2019ACCA这些免考福利政策你都清楚了吗?
发布时间:2019-07-19
据2019年ACCA官网信息了解到,2019-2020年部分财务相关专业大学在校或毕业学生,在参加ACCA考试注册时,将获得一定科目的免试权。ACCA对于参加专业会计师考试(ACCA)的中国学员的免试政策详情如下:
一、ACCA对中国教育部认可的全日制大学在读生(会计或金融专业)设置的免试政策
1. 会计学或金融学(完成第一学年课程):可以注册为ACCA正式学员,无免试
2. 会计学或金融学(完成第二学年课程):免试3门课程(F1-F3)
3. 会计学或金融学(完成第三学年课程):免试3门课程(F1-F3)
4. 其他专业(在校生完成大一后):可以注册但无免试
*大学在读考生准备时间相对充足,可以每次报考三门课程,不建议报考四门,科目可以以F5/F6/F7三门计算类科目为主,通过逐步的学习加强英文能力,然后再学习F4、F8、F9有文字写作要求的科目。
二、ACCA对中国教育部认可高校毕业生设置的免试政策
1. 会计学(获得学士学位):免试5门课程(F1-F5)
2. 会计学(辅修专业):免试3门课程(F1-F3)
3. 金融专业:免试5门课程(F1-F5)
4. 法律专业:免试1门课程(F4)
5. 商务及管理专业:免试1门课程(F1)
6. MPAcc专业(获得MPAcc学位或完成MPAcc大纲规定的所有课程、只有论文待完成):原则上免试九门课程(F1–F9),其中F6(税务)的免试条件:CICPA全科通过或MPAcc课程中选修了"中国税制"课程。
7. MBA学位(获得MBA学位):免试3门课程(F1-F3)
8. 非相关专业:无免试
高校毕业生(即:在职人士),可以每次报考两门课程,小编建议不要超过三门课程,科目可以F5/F6/F7三门计算类科目为主,通过逐步的学习加强英文能力,然后再学习F4、F8、F9有文字写作要求的科目。
三、注册会计师考生
1. 2009年CICPA"6+1"新制度实行之前获得CICPA全科通过的人员:免试5门课程(F1-F4和F6)
2. 2009年CICPA"6+1"新制度实行之后获得CICPA全科通过的人员:免试9们课程(F1-F9)
3. 如果在学习ACCA基础阶段科目的过程中获得了CICPA全科合格证(须2009年"6+1"制度实行后的新版证书),可以自行决定是否申请追加免试。
*通过注会考试的考生对于财务知识基础相对好,一般F7、F8、F9通过率比其他考生高很多,建议从这些科目入手,加强英语的阅读和写作能力,注会考试大纲与ACCA考试大纲类似,只其是在审计及财务管理类的科目上,基本上知识点是相通的。F7会计科目中国际会计准则会计处理上略有不同。
四、其他
1. CMA(美国注册管理会计师)全科通过并取得证书:免试F1-F5、F8、F9(共免7门)
2. USCPA(美国注册会计师)全科通过:免试F1-F6、F8、F9(共免8门)
五、注意事项
1.在校生只有顺利通过整学年的课程才能够申请免试。
2.针对在校生的部分课程免试政策只适用于会计学专业全日制大学本科的在读学生,而不适用于硕士学位或大专学历的在读学生。
3.已完成MPAcc学位大纲规定课程,还需完成论文的学员也可注册并申请免试。但须提交由学校出具的通过所有MPAcc学位大纲规定课程的成绩单,并附注"该学员已通过所有MPAcc学位大纲规定课程,论文待完成"的说明。
4.特许学位(即海外大学与中国本地大学合作而授予海外大学学位的项目)— 部分完成时不能申请免试。
5.政策适用于在中国教育部认可的高等院校全部完成或部分完成本科课程的学生,而不考虑目前居住地点。
6.欲申请牛津•布鲁克斯大学学士学位的学员需放弃F7-F9的免试。
综合以上就是关于2019ACCA免试政策的全部内容,希望对于正在备考的小伙伴么有帮助,小编将持续更新相关ACCA的相关资讯。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
2 Tyre, a public limited company, operates in the vehicle retailing sector. The company is currently preparing its financial
statements for the year ended 31 May 2006 and has asked for advice on how to deal with the following items:
(i) Tyre requires customers to pay a deposit of 20% of the purchase price when placing an order for a vehicle. If the
customer cancels the order, the deposit is not refundable and Tyre retains it. If the order cannot be fulfilled by
Tyre, the company repays the full amount of the deposit to the customer. The balance of the purchase price
becomes payable on the delivery of the vehicle when the title to the goods passes. Tyre proposes to recognise
the revenue from the deposits immediately and the balance of the purchase price when the goods are delivered
to the customer. The cost of sales for the vehicle is recognised when the balance of the purchase price is paid.
Additionally, Tyre had sold a fleet of cars to Hub and gave Hub a discount of 30% of the retail price on the
transaction. The discount given is normal for this type of transaction. Tyre has given Hub a buyback option which
entitles Hub to require Tyre to repurchase the vehicles after three years for 40% of the purchase price. The normal
economic life of the vehicles is five years and the buyback option is expected to be exercised. (8 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors of Tyre on how to treat the above items in the financial statements for the year ended
31 May 2006.
(The mark allocation is shown against each of the above items)
2 Advice on sundry accounting issues: year ended 31 May 2006
The following details the nature of the advice relevant to the accounting issues.
Revenue recognition
(i) Sale to customers
IAS18 ‘Revenue’ requires that revenue relating to the sale of goods is recognised when the significant risks and rewards are
transferred to the buyer. Also the company should not retain any continuing managerial involvement associated with
ownership or control of the goods. Additionally the revenue and costs must be capable of reliable measurement and it should
be probable that the economic benefits of the transaction will go to the company.
Although the deposit is non refundable on cancellation of the order by the customer, there is a valid expectation that the
deposit will be repaid where the company does not fulfil its contractual obligation in supplying the vehicle. The deposit should,
therefore, only be recognised in revenue when the vehicle has been delivered and accepted by the customer. It should be
treated as a liability up to this point. At this point also, the balance of the sale proceeds will be recognised. If the customer
does cancel the order, then the deposit would be recognised in revenue at the date of the cancellation of the order.
The appendix to IAS18, although not part of the standard, agrees that revenue is recognised when goods of this nature are
delivered to the buyer.
Sale of Fleet cars
The company has not transferred the significant risks and rewards of ownership as required by IAS18 as the buyback option
is expected to occur. The reason for this conclusion is that the company has retained the risk associated with the residual
value of the vehicles. Therefore, the transaction should not be treated as a sale. The vehicles should be treated as an operating
lease as essentially only 60% of the purchase price will be received by Tyre. Ownership of the assets are not expected to be
transferred to Hub, the lease term is arguably not for the major part of the assets’ life, and the present value of the minimum
lease payments will not be substantially equivalent to the fair value of the asset. Therefore it is an operating lease (IAS17).
No ‘outright sale profit’ will be recognised as the risks and rewards of ownership have been retained and no sale has occurred.
The vehicles will be shown in property, plant and equipment at their carrying amount. The lease income should be recognised
on a straight line basis over the lease term of three years unless some other basis is more representative. The vehicles will
be depreciated in accordance with IAS16, ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’. If there is any indication of impairment then the
company will apply IAS36 ‘Impairment of Assets’. As the discount given is normal for this type of transaction, it will not be
taken into account in estimating the fair value of the assets.
The buyback option will probably meet the definition of a financial liability and will be accounted for under IAS39 ‘Financial
Instruments: recognition and measurement’. The liability should be measured at ‘fair value’ and subsequently at amortisedcost unless designated at the outset as being at fair value through profit or loss.
(b) State the immediate tax implications of the proposed gift of the share portfolio to Avril and identify an
alternative strategy that would achieve Crusoe’s objectives whilst avoiding a possible tax liability in the
future. State any deadline(s) in connection with your proposed strategy. (5 marks)
(b) Gift of the share portfolio to Avril
Inheritance tax
The gift would be a potentially exempt transfer at market value. No inheritance tax would be due at the time of the gift.
Capital gains tax
The gift would be a disposal by Crusoe deemed to be made at market value for the purposes of capital gains tax. No gain
would arise as the deemed proceeds will equal Crusoe’s base cost of probate value.
Stamp duty
There is no stamp duty on a gift of shares for no consideration.
Strategy to avoid a possible tax liability in the future
Crusoe should enter into a deed of variation directing the administrators to transfer the shares to Avril rather than to him. This
will not be regarded as a gift by Crusoe. Instead, provided the deed states that it is intended to be effective for inheritance tax
purposes, it will be as if Noland had left the shares to Avril in a will.
This strategy is more tax efficient than Crusoe gifting the shares to Avril as such a gift would be a potentially exempt transfer
and inheritance tax may be due if Crusoe were to die within seven years.
The deed of variation must be entered into by 1 October 2009, i.e. within two years of the date of Noland’s death.
(ii) Assuming the relief in (i) is available, advise Sharon on the maximum amount of cash she could receive
on incorporation, without triggering a capital gains tax (CGT) liability. (3 marks)
(ii) As Sharon is entitled to the full rate of business asset taper relief, any gain will be reduced by 75%. The position is
maximised where the chargeable gain equals Sharon’s unused capital gains tax annual exemption of £8,500. Thus,
before taper relief, the gain she requires is £34,000 (1/0·25 x £8,500).
The amount to be held over is therefore £46,000 (80,000 – 34,000). Where part of the consideration is in the form
of cash, the gain eligible for incorporation relief is calculated using the formula:
Gain deferred = Gain x value of shares issued/total consideration
The formula is manipulated on the following basis:
£46,000 = £80,000 x (shares/120,000)
Shares/120,000 = £46,000/80,000
Shares = £46,000 x 120,000/80,000
i.e. £69,000.
As the total consideration is £120,000, this means that Sharon can take £51,000 (£120,000 – £69,000) in cash
without any CGT consequences.
(b) Using the information contained in Appendix 1.1, discuss the financial performance of HLP and MAS,
incorporating details of the following in your discussion:
(i) Overall client fees (total and per consultation)
(ii) Advisory protection scheme consultation ‘utilisation levels’ for both property and commercial clients
(iii) Cost/expense levels. (10 marks)
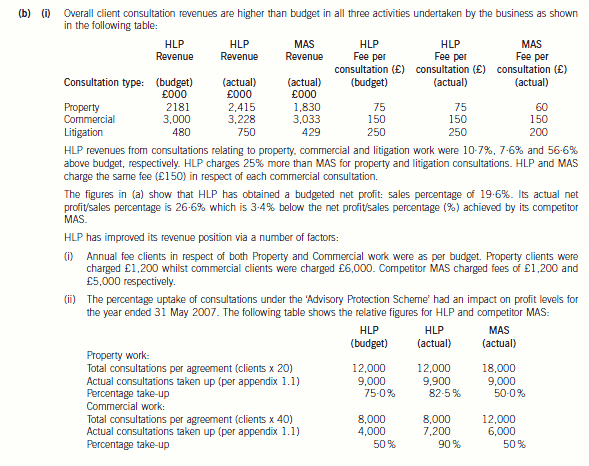
(ii) As far as annual agreements relating to property work are concerned, HLP had a take up rate of 82·5% whereas MAS
had a take up rate of only 50%. Therefore, HLP has ‘lost out’ to competitor MAS in relative financial terms as regards
the ‘take-up’ of consultations relating to property work. This is because both HLP and MAS received an annual fee from
each property client irrespective of the number of consultations given. MAS should therefore have had a better profit
margin from this area of business than HLP. However, the extent to which HLP has ‘lost out’ cannot be quantified since
we would need to know the variable costs per consultation and this detail is not available. What we do know is that
HLP earned actual revenue per effective consultation amounting to £90·90 whereas the budgeted revenue per
consultation amounted to £100. MAS earned £120 per effective consultation.
The same picture emerges from annual agreements relating to commercial work. HLP had a budgeted take up rate of
50%, however the actual take up rate during the period was 90%. MAS had an actual take up rate of 50%. The actual
revenue per effective consultation earned by HLP amounted to £167 whereas the budgeted revenue per consultation
amounted to £300. MAS earned £250 per effective consultation.
There could possibly be an upside to this situation for HLP in that it might be the case that the uptake of 90% of
consultations without further charge by clients holding annual agreements in respect of commercial work might be
indicative of a high level of customer satisfaction. It could on the other hand be indicative of a mindset which says ‘I
have already paid for these consultations therefore I am going to request them’.
(iii) Budgeted and actual salaries in HLP were £50,000 per annum, per advisor. Two additional advisors were employed
during the year in order to provide consultations in respect of commercial work. MAS paid a salary of £60,000 to each
advisor which is 20% higher than the salary of £50,000 paid to each advisor by HLP. Perhaps this is indicative that
the advisors employed by MAS are more experienced and/or better qualified than those employed by HLP.
HLP paid indemnity insurance of £250,000 which is £150,000 (150%) more than the amount of £100,000 paid by
MAS. This excess cost may well have arisen as a consequence of successful claims against HLP for negligence in
undertaking commercial work. It would be interesting to know whether HLP had been the subject of any successful
claims for negligent work during recent years as premiums invariably reflect the claims history of a business. Rather
worrying is the fact that HLP was subject to three such claims during the year ended 31 May 2007.
Significant subcontract costs were incurred by HLP during the year probably in an attempt to satisfy demand and retain
the goodwill of its clients. HLP incurred subcontract costs in respect of commercial properties which totalled £144,000.
These consultations earned revenue amounting to (320 x £150) = £48,000, hence a loss of £96,000 was incurred
in this area of the business.
HLP also paid £300,000 for 600 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned
revenue amounting to (600 x £250) = £150,000, hence a loss of £150,000 was incurred in this area of the business.
In contrast, MAS paid £7,000 for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of commercial work and an identical amount
for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned revenue amounting to
20 x (£150 + £200) =£7,000. Therefore, a loss of only £7,000 was incurred in respect of subcontract consultations
by MAS.
Other operating expenses were budgeted at 53·0% of sales revenue. The actual level incurred was 40·7% of sales
revenue. The fixed/variable split of such costs is not given but it may well be the case that the fall in this percentage is
due to good cost control by HLP. However, it might simply be the case that the original budget was flawed. Competitor
MAS would appear to have a slightly superior cost structure to that of HLP since its other operating expenses amounted
to 38·4% of sales revenue. Further information is required in order to draw firmer conclusions regarding cost control
within both businesses.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-05-08
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-02-19
- 2019-10-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-01-04
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-03-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-14
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-04-02
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-09