ACCA考哪几门课程?ACCA考试科目介绍!
发布时间:2020-03-05
随着近年来ACCA考试热度的不断上升,网上也增加了许多关于ACCA考试信息的询问。比如,有网友就在问ACCA考哪几门课程。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来2020年ACCA考试科目的相关信息,以供参考。
ACCA考试科目较多,考试范围也比较广。自2007年12月起,ACCA实施新的考试大纲。新大纲下ACCA共有16门课程,通过14科就可以拿到ACCA准会员证书(最后四科为四选二,考生可根据自身情况自行选择)。这16门课程共分为两个部分:基础阶段课程及专业阶段课程。除了分为两大课程之外,ACCA的16门课程又分为四个大模块:知识模块(F1-F3)、技能模块(F4-F9)、核心模块(P1-P3)、选修模块(P4-P7)。下面是具体的考试科目:

另外,各位小伙伴们要注意ACCA的 16门课程的考试顺序也是有规定的,考试必须按照模块顺序来进行,考试顺序为知识模块-技能模块-核心模块-选修模块。虽然考生必须按照模块顺序报考,但是各个模块内部的科目是可以打乱顺序考的。比如在知识课程阶段(F1-F3),可以先考F3,再考F2,再考F1,后面的依此类推。但是,ACCA官方是建议各位考生按照课程顺序报考的,这样是比较科学的考试顺序。
以上就是关于ACCA考试科目的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:ACCA考试中F阶段的部分科目与P阶段的部分科目对应,因此小伙伴们在学习这些科目时,要注意及时复习哦。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
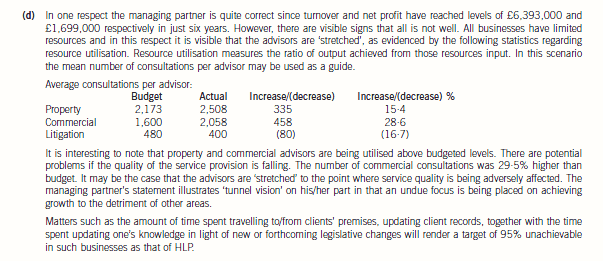
(d) The managing partner of HLP stated at a recent partners’ meeting that ‘every advisor should aim to ensure that
95% of all hours he/she works are billed to clients. This will ensure that we remain both profitable and
competitive’.
Required:
Discuss the statement of the managing partner, drawing attention to any concerns that you may have
regarding the statement. (6 marks)
6 The accountant communicates information to others in reports and statements. Understanding the nature and
importance of communication is therefore an important part of the accountant’s role.
Required:
(a) Explain the importance of good communication. (5 marks)
6 Overview:
The need for clear and concise communication and the consequences of poor communication must be understood by a profession
which exists to provide information to others. Poor communication leads to ineffective control, poor co-ordination and management
failure.
Part (a):
Good communication ensures that individuals know what is expected of them. Co-ordination takes place within the organisation
and there is control of the organisation’s plans, procedures and staff. Instructions of management need to be clearly understood in
assisting group and team cohesiveness and reducing stress from misunderstood instructions. Bias, distortion and omission is
removed with clear communication, as is secrecy, innuendo and rumour. Good communication ensures that the right information
is received by the correct person and thus acted upon, reducing conflict within and between different parts of the organisation.
(ii) Briefly outline the tax consequences for Henry if the types of protection identified in (i) were to be
provided for him by Happy Home Ltd compared to providing them for himself. You are not required to
discuss the corporation tax (CT) consequences for Happy Home Ltd. (4 marks)
(ii) Provision of protection: company or individual
If any of the policies are taken out and paid for by Henry personally, then there will be no tax relief on the premiums,
but neither will there normally be any tax payable on the proceeds or benefits received.
If Happy Home Ltd were to pay the premiums on a policy taken out by Henry, and of which he was the direct beneficiary,
then this will constitute a benefit, on the grounds that the company will have satisfied a personal liability of Henry’s.
Accordingly, income tax and Class 1A national insurance contributions will be payable on the benefit.
If, however, Happy Home Ltd were to decide to offer protection benefits to their employees on a group basis (and not
just to Henry), then it would be possible to avoid a charge under the benefits rules and/or obtain a lower rate of premium
under a collective policy. For example:
– A death in service benefit of up to four times remuneration can be provided as part of an approved pension scheme.
No benefit charge arises on Henry and any lump sum will be paid tax free. This could be considered a substitute
for a term assurance policy.
– If a group permanent health insurance policy were taken out, no benefit charge would arise on Henry, but any
benefits payable under the policy would be paid to Happy Home Ltd in the first instance. When subsequently paid
on to Henry, such payments would be treated as arising from his employment and subject to PAYE and national
insurance as for normal salary payments.
– If a group critical illness policy were taken out, again no benefit charge would arise on Henry, but in this case also,
any benefits received by Henry directly from Happy Home Ltd as a result of the payments under the policy would
be considered as derived from his employment and subject to income tax and national insurance. Such a charge
to tax and national insurance would however be avoided if these payments were made in terms of a trust.
5 You are an audit manager in Fox & Steeple, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants, responsible for allocating staff
to the following three audits of financial statements for the year ending 31 December 2006:
(a) Blythe Co is a new audit client. This private company is a local manufacturer and distributor of sportswear. The
company’s finance director, Peter, sees little value in the audit and put it out to tender last year as a cost-cutting
exercise. In accordance with the requirements of the invitation to tender your firm indicated that there would not
be an interim audit.
(b) Huggins Co, a long-standing client, operates a national supermarket chain. Your firm provided Huggins Co with
corporate financial advice on obtaining a listing on a recognised stock exchange in 2005. Senior management
expects a thorough examination of the company’s computerised systems, and are also seeking assurance that
the annual report will not attract adverse criticism.
(c) Gray Co has been an audit client since 1999 after your firm advised management on a successful buyout. Gray
provides communication services and software solutions. Your firm provides Gray with technical advice on
financial reporting and tax services. Most recently you have been asked to conduct due diligence reviews on
potential acquisitions.
Required:
For these assignments, compare and contrast:
(i) the threats to independence;
(ii) the other professional and practical matters that arise; and
(iii) the implications for allocating staff.
(15 marks)
5 FOX & STEEPLE – THREE AUDIT ASSIGNMENTS
(i) Threats to independence
Self-interest
Tutorial note: This threat arises when a firm or a member of the audit team could benefit from a financial interest in, or
other self-interest conflict with, an assurance client.
■ A self-interest threat could potentially arise in respect of any (or all) of these assignments as, regardless of any fee
restrictions (e.g. per IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’), the auditor is remunerated by clients for
services provided.
■ This threat is likely to be greater for Huggins Co (larger/listed) and Gray Co (requires other services) than for Blythe Co
(audit a statutory necessity).
■ The self-interest threat may be greatest for Huggins Co. As a company listed on a recognised stock exchange it may
give prestige and credibility to Fox & Steeple (though this may be reciprocated). Fox & Steeple could be pressurised into
taking evasive action to avoid the loss of a listed client (e.g. concurring with an inappropriate accounting treatment).
Self-review
Tutorial note: This arises when, for example, any product or judgment of a previous engagement needs to be re-evaluated
in reaching conclusions on the audit engagement.
■ This threat is also likely to be greater for Huggins and Gray where Fox & Steeple is providing other (non-audit) services.
■ A self-review threat may be created by Fox & Steeple providing Huggins with a ‘thorough examination’ of its computerised
systems if it involves an extension of the procedures required to conduct an audit in accordance with International
Standards on Auditing (ISAs).
■ Appropriate safeguards must be put in place if Fox & Steeple assists Huggins in the performance of internal audit
activities. In particular, Fox & Steeple’s personnel must not act (or appear to act) in a capacity equivalent to a member
of Huggins’ management (e.g. reporting, in a management role, to those charged with governance).
■ Fox & Steeple may provide Gray with accounting and bookkeeping services, as Gray is not a listed entity, provided that
any self-review threat created is reduced to an acceptable level. In particular, in giving technical advice on financial
reporting, Fox & Steeple must take care not to make managerial decisions such as determining or changing journal
entries without obtaining Gray’s approval.
■ Taxation services comprise a broad range of services, including compliance, planning, provision of formal taxation
opinions and assistance in the resolution of tax disputes. Such assignments are generally not seen to create threats to
independence.
Tutorial note: It is assumed that the provision of tax services is permitted in the jurisdiction (i.e. that Fox and Steeple
are not providing such services if prohibited).
■ The due diligence reviews for Gray may create a self-review threat (e.g. on the fair valuation of net assets acquired).
However, safeguards may be available to reduce these threats to an acceptable level.
■ If staff involved in providing other services are also assigned to the audit, their work should be reviewed by more senior
staff not involved in the provision of the other services (to the extent that the other service is relevant to the audit).
■ The reporting lines of any staff involved in the audit of Huggins and the provision of other services for Huggins should
be different. (Similarly for Gray.)
Familiarity
Tutorial note: This arises when, by virtue of a close relationship with an audit client (or its management or employees) an
audit firm (or a member of the audit team) becomes too sympathetic to the client’s interests.
■ Long association of a senior member of an audit team with an audit client may create a familiarity threat. This threat
is likely to be greatest for Huggins, a long-standing client. It may also be significant for Gray as Fox & Steeple have had
dealings with this client for seven years now.
■ As Blythe is a new audit client this particular threat does not appear to be relevant.
■ Senior personnel should be rotated off the Huggins and Gray audit teams. If this is not possible (for either client), an
additional professional accountant who was not a member of the audit team should be required to independently review
the work done by the senior personnel.
■ The familiarity threat of using the same lead engagement partner on an audit over a prolonged period is particularly
relevant to Huggins, which is now a listed entity. IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’ requires that the
lead engagement partner should be rotated after a pre-defined period, normally no more than seven years. Although it
might be time for the lead engagement partner of Huggins to be changed, the current lead engagement partner may
continue to serve for the 2006 audit.
Tutorial note: Two additional years are permitted when an existing client becomes listed, since it may not be in the
client’s best interests to have an immediate rotation of engagement partner.
Intimidation
Tutorial note: This arises when a member of the audit team may be deterred from acting objectively and exercising
professional skepticism by threat (actual or perceived), from the audit client.
■ This threat is most likely to come from Blythe as auditors are threatened with a tendering process to keep fees down.
■ Peter may have already applied pressure to reduce inappropriately the extent of audit work performed in order to reduce
fees, by stipulating that there should not be an interim audit.
■ The audit senior allocated to Blythe will need to be experienced in standing up to client management personnel such as
Peter.
Tutorial note: ‘Correct’ classification under ‘ethical’, ‘other professional’, ‘practical’ or ‘staff implications’ is not as important
as identifying the matters.
(ii) Other professional and practical matters
Tutorial note: ‘Other professional’ includes quality control.
■ The experience of staff allocated to each assignment should be commensurate with the assessment of associated risk.
For example, there may be a risk that insufficient audit evidence is obtained within the budget for the audit of Blythe.
Huggins, as a listed client, carries a high reputational risk.
■ Sufficient appropriate staff should be allocated to each audit to ensure adequate quality control (in particular in the
direction, supervision, review of each assignment). It may be appropriate for a second partner to be assigned to carry
out a ‘hot review’ (before the auditor’s report is signed) of:
– Blythe, because it is the first audit of a new client; and
– Huggins, as it is listed.
■ Existing clients (Huggins and Gray) may already have some expectation regarding who should be assigned to their
audits. There is no reason why there should not be some continuity of staff providing appropriate safeguards are put in
place (e.g. to overcome any familiarity threat).
■ Senior staff assigned to Blythe should be alerted to the need to exercise a high degree of professional skepticism (in the
light of Peter’s attitude towards the audit).
■ New staff assigned to Huggins and Gray would perhaps be less likely to assume unquestioned honesty than staff
previously involved with these audits.
Logistics (practical)
■ All three assignments have the same financial year end, therefore there will be an element of ‘competition’ for the staff
to be assigned to the year-end visits and final audit assignments. As a listed company, Huggins is likely to have the
tightest reporting deadline and so have a ‘priority’ for staff.
■ Blythe is a local and private company. Staff involved in the year-end visit (e.g. to attend the physical inventory count)
should also be involved in the final audit. As this is a new client, staff assigned to this audit should get involved at every
stage to increase their knowledge and understanding of the business.
■ Huggins is a national operation and may require numerous staff to attend year-end procedures. It would not be expected
that all staff assigned to year-end visits should all be involved in the final audit.
Time/fee/staff budgets
■ Time budgets will need to be prepared for each assignment to determine manpower requirements (and to schedule audit
work).
(iii) Implications for allocating staff
■ Fox & Steeple should allocate staff so that those providing other services to Huggins and Gray (that may create a selfreview
threat) do not participate in the audit engagement.
Competence and due care (Qualifications/Specialisation)
■ All audit assignments will require competent staff.
■ Huggins will require staff with an in-depth knowledge of their computerised system.
■ Gray will require senior audit staff to be experienced in financial reporting matters specific to communications and
software solutions (e.g. in revenue recognition issues and accounting for internally-generated intangible assets).
■ Specialists providing tax services and undertaking the due diligence reviews for Gray may not be required to have any
involvement in the audit assignment.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-14
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-03-09
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-03-13
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-03-13
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-08-08
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-05-03
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-01
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-02
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-08-05
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-03-04
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-13