你知道大学生报考ACCA在什么情况下不需要提供成绩单吗?
发布时间:2020-01-10
最近好多小伙伴都在问51题库考试学习网2020年3月ACCA考试时间安排和考试成绩查询的问题,今天51题库考试学习网就为各位小伙伴说说吧!
ACCA学员一般情况下是需要提供成绩单的,请准备好您的以下证件待上传,所有上传文件为彩色扫描件或者照片格式。
提醒:符合下列情形之一者,可以不提供成绩单
(1)会计学、国际会计、注册会计师专业学士学位。
(2)非相关专业。如英语专业,机械工程专业等。
(3)不要牛津·布鲁克斯大学的应用会计的(荣誉)理学士学位,同时具有注册会计师的全科合格证。
(4)要学位,毕业证书是10年前的。
(5)放弃免试。
(6)国内MBA
如果已经获得了免考的资格,则只需要把成绩单向ACCA官方提交就可以,一般是需要扫描在网上提交,或者是直接邮寄。
ACCA对有志参加ACCA专业资格考试的中国学员将执行以下免试政策,详情如下:
一、注册报名资格 免试情况
教育部认可高校毕业生。
会计学 – 获得学士学位 免试5门课程(F1-F5)。
会计学 – 辅修专业 免试3门课程(F1-F3)。
金融专业 免试5门课程(F1-F5)。
法律专业 免试1门课程(F4)。
商务及管理专业 免试1门课程(F1)。
MPAcc专业(获得MPAcc学位或完成MPAcc大纲规定的所有课程、只有论文待完成) 原则上免试九门课程(F1–F9),其中F6(税务)的免试条件:CICPA全科通过或MPAcc课程中选修了“中国税制”课程。。
MBA学位 – 获得MBA学位 免试3门课程(F1-F3)。
非相关专业 无免试。
二、教育部认可高校在校生。
会计学-完成第一学年课程 可以注册为ACCA正式学员,无免试。
会计学-完成第二学年课程 免试3门课程(F1-F3)。
会计学-完成第三学年课程 免试3门课程( F1-F3)。
其他专业 -在校生,无免试。
中国注册会计师资格。
CICPA全科通过 免试5门课程(F1-F4和F6)
以上就是51题库考试学习网为大家带来的相关内容,希望能给各位小伙伴带来帮助。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Illustrate EACH of the six problems chosen in (a) using the data from the Bettamould division/TRG scenario;
and (6 marks)
(b) An illustration of each of the problems using the data from the Battamould division/TRG scenario is as follows:
Meeting only the lowest targets
– In the scenario, the budgeted variable cost of $200 per tonne has been agreed. There is no specific incentive for the
Bettamould division to try to achieve a better level of performance.
Using more resources than necessary
– In the scenario, the current budget allows for 5% machine idle time. There is evidence that a move to outsourcing
machine maintenance from a specialist company could help reduce idle time levels and permit annual output in excess
of 100,000 tonnes.
Making the bonus – whatever it takes
– At present, the only sanction/incentive is to achieve 100,000 tonnes of output. There is no mention of any sanction for
example, if processing losses (and hence costs) rise to 20% of material inputs.
Competing against other divisions, business units and departments
– At present, the Bettamould division sources its materials from chosen suppliers who have been used for some years.
There is evidence that materials of equal specification could be sourced for 40% of the annual requirement from another
TRG division which has spare capacity. Why has this not been investigated?
Ensuring that what is in the budget is spent
– In the Bettamould scenario, there is a fixed cost budget allowance of $50,000,000. We are told in the question that
salaries of all employees and management are paid on a fixed salary basis. Bettamould’s management will not want a
reduction in the fixed budget allowance, since this could lead to the need to reduce the number of employees, which
they may see as having a detrimental effect on the ability of the division to meet its annual budget output target of
100,000 tonnes.
Providing inaccurate forecasts
– In the scenario there may have been deliberate efforts to increase the agreed budget level of aspects of measures and
costs. For example, by putting forward the argument that the budget requirement of 15% processing losses is acceptable
because of the likelihood that ageing machinery will be less effective in the coming budget period.
Meeting the target but not beating it
– In the scenario the bonus of 5% of salary is payable as long as the 100,000 tonnes of output is achieved. This does
not require that actual results will show any other aspects of the budget being improved upon. For example there is no
need to consider a reduction in the current level of quality checks (25% of daily throughput) to the 10% level that current
evidence suggests is achieved by competitor companies. The current budget agreement allows the Bettamould division
to transfer its output to market based profit centres at $200 + $500 = $700 per tonne. There is no specified penalty
if costs exceed this target level.
Avoiding risks
– Bettamould has not yet incorporated the changes listed in note 4 in the question. For example why has the sourcing of
40% of required materials from another TRC division not been quantified and evaluated. It is possible that the division
with spare capacity could supply the material at cost (possibly based on marginal cost) which would be less than
currently paid to a supplier external to TRC. It may be that Bettamould have not pursued this possibility because of risk
factors relating to the quality of the material transferred or its continued availability where the supplying division had an
upturn in the level of more profitable external business.
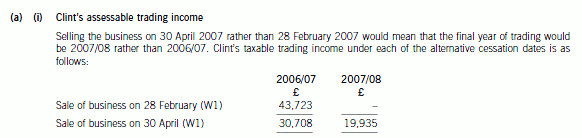
3 The Stiletto Partnership consisted of three partners, Clint, Ben and Amy, who shared the profits of the business
equally. On 28 February 2007 the partners sold the business to Razor Ltd, in exchange for shares in Razor Ltd, with
each former partner owning one third of the new company.
The recent, tax adjusted, trading profits of the Stiletto Partnership have been as follows:
£
Year ended 30 June 2006 92,124
1 July 2006 to 28 February 2007 81,795
Clint, who was 65 on 5 October 2006, retired when the business was sold to Razor Ltd. He is now suggesting that
if the sale of the partnership, and his retirement, had been delayed until 30 April 2007, his total tax liability would
have been reduced. Clint’s only other income is gross pension income of £6,100 per year, which he began receiving
in the tax year 2005/06. Clint did not receive any salary or dividends from Razor Ltd. It is estimated that the
partnership’s tax adjusted trading profits for the period from 1 March 2007 to 30 April 2007 would have been
£20,760. Clint has overlap profits of £14,250 brought forward from when the partnership began trading.
Razor Ltd manufactures industrial cutting tools. On 1 July 2007, Razor Ltd will subscribe for the whole of the ordinary
share capital of Cutlass Inc, a company newly incorporated in the country of Sharpenia. It is intended that Cutlass
Inc will purchase partly finished tools from Razor Ltd and customise them in Sharpenia. It is anticipated that Cutlass
Inc’s annual profits chargeable to corporation tax will be approximately £120,000.
Ben and Amy will be the directors of Cutlass Inc, although Ben will not be involved in the company’s business on a
day-to-day basis. Amy intends to spend one or two weeks each month in the country of Sharpenia looking after the
company’s affairs. The remainder of her time will be spent in the UK. Amy has employment contracts with both Razor
Ltd and Cutlass Inc and her duties for Cutlass Inc will be carried out wholly in Sharpenia. Cutlass Inc will pay for
Amy’s flights to and from Sharpenia and for her husband and baby to visit her there twice a year. Amy is currently
UK resident and ordinarily resident.
The system of income tax and corporation tax in the country of Sharpenia is broadly similar to that in the UK although
the rate of corporation tax is 38% regardless of the level of profits. There is a double tax treaty between the UK and
Sharpenia based on the OECD model treaty. The clause in the treaty dealing with company residency states that a
company resident in both countries under domestic law will be regarded under the treaty as being resident only in the
country where it is effectively managed and controlled. Sharpenia is not a member of the European Union.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate Clint’s taxable trading profits for the tax years 2006/07 and 2007/08 for both of the
alternative retirement dates (28 February 2007 and 30 April 2007). (3 marks)
(ii) equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue; and (4 marks)
(ii) Equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue
Tutorial note: In the context of GVF, the principal issue to be addressed is whether or not the impairment loss previously
recognised should be reversed (by considering the determination of value in use). Marks will also be awarded for
consideration of depreciation, additions etc made specific to this equipment.
■ Agree cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses at the beginning of the year to prior year working
papers (and/or last year’s published financial statements).
■ Recalculate the current year depreciation charge based on the carrying amount (as reduced by the impairment
loss).
■ Calculate the carrying amount of the equipment as at 30 September 2005 without deduction of the impairment
loss.
Tutorial note: The equipment cannot be written back up to above this amount (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ Agree management’s schedule of future cash flows estimated to be attributable to the equipment for a period of up
to five years (unless a longer period can be justified) to approved budgets and forecasts.
■ Recalculate:
– on a sample basis, the make up of the cash flows included in the forecast;
– GVF’s weighted average cost of capital.
■ Review production records and sales orders for the year, as compared with the prior period, to confirm a ‘steady
increase’.
■ Compare sales volume at 30 September 2005 with the pre-‘scare’ level to assess how much of the previously
recognised impairment loss it would be prudent to write back (if any).
■ Scrutinize sales orders in the post balance sheet event period. Sales of such produce can be very volatile and
another ‘incident’ could have sales plummeting again – in which case the impairment loss should not be reversed.
4 (a) ISA 701 Modifications to The Independent Auditor’s Report includes ‘suggested wording of modifying phrases
for use when issuing modified reports’.
Required:
Explain and distinguish between each of the following terms:
(i) ‘qualified opinion’;
(ii) ‘disclaimer of opinion’;
(iii) ‘emphasis of matter paragraph’. (6 marks)
4 PETRIE CO
(a) Independent auditor’s report terms
(i) Qualified opinion – A qualified opinion is expressed when the auditor concludes that an unqualified opinion cannot be
expressed but that the effect of any disagreement with management, or limitation on scope is not so material and
pervasive as to require an adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion.
(ii) Disclaimer of opinion – A disclaimer of opinion is expressed when the possible effect of a limitation on scope is so
material and pervasive that the auditor has not been able to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence and accordingly
is unable to express an opinion on the financial statements.
(iii) Emphasis of matter paragraph – An auditor’s report may be modified by adding an emphasis of matter paragraph to
highlight a matter affecting the financial statements that is included in a note to the financial statements that more
extensively discusses the matter. Such an emphasis of matter paragraph does not affect the auditor’s opinion. An
emphasis of matter paragraph may also be used to report matters other than those affecting the financial statements
(e.g. if there is a misstatement of fact in other information included in documents containing audited financial
statements).
(iii) is clearly distinguishable from (i) and (ii) because (i) and (ii) affect the opinion paragraph, whereas (iii) does not.
(i) and (ii) are distinguishable by the degree of their impact on the financial statements. In (i) the effects of any disagreement
or limitation on scope can be identified with an ‘except for …’ opinion. In (ii) the matter is pervasive, that is, affecting the
financial statements as a whole.
(ii) can only arise in respect of a limitation in scope (i.e. insufficient evidence) that has a pervasive effect. (i) is not pervasive
and may also arise from disagreement (i.e. where there is sufficient evidence).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-12
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-03-28
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-21
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-04-17
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-05-20