了解一下:ACCA免考申请流程和相关注意事项
发布时间:2020-09-04
各位小伙伴请注意了!大家知道ACCA考试吗?大家知道ACCA免考的相关政策吗?为了帮助大家了解更多,51题库考试学习网为大家带来了ACCA考试的免考申请流程以及相关注意事项,让我们一起来看看吧!
ACCA免考申请流程:
已注册成功的学员,在获得相关可申请免考的证书(例如会计学位、CPA证书)后可向ACCA申请追加免考:
1、将证书的原件和翻译件以电子版形式发送至 students@accaglobal.com
2、请注意查收邮件或登录MYACCA学员账户查看免试信息。
3、免考申请成功后,结果会显示接下来的一个考季,例如学员在4月份免试申请成功获得F1-3,那么该免试结果显示的时间是6月份。
关于ACCA免考政策相关注意事项,详情如下:
1、申请牛津布鲁克斯大学的学士学位,不再需要英语资格证明
2、学员只有顺利通过整学年的课程才能够申请免考。
3、针对在校生的部分课程免考政策只适用于大学本科的在读学生,而不适用于硕士学位或大专学历的在读学生。
4、获得硕士学位和大专文凭的学生的免试课程只能按所学课程的相关性由ACCA免考评估部门进行逐门评估而定。
5、在中国,会计学学士学位是指会计学士、会计学学士、会计与金融学士或经济学学士(专业方向为会计学,会计与金融,国际会计,注册会计师)。
6、取得与会计学相关领域专业的学位都按“其他专业”对待,例如财务会计、工业会计、外贸会计、会计电算化、铁路会计等。
7、在大学第一学年所学过的课程不能作为申请免考的依据。
8、特许学位(即海外大学与中国本地大学合作而授予海外大学学位的项目),部分完成时不能申请免考。
9、本政策适用于在中国教育部认可的高等院校全部完成或部分完成本科课程的学生,而不考虑目前居住地点。
10、欲申请牛津·布鲁克斯大学学士学位的学员在取得本科学位之前,不能申请F7-F9课程的免考。
11、学员以国外大学学位申请免考,请直接到ACCA官方网站查询可免课程,一般不需要再提供国内的学历证明。
以上就是今天分享的全部内容了,各位小伙伴根据自己的情况进行查阅,希望本文对各位有所帮助,预祝各位取得满意的成绩,如需了解更多相关内容,请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
Assume that the rates and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this part.
(b) Explain the consequences of filing the VAT returns late and advise Fred how he should deal with the
underpayment and bad debt for VAT purposes. Your explanation should be supported by relevant
calculations. (10 marks)
(b) Late filing of VAT returns
The late filing of two or more VAT returns within the period of one year will give rise to a default surcharge. This occurs when
either
– The return is late and/or
– The payment is late.
Customs & Excise will serve a surcharge liability notice on the taxpayer when a single return is filed late and/or the VAT due
is paid late. The surcharge period will run from the date of notice to the anniversary of the quarter end of the period in which
the trader is in default.
Any further defaults within the surcharge period will extend the surcharge period.
If there is a late payment of VAT in the surcharge period, a surcharge will be levied at the rate of 2% on the first occasion,
rising progressively to a maximum of 15% if there are several defaults. One complete year of correct compliance is necessary
to escape the default surcharge regime.
For Flop Ltd, the surcharge period originally ran to 31 December 2005 but was extended to 31 March 2006 as the second
return is late. This could be extended again if the June return is late. The second default (31 March return) will give rise to
a 2% surcharge, based on the tax paid late of £24,000. This gives a surcharge of £480. This exceeds the de minimus level
of £400, so will be collected.
To avoid a further surcharge, the VAT return to 30 June 2005 should be submitted by 31 July at the latest. This would save
5% x £8,250 = £412.
In addition, Flop Ltd should obtain a refund of the VAT on the bad debt. Relief is available where;
(i) the debt is more than six months old, and
(ii) the debt has been written off in the creditor’s accounts.
The claim must be made within three years. The amount of VAT repayable is 17·5% of £50,000 = £8,750. If this is claimed
though the VAT return to 30 June 2005, there should be a net VAT repayment of (£8,250 - £8,750) = £500. Even if this
return is submitted late, the fact that no VAT is outstanding means that there will be no surcharge actually payable (as
calculated above), but the surcharge period will nevertheless be extended.
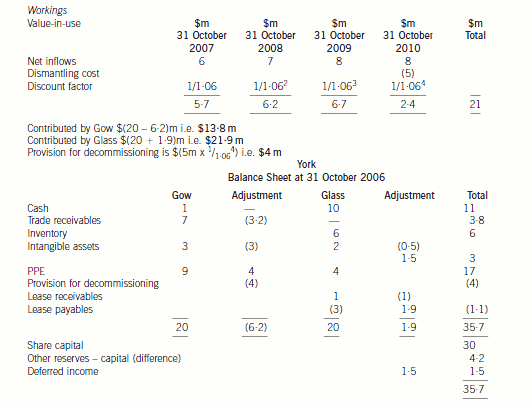
(b) Prepare the balance sheet of York at 31 October 2006, using International Financial Reporting Standards,
discussing the nature of the accounting treatments selected, the adjustments made and the values placed
on the items in the balance sheet. (20 marks)

Gow’s net assets
IAS36 ‘Impairment of Assets’, sets out the events that might indicate that an asset is impaired. These circumstances include
external events such as the decline in the market value of an asset and internal events such as a reduction in the cash flows
to be generated from an asset or cash generating unit. The loss of the only customer of a cash generating unit (power station)
would be an indication of the possible impairment of the cash generating unit. Therefore, the power station will have to be
impairment tested.
The recoverable amount will have to be determined and compared to the value given to the asset on the setting up of the
joint venture. The recoverable amount is the higher of the cash generating unit’s fair value less costs to sell, and its value-inuse.
The fair value less costs to sell will be $15 million which is the offer for the purchase of the power station ($16 million)
less the costs to sell ($1 million). The value-in-use is the discounted value of the future cash flows expected to arise from the
cash generating unit. The future dismantling costs should be provided for as it has been agreed with the government that it
will be dismantled. The cost should be included in the future cash flows for the purpose of calculating value-in-use and
provided for in the financial statements and the cost added to the property, plant and equipment ($4 million ($5m/1·064)).
The value-in-use based on a discount rate of 6 per cent is $21 million (working). Therefore, the recoverable amount is
$21 million which is higher than the carrying value of the cash generating unit ($20 million) and, therefore, the value of the
cash generating unit is not impaired when compared to the present carrying value of $20 million (value before impairment
test).
Additionally IAS39, ‘Financial Instruments: recognition and measurement’, says that an entity must assess at each balance
sheet date whether a financial asset is impaired. In this case the receivable of $7 million is likely to be impaired as Race is
going into administration. The present value of the estimated future cash flows will be calculated. Normally cash receipts from
trade receivables will not be discounted but because the amounts are not likely to be received for a year then the anticipated
cash payment is 80% of ($5 million × 1/1·06), i.e. $3·8 million. Thus a provision for the impairment of the trade receivables
of $3·2 million should be made. The intangible asset of $3 million would be valueless as the contract has been terminated.
Glass’s Net Assets
The leased property continues to be accounted for as property, plant and equipment and the carrying amount will not be
adjusted. However, the remaining useful life of the property will be revised to reflect the shorter term. Thus the property will
be depreciated at $2 million per annum over the next two years. The change to the depreciation period is applied prospectively
not retrospectively. The lease liability must be assessed under IAS39 in order to determine whether it constitutes a
de-recognition of a financial liability. As the change is a modification of the lease and not an extinguishment, the lease liability
would not be derecognised. The lease liability will be adjusted for the one off payment of $1 million and re-measured to the
present value of the revised future cash flows. That is $0·6 million/1·07 + $0·6 million/(1·07 × 1·07) i.e. $1·1 million. The
adjustment to the lease liability would normally be recognised in profit or loss but in this case it will affect the net capital
contributed by Glass.
The termination cost of the contract cannot be treated as an intangible asset. It is similar to redundancy costs paid to terminate
a contract of employment. It represents compensation for the loss of future income for the agency. Therefore it must be
removed from the balance sheet of York. The recognition criteria for an intangible asset require that there should be probable
future economic benefits flowing to York and the cost can be measured reliably. The latter criterion is met but the first criterion
is not. The cost of gaining future customers is not linked to this compensation.
IAS18 ‘Revenue’ contains a concept of a ‘multiple element’ arrangement. This is a contract which contains two or more
elements which are in substance separate and are separately identifiable. In other words, the two elements can operate
independently from each other. In this case, the contract with the overseas company has two distinct elements. There is a
contract not to supply gas to any other customer in the country and there is a contract to sell gas at fair value to the overseas
company. The contract has not been fulfilled as yet and therefore the payment of $1·5 million should not be taken to profit
or loss in its entirety at the first opportunity. The non supply of gas to customers in that country occurs over the four year
period of the contract and therefore the payment should be recognised over that period. Therefore the amount should be
shown as deferred income and not as a deduction from intangible assets. The revenue on the sale of gas will be recognised
as normal according to IAS18.
There may be an issue over the value of the net assets being contributed. The net assets contributed by Glass amount to
$21·9 million whereas those contributed by Gow only total $13·8 million after taking into account any adjustments required
by IFRS. The joint venturers have equal shareholding in York but no formal written agreements, thus problems may arise ifGlass feels that the contributions to the joint venture are unequal.
(iii) The effect of the restructuring on the group’s ability to recover directly and non-directly attributable input
tax. (6 marks)
You are required to prepare calculations in respect of part (ii) only of this part of this question.
Note: – You should assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year 2006 apply
throughout this question.
(iii) The effect of the restructuring on the group’s ability to recover its input tax
Prior to the restructuring
Rapier Ltd and Switch Ltd make wholly standard rated supplies and are in a position to recover all of their input tax
other than that which is specifically blocked. Dirk Ltd and Flick Ltd are unable to register for VAT as they do not make
taxable supplies. Accordingly, they cannot recover any of their input tax.
Following the restructuring
Rapier Ltd will be carrying on four separate trades, two of which involve the making of exempt supplies such that it will
be a partially exempt trader. Its recoverable input tax will be calculated as follows.
– Input tax in respect of inputs wholly attributable to taxable supplies is recoverable.
– Input tax in respect of inputs wholly attributable to exempt supplies cannot be recovered (subject to the de minimis
limits below).
– A proportion of the company’s residual input tax, i.e. input tax in respect of inputs which cannot be directly
attributed to particular supplies, is recoverable. The proportion is taxable supplies (VAT exclusive) divided by total
supplies (VAT exclusive). This proportion is rounded up to the nearest whole percentage where total residual input
tax is no more than £400,000 per quarter.
The balance of the residual input tax cannot be recovered (subject to the de minimis limits below).
– If the de minimis limits are satisfied, Rapier Ltd will be able to recover all of its input tax (other than that which is
specifically blocked) including that which relates to exempt supplies. The de minimis limits are satisfied where the
irrecoverable input tax:
– is less than or equal to £625 per month on average; and
– is less than or equal to 50% of total input tax.
The impact of the restructuring on the group’s ability to recover its input tax will depend on the level of supplies made
by the different businesses and the amounts of input tax involved. The restructuring could result in the group being able
to recover all of its input tax (if the de minimis limits are satisfied). Alternatively the amount of irrecoverable input tax
may be more or less than the amounts which cannot be recovered by Dirk Ltd and Flick Ltd under the existing group
structure.

2 Your audit client, Prescott Co, is a national hotel group with substantial cash resources. Its accounting functions are
well managed and the group accounting policies are rigorously applied. The company’s financial year end is
31 December.
Prescott has been seeking to acquire a construction company for some time in order to bring in-house the building
and refurbishment of hotels and related leisure facilities (e.g. swimming pools, squash courts and restaurants).
Prescott’s management has recently identified Robson Construction Co as a potential target and has urgently requested
that you undertake a limited due diligence review lasting two days next week.
Further to their preliminary talks with Robson’s management, Prescott has provided you with the following brief on
Robson Construction Co:
The chief executive, managing director and finance director are all family members and major shareholders. The
company name has an established reputation for quality constructions.
Due to a recession in the building trade the company has been operating at its overdraft limit for the last 18
months and has been close to breaching debt covenants on several occasions.
Robson’s accounting policies are generally less prudent than those of Prescott (e.g. assets are depreciated over
longer estimated useful lives).
Contract revenue is recognised on the percentage of completion method, measured by reference to costs incurred
to date. Provisions are made for loss-making contracts.
The company’s management team includes a qualified and experienced quantity surveyor. His main
responsibilities include:
(1) supervising quarterly physical counts at major construction sites;
(2) comparing costs to date against quarterly rolling budgets; and
(3) determining profits and losses by contract at each financial year end.
Although much of the labour is provided under subcontracts all construction work is supervised by full-time site
managers.
In August 2005, Robson received a claim that a site on which it built a housing development in 2002 was not
properly drained and is now subsiding. Residents are demanding rectification and claiming damages. Robson
has referred the matter to its lawyers and denied all liability, as the site preparation was subcontracted to Sarwar
Services Co. No provisions have been made in respect of the claims, nor has any disclosure been made.
The auditor’s report on Robson’s financial statements for the year to 30 June 2005 was signed, without
modification, in March 2006.
Required:
(a) Identify and explain the specific matters to be clarified in the terms of engagement for this due diligence
review of Robson Construction Co. (6 marks)
2 PRESCOTT CO
(a) Terms of engagement – matters to be clarified
Tutorial note: This one-off assignment requires a separate letter of engagement. Note that, at this level, a standard list of
contents will earn few, if any, marks. Any ‘ideas list’ must be tailored to generate answer points specific to the due diligence
review of this target company.
■ Objective of the review: for example, to find and report facts relevant to Prescott’s decision whether to acquire Robson.
The terms should confirm whether Prescott’s interest is in acquiring the company (i.e. the share capital) or its trading
assets (say), as this will affect the nature and scope of the review.
Tutorial note: This is implied as Prescott ‘has been seeking to acquire ... to bring building … in-house’.
■ Prescott’s management will be solely responsible for any decision made (e.g. any offer price made to purchase Robson).
■ The nature and scope of the review and any standards/guidelines in accordance with which it will be conducted. That
investigation will consist of enquiry (e.g. of the directors and the quantity surveyor) and analytical procedures (e.g. on
budgeted information and prior period financial statements).
Tutorial note: This is not going to be a review of financial statements. The prior year financial statements have only
recently been audited and financial statements for the year end 30 June 2006 will not be available in time for the
review.
■ The level of assurance will be ‘negative’. That is, that the material subject to review is free of material misstatement. It
should be stated that an audit is not being performed and that an audit opinion will not be expressed.
■ The timeframe. for conducting the investigation (two days next week) and the deadline for reporting the findings.
■ The records, documentation and other information to which access will be unrestricted. This will be the subject of
agreement between Prescott and Robson.
■ A responsibility/liability disclaimer that the engagement cannot be relied upon to disclose errors, illegal acts or other
irregularities (e.g. fraudulent financial reporting or misappropriations of Robson’s assets).
Tutorial note: Third party reliance on the report seems unlikely as Prescott has ‘substantial cash resources’ and may not
need to obtain loan finance.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-02-04
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-07
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-05-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-04
- 2020-03-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-05-14
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-05-03
- 2020-02-19