The chief executive, managing director and finance director are all family members and major shareholders. The
company name has an established reputation for quality constructions.
Due to a recession in the building trade the company has been operating at its overdraft limit for the last 18
months and has been close to breaching debt covenants on several occasions.
Robson’s accounting policies are generally less prudent than those of Prescott (e.g. assets are depreciated over
longer estimated useful lives).
Contract revenue is recognised on the percentage of completion method, measured by reference to costs incurred
to date. Provisions are made for loss-making contracts.
The company’s management team includes a qualified and experienced quantity surveyor. His main
responsibilities include:
(1) supervising quarterly physical counts at major construction sites;
(2) comparing costs to date against quarterly rolling budgets; and
(3) determining profits and losses by contract at each financial year end.
Although much of the labour is provided under subcontracts all construction work is supervised by full-time site
managers.
In August 2005, Robson received a claim that a site on which it built a housing development in 2002 was not
properly drained and is now subsiding. Residents are demanding rectification and claiming damages. Robson
has referred the matter to its lawyers and denied all liability, as the site preparation was subcontracted to Sarwar
Services Co. No provisions have been made in respect of the claims, nor has any disclosure been made.
The auditor’s report on Robson’s financial statements for the year to 30 June 2005 was signed, without
modification, in March 2006.
Required:
(a) Identify and explain the specific matters to be clarified in the terms of engagement for this due diligence
review of Robson Construction Co. (6 marks)
2 PRESCOTT CO
(a) Terms of engagement – matters to be clarified
Tutorial note: This one-off assignment requires a separate letter of engagement. Note that, at this level, a standard list of
contents will earn few, if any, marks. Any ‘ideas list’ must be tailored to generate answer points specific to the due diligence
review of this target company.
■ Objective of the review: for example, to find and report facts relevant to Prescott’s decision whether to acquire Robson.
The terms should confirm whether Prescott’s interest is in acquiring the company (i.e. the share capital) or its trading
assets (say), as this will affect the nature and scope of the review.
Tutorial note: This is implied as Prescott ‘has been seeking to acquire ... to bring building … in-house’.
■ Prescott’s management will be solely responsible for any decision made (e.g. any offer price made to purchase Robson).
■ The nature and scope of the review and any standards/guidelines in accordance with which it will be conducted. That
investigation will consist of enquiry (e.g. of the directors and the quantity surveyor) and analytical procedures (e.g. on
budgeted information and prior period financial statements).
Tutorial note: This is not going to be a review of financial statements. The prior year financial statements have only
recently been audited and financial statements for the year end 30 June 2006 will not be available in time for the
review.
■ The level of assurance will be ‘negative’. That is, that the material subject to review is free of material misstatement. It
should be stated that an audit is not being performed and that an audit opinion will not be expressed.
■ The timeframe. for conducting the investigation (two days next week) and the deadline for reporting the findings.
■ The records, documentation and other information to which access will be unrestricted. This will be the subject of
agreement between Prescott and Robson.
■ A responsibility/liability disclaimer that the engagement cannot be relied upon to disclose errors, illegal acts or other
irregularities (e.g. fraudulent financial reporting or misappropriations of Robson’s assets).
Tutorial note: Third party reliance on the report seems unlikely as Prescott has ‘substantial cash resources’ and may not
need to obtain loan finance.
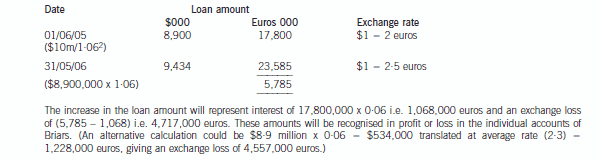
(b) Describe with suitable calculations how the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Briars will be dealt with in
the group financial statements and how the loan to Briars should be treated in the financial statements of
Briars for the year ended 31 May 2006. (9 marks)
(b) IAS21 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’ requires goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation
and fair value adjustments to acquired assets and liabilities to be treated as belonging to the foreign operation. They should
be expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate at each balance sheet date.
Effectively goodwill is treated as a foreign currency asset which is retranslated at the closing rate. In this case the goodwillarising on the acquisition of Briars would be treated as follows:

At 31 May 2006, the goodwill will be retranslated at 2·5 euros to the dollar to give a figure of $4·4 million. Therefore this
will be the figure for goodwill in the balance sheet and an exchange loss of $1·4 million recorded in equity (translation
reserve). The impairment of goodwill will be expensed in profit or loss to the value of $1·2 million. (The closing rate has been
used to translate the impairment; however, there may be an argument for using the average rate.)
The loan to Briars will effectively be classed as a financial liability measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for
financial liabilities that do not meet the definition of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. For most entities,
most financial liabilities will fall into this category. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the
liability is measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled, between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. In other words, fair value is an actual or estimated transaction price on the reporting
date for a transaction taking place between unrelated parties that have adequate information about the asset or liability being
measured.
Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value generally is assumed to equal the amount of
consideration paid or received for the financial asset or financial liability. Accordingly, IAS39 specifies that the best evidence
of the fair value of a financial instrument at initial recognition generally is the transaction price. However for longer-term
receivables or payables that do not pay interest or pay a below-market interest, IAS39 does require measurement initially at
the present value of the cash flows to be received or paid.
Thus in Briars financial statements the following entries will be made:
(ii) Comment briefly on how divisional managers might respond to the results achieved and ONE potential
problem that might be experienced by Our Timbers Ltd. (2 marks)
The town of Brighttown in Euraria has a mayor (elected every five years by the people in the town) who is responsible for, amongst other things, the transport policy of the town.
A year ago, the mayor (acting as project sponsor) instigated a ‘traffic lite’ project to reduce traffic congestion at traffic lights in the town. Rather than relying on fixed timings, he suggested that a system should be implemented which made the traffic lights sensitive to traffic flow. So, if a queue built up, then the lights would automatically change to green (go). The mayor suggested that this would have a number of benefits. Firstly, it would reduce harmful emissions at the areas near traffic lights and, secondly, it would improve the journey times for all vehicles, leading to drivers ‘being less stressed’. He also cited evidence from cities overseas where predictable journey times had been attractive to flexible companies who could set themselves up anywhere in the country. He felt that the new system would attract such companies to the town.
The Eurarian government has a transport regulation agency called OfRoad. Part of OfRoad’s responsibilities is to monitor transport investments and it was originally critical of the Brighttown ‘traffic lite’ project because the project’s benefits were intangible and lacked credibility. The business case did not include a quantitative cost/benefit analysis. OfRoad has itself published a benefits management process which classifies benefits in the following way.
Financial: A financial benefit can be confidently allocated in advance of the project. Thus if the investment will save $90,000 per year in staff costs then this is a financial benefit.
Quantifiable: A quantifiable benefit is a benefit where there is sufficient credible evidence to suggest, in advance, how much benefit will result from the project. This benefit may be financial or non-financial. For example, energy savings from a new building might be credibly predicted in advance. However, the exact amount of savings cannot be accurately forecast.
Measurable benefit: A measurable benefit is a benefit which can only be confidently assessed post-implementation, and so cannot be reliably predicted in advance. Increase in sales from a particular initiative is an example of a measurable benefit. Measurable benefits may either be financial or non-financial.
Observable benefit: An observable benefit is a benefit which a specific individual or group will decide, using agreed criteria, has been realised or not. Such benefits are usually non-financial. Improved staff morale might be an example of an observable benefit.
One month ago, the mayoral elections saw the election of a new mayor with a completely distinct transport policy with different objectives. She wishes to address traffic congestion by attracting commuters away from their cars and onto public transport. Part of her policy is a traffic light system which gives priority to buses. The town council owns the buses which operate in the town and they have invested heavily in buses which are comfortable and have significantly lower emissions than the conventional cars used by most people in the town. The new mayor wishes to improve the frequency, punctuality and convenience of these buses, so that they tempt people away from using their cars. This will require more buses and more bus crews, a requirement which the mayor presents as ‘being good for the unemployment rate in this town’. It will also help the bus service meet the punctuality service level which it published three years ago, but has never yet met. ‘A reduction in cars and an increase in buses will help us meet our target’, the mayor claims.
The mayor has also suggested a number of initiatives to discourage people from taking their cars into the town. She intends to sell two car parks for housing land (raising $325,000) and this will reduce car park capacity from 1,000 to 800 car spaces per day. She also intends to raise the daily parking fee from $3 to $4. Car park occupancy currently stands at 95% (it is difficult to achieve 100% for technical reasons) and the same occupancy rate is expected when the car park capacity is reduced.
The new mayor believes that her policy signals the fact that Brighttown is serious about its green credentials. ‘This’, she says, ‘will attract green consumers to come and live in our town and green companies to set up here. These companies and consumers will bring great benefit to our community.’ To emphasise this, she has set up a Go Green team to encourage green initiatives in the town.
The ‘traffic lite’ project to tackle congestion proposed by the former mayor is still in the development stage. The new mayor believes that this project can be modified to deliver her vision and still be ready on the date promised by her predecessor.
Required:
(a) A ‘terms of reference’ (project initiation document, project charter) was developed for the ‘traffic lite’ project to reduce traffic congestion.
Discuss what changes will have to be made to this ‘terms of reference’ (project initiation document, project charter) to reflect the new mayor’s vision of the project. (5 marks)
(b) The new mayor wishes to re-define the business case for the project, using the benefits categorisation suggested by OfRoad. Identify costs and benefits for the revised project, classifying each benefit using the guidance provided by OfRoad. (14 marks)
(c) Stakeholder management is the prime responsibility of the project manager.
Discuss the appropriate management of each of the following three stakeholders identified in the revised (modified) project.
(i) The new mayor;
(ii) OfRoad;
(iii) A private motorist in Brighttown who uses his vehicle to commute to his job in the town. (6 marks)
(a) Objectives and scope
From the perspective of the ‘traffic lite’ project, the change in mayor has led to an immediate change in the objectives driving the project. This illustrates how public sector projects are susceptible to sudden external environmental changes outside their control. The project initially proposed to reduce traffic congestion by making traffic lights sensitive to traffic flow. It was suggested that this would improve journey times for all vehicles using the roads of Brighttown. However, the incoming mayor now wishes to reduce traffic congestion by attracting car users onto public transport. Consequently she wants to develop a traffic light system which will give priority to buses. This should ensure that buses run on time. The project is no longer concerned with reducing journey times for all users. Indeed, congestion for private cars may get worse and this could further encourage car users to switch to public transport.
An important first step would be to confirm that the new mayor wishes to be the project sponsor for the project, because the project has lost its sponsor, the former mayor. The project scope also needs to be reviewed. The initial project was essentially a self-contained technical project aimed at producing a system which reduced queuing traffic. The revised proposal has much wider political scope and is concerned with discouraging car use and improving public bus services. Thus there are also proposals to increase car parking charges, to reduce the number of car park spaces (by selling off certain car parks for housing development) and to increase the frequency, quality and punctuality of buses. The project scope appears to have been widened considerably, although this will have to be confirmed with the new project sponsor.
Only once the scope of the revised project been agreed can revised project objectives be agreed and a new project plan developed, allocating the resources available to the project to the tasks required to complete the project. It is at this stage that the project manager will be able to work out if the proposed delivery date (a project constraint) is still manageable. If it is not, then some kind of agreement will have to be forged with the project sponsor. This may be to reduce the scope of the project, add more resources, or some combination of the two.
(b) Cost benefit
The re-defined project will have much more tangible effects than its predecessor and these could be classified using the standard approach suggested in the scenario. Benefits would include:
– One-off financial benefit from selling certain car parks
– this appears to be a predictable financial benefit of $325,000 which can be confidently included in a cost/benefit analysis.
– Increased income from public bus use – this appears to be a measurable benefit, in that it is an aspect of performance which can be measured (for example, bus fares collected per day), but it is not possible to estimate how much income will actually increase until the project is completed. – Increased income from car parks
– this appears to be a quantifiable benefit if the assumption is made that usage of the car parks will stay at 95%. There may indeed be sufficient confidence to define it as a financial benefit. Car park places will be reduced from 1,000 to 800, but the increase in fees will compensate for this reduction in capacity. Current expected daily income is 1,000 x $3 x 0·95 = $2,850. Future expected income will be 800 x $4 x 0·95 = $3,040.
– Improved punctuality of buses – this will again be a measurable benefit. It will be defined in terms of a Service Level promised to the residents of Brighttown. Improved punctuality might also help tempt a number of vehicle users to use public transport instead.
– Reduced emissions – buses are more energy efficient and emit less carbon dioxide than the conventional vehicles used by most of the inhabitants of Brighttown. This benefit should again be measurable (but non-financial) and should benefit the whole of the town, not just areas around traffic lights.
– Improved perception of the town – the incoming mayor believes that her policy will help attract green consumers and green companies to the town. Difficulties in classifying what is meant by these terms makes this likely to be an observable benefit, where a group, such as the Go Green team, established by the council itself can decide (based on their judgement) whether the benefit has been realised or not.
The costs of implementing the project will also have to be re-assessed. These costs will now include:
– The cost of purchasing more buses to meet the increased demand and frequency of service.
– The operational costs of running more buses, including salary costs of more bus drivers.
– Costs associated with the disposal of car parks.
– Costs associated with slowing down drivers (both economic and emotional).
The technical implementation requirements of the project will also change and this is almost certain to have cost implications because a solution will have to be developed which allows buses to be prioritised. A feasibility study will have to be commissioned to examine whether such a solution is technically feasible and, if it is, the costs of the solution will have to be estimated and entered into the cost-benefit analysis.
(c) A stakeholder grid (Mendelow) provides a framework for understanding how project team members should communicate with each stakeholder or stakeholder group. The grid itself has two axes. One axis is concerned with the power or influence of the stakeholder in this particular project. The other axis is concerned with the stakeholder’s interest in the project.
The incoming mayor: High power and high interest. The mayor is a key player in the project and should be carefully and actively managed throughout. The mayor is currently enthusiastic about the project and this enthusiasm has to be sustained. As the likely project sponsor, it will be the mayor’s responsibility to promote the project internally and to make resources available to it. It will also be up to her to ensure that the promised business benefits are actually delivered. However, she is also the person who can cancel the project at any time.
OfRoad – a government agency: OfRoad were critical of the previous mayor’s justification for the project. They felt that the business case was solely based on intangible benefits and lacked credibility. It is likely that they will be more supportive of the revised proposals for two reasons. Firstly, the proposal uses the classification of benefits which it has suggested. Secondly, the proposal includes tangible benefits which can confidently be included in a cost-benefit analysis. OfRoad is likely to have high power (because it can intervene in local transport decisions) but relatively low interest in this particular project as the town appears to be following its guidelines. An appropriate management strategy would be to keep watch and monitor the situation, making sure that nothing happens on the project which would cause the agency to take a sudden interest in it.
The private motorist of Brighttown: Most of these motorists will have a high interest in the project, because it impacts them directly; but, individually, they have very little power. Their chance to influence policy has just passed, and mayoral elections are not due for another five years. The suggested stakeholder management approach here is to keep them informed. However, their response will have to be monitored. If they organise themselves and band together as a group, they might be able to stage disruptive actions which might raise their power and have an impact on the project. This makes the point that stakeholder management is a continual process, as stakeholders may take up different positions in the grid as they organise themselves or as the project progresses.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-08
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-02-03
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-03-09
- 2020-03-13
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-13
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-03-05
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2021-06-19
- 2021-05-14
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-03-13
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-13
- 2021-06-19
- 2019-07-19