四川省考生注意:在ACCA考试中提前交卷后果怎么样?不堪设想……
发布时间:2020-01-09
近期,有不少第一次备考ACCA考试的小伙伴来咨询51题库考试学习网,问:考试能不能提前交卷呢?在这里告诉大家,根据考试的相关规定是不允许的。什么?还有些小伙伴不知道考试时应当注意些什么?没关系,现在了解还来得及,51题库考试学习网这就将相关注意事项告诉大家:
ACCA考试之前注意事项:
1.考生必须准时到场考试,一旦迟到,考试时间不会延长。因此,再次强调考生必须时刻关注考试时间,以防迟到。
2.三小时答题时间及15分钟的读题时间以准考证时间为准。阅读过程中,考生可以浏览试题册,但是不能打开并书写答题册。如果违法相关规定,有可能会取消考试资格
3.需要注意的还有,考试开始一小时后,考生不允许再进入考场。
4.直到考试结束,考生才允许离开考场。
5.如果考生要求短时间离开考场,必须有监考人员陪同。
6.不得私自携带手机等电子工具,考生必须将书包和公文包放置监考人员规定处。
7.对于笔考的科目,考生只能用黑色圆珠笔作答。
8.考生必须确认自己参加的考试的代号与准考证上的考试科目代号一致。
ACCA考试时的注意事项有哪些?
1.在新版的考生答题册上(candidate answer booklet)的第一页仔细填涂以下项目
1)考试的科目和版本(注:如P2,应填INT;F4填写ENG;F6填写UK等)
2)考场代码(包括Hall code)考场名字和座位号
3)以上信息均在你个人的准考证(Exam Attendance Docket)上有显示;
2.在新的一页上开始每答一道新题,要在这页上部填涂题号;
3.所有答题均使用黑色圆珠笔作答,(铅笔,黑色签字笔,荧光笔等不允许);
4.答错可划掉错误的答案,不允许使用涂改液;51题库考试学习网建议考生在不确定答案的时候最好不要填写,卷面也是影响得分的一大因素
5.不能将答案写在答题纸边缘及答题本两页的中间位置,否则将视为无效作答;
学生如需要,可索要第二本答题本,第二本答题本上同样必须填写完整个人信息。
当然,对于笔考,机考的确是有些差别的。这主要体现在:
1、大题部分需要通过计算机进行解答,相较于笔试,计算机打字能力和某些公式的熟练度会间接地影响考试结果;
2、考试时间有所不同。目前,应用技能课程的机考时间均为3个小时,而战略课程的笔试一般为3小时15分钟,SBL为4个小时。因此,考试在考试之前需要提前了解是机考还是笔考,以免出现战略层面上的失误。
以上ACCA考试的注意事项大家要提高警觉哦,遇到了上文提到以外突发事故及时向监考老师提出来,听从监考老师的安排即可,不要因为突发事件而影响了自己的考试心态从而影响到成绩。调整好心态,重新积极考试!~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(d) Explain whether or not Dovedale Ltd, Hira Ltd and Atapo Inc can register as a group for the purposes of value
added tax. (3 marks)
(d) Dovedale Ltd and Hira Ltd can register as a group for the purposes of value added tax (VAT) because Dovedale Ltd controls
Hira Ltd and both companies are established in the UK in that their head offices are in the UK.
Dovedale Ltd will also control Atapo Inc. However, Atapo Inc cannot be part of a group registration unless it is established
in the UK or has a fixed establishment in the UK. It will be regarded as established in the UK if it is centrally managed and
controlled in the UK or if its head office is in the UK. A fixed establishment is a place where the company has staff and
equipment and where its business is carried on.
2 Clifford and Amanda, currently aged 54 and 45 respectively, were married on 1 February 1998. Clifford is a higher
rate taxpayer who has realised taxable capital gains in 2007/08 in excess of his capital gains tax annual exemption.
Clifford moved into Amanda’s house in London on the day they were married. Clifford’s own house in Oxford, where
he had lived since acquiring it for £129,400 on 1 August 1996, has been empty since that date although he and
Amanda have used it when visiting friends. Clifford has been offered £284,950 for the Oxford house and has decided
that it is time to sell it. The house has a large garden such that Clifford is also considering an offer for the house and
a part only of the garden. He would then sell the remainder of the garden at a later date as a building plot. His total
sales proceeds will be higher if he sells the property in this way.
Amanda received the following income from quoted investments in 2006/07:
£
Dividends in respect of quoted trading company shares 1,395
Dividends paid by a Real Estate Investment Trust out of tax exempt property income 485
On 1 May 2006, Amanda was granted a 22 year lease of a commercial investment property. She paid the landlord
a premium of £6,900 and also pays rent of £2,100 per month. On 1 June 2006 Amanda granted a nine year
sub-lease of the property. She received a premium of £14,700 and receives rent of £2,100 per month.
On 1 September 2006 Amanda gave quoted shares with a value of £2,200 to a registered charity. She paid broker’s
fees of £115 in respect of the gift.
Amanda began working for Shearer plc, a quoted company, on 1 June 2006 having had a two year break from her
career. She earns an annual salary of £38,600 and was paid a bonus of £5,750 in August 2006 for agreeing to
come and work for the company. On 1 August 2006 Amanda was provided with a fully expensed company car,
including the provision of private petrol, which had a list price when new of £23,400 and a CO2 emissions rate of
187 grams per kilometre. Amanda is required to pay Shearer plc £22 per month in respect of the private use of the
car. In June and July 2006 Amanda used her own car whilst on company business. She drove 720 business miles
during this two month period and was paid 34 pence per mile. Amanda had PAYE of £6,785 deducted from her gross
salary in the tax year 2006/07.
After working for Shearer plc for a full year, Amanda becomes entitled to the following additional benefits:
– The opportunity to purchase a large number of shares in Shearer plc on 1 July 2007 for £3·30 per share. It is
anticipated that the share price on that day will be at least £7·50 per share. The company will make an interestfree
loan to Amanda equal to the cost of the shares to be repaid in two years.
– Exclusive free use of the company sailing boat for one week in August 2007. The sailing boat was purchased by
Shearer plc in January 2005 for use by its senior employees and costs the company £1,400 a week in respect
of its crew and other running expenses.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate Clifford’s capital gains tax liability for the tax year 2007/08 on the assumption that the Oxford
house together with its entire garden is sold on 31 July 2007 for £284,950. Comment on the relevance
to your calculations of the size of the garden; (5 marks)
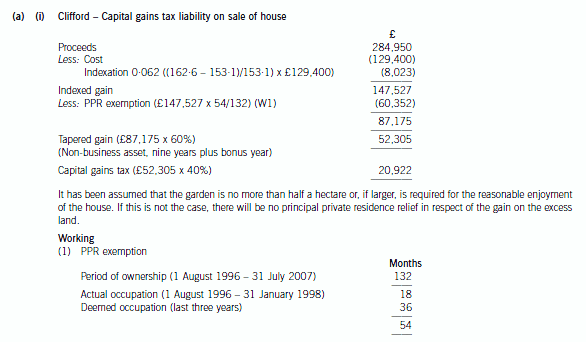
(b) State the immediate tax implications of the proposed gift of the share portfolio to Avril and identify an
alternative strategy that would achieve Crusoe’s objectives whilst avoiding a possible tax liability in the
future. State any deadline(s) in connection with your proposed strategy. (5 marks)
(b) Gift of the share portfolio to Avril
Inheritance tax
The gift would be a potentially exempt transfer at market value. No inheritance tax would be due at the time of the gift.
Capital gains tax
The gift would be a disposal by Crusoe deemed to be made at market value for the purposes of capital gains tax. No gain
would arise as the deemed proceeds will equal Crusoe’s base cost of probate value.
Stamp duty
There is no stamp duty on a gift of shares for no consideration.
Strategy to avoid a possible tax liability in the future
Crusoe should enter into a deed of variation directing the administrators to transfer the shares to Avril rather than to him. This
will not be regarded as a gift by Crusoe. Instead, provided the deed states that it is intended to be effective for inheritance tax
purposes, it will be as if Noland had left the shares to Avril in a will.
This strategy is more tax efficient than Crusoe gifting the shares to Avril as such a gift would be a potentially exempt transfer
and inheritance tax may be due if Crusoe were to die within seven years.
The deed of variation must be entered into by 1 October 2009, i.e. within two years of the date of Noland’s death.
(b) State the enquiries you would make of the directors of Mulligan Co to ascertain the adequacy of the
$3 million finance requested for the new production facility. (7 marks)
(b) It is important to appreciate that the finance request should cover not only the cost of the construction of the new facility, but
also costs in order to get the business unit up and running, and enough cash to meet initial working capital requirements.
Mulligan Co may have sufficient cash to cover such additional expenses, but the bank will want comfort that this is the case.
Enquiries would include the following:
Who has prepared the forecast? It is important to evaluate the experience and competence of the preparer. If management
has previously prepared forecasts and capital expenditure budgets that were reliable and accurate, this adds a measure of
confidence in the preparation of the new forecast and the underlying assumptions used.
To what extent is internal finance available to cover any shortfall in the finance requirement? If there is surplus cash within
the organisation then the bank need not provide the full amount of finance necessary to start up the new business operation.
Has the cost of finance been included in the forecast? It appears that this cost is missing. Finance costs should be calculated
based on the anticipated interest rate to be applied to the loan advanced, and included in the total finance requirement.
What is the forecast operating cycle of the new business unit? In particular how long is the work in progress period, and how
much credit will be extended to customers? i.e. when will cash inflows specific to the new business unit be received? More
finance might be required to fund initial working capital shortfalls during the period when work in progress is occurring, and
before cash receipts from customers are received.
Will further raw materials be required? A request has been made for $250,000 for raw materials of timber. Other materials
may need to be purchased, for example, non-timber raw materials, and inventory of other consumables such as nuts and
bolts.
How long will the ‘initial’ inventory of raw material last? What is the planned work in progress time for the new product? More
finance may be needed to avoid a stock out of raw materials.
Construction of the new factory – is there any documentation to support the capital expenditure? For example, architect’s
plans, surveyor’s reports. This will support the accuracy of the finance requested and is an important source of evidence given
the materiality of the premises to the total amount of finance requested.
How likely is it that costs may be subject to inflation before actually being incurred? This could increase the amount of finance
required by several percentage points.
Have quotes been obtained for the new machinery to be purchased?
Purchase of new machinery – will any specific installation costs be incurred? These costs can be significant for large pieces
of capital equipment. Also, enquiries should be made regarding any delivery costs.
The budget does not appear to contain any finance request for overheads such as use of electricity during the construction
period, and hire of installation equipment. Have these overheads been included in the construction cost estimate?
Will staff need to be trained in using the new machinery? If so, any incremental costs should be included in the finance
request.
Advertising and marketing of new product – enquire of Patrick Tiler the methods that will be used to market the new product.
Some types of advertising are more of a cash drain due to their high expense e.g. television advertising is expensive and ‘up
front’ compared to magazine advertising, which is cheap and spread out. As Patrick Tiler is new to Mulligan Co, his forecast
is not based on past experience of this particular business.
LCT Bank will also consider the recoverability of the amount advanced by looking at the cash generating potential of the new
business unit. Enquiries should therefore be made regarding the likely success of the new products, for example:
– Has any market research been carried out to support the commercial viability of the new products?
– Have any contracts with retailers to carry the new products been negotiated?
– How quickly have past products generated a cash inflow?
– Is there a contingency plan in place in case the new products fail to be successful?
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-11
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-06-24
- 2020-02-14
- 2020-02-04
- 2020-04-12
- 2020-04-18
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-04-20
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-01-09