2020年澳门ACCA国际会计师考场规则,可以带计算器!
发布时间:2020-01-09
ACCA考场规则是什么呢?跟国内考试的规定有区别吗?这些问题是许多即将参加2020年3月份ACCA考试的同学们最关心的问题,害怕自己辛辛苦苦准备了几个月之久的考试就因为一个不小心触犯了相关的规定,那就得不偿失了。接下来,51题库考试学习网为大家盘点历年来ACCA考试的相关规定,希望大家引以为戒,小心不要触犯哟~
具体点来说,ACCA考试的考场规则主要分为两部分,一个就是进入考场前,另一个就是进入考场之后
ACCA考前规则:
1.考生须在开始考试之前30分钟到达ACCA考试地点,以免在出现突发情况。监考老师对考生进行核查考生本人身份证、ACCA注册号。
2.考生可选择开考前进行网上测试(见机考中心通知),也可选择开考前1小时到达考点,在机考中心进行测试,熟悉机考流程。(建议考生最好选择前者,后者可能出现在机考中心测试的人数太多而不能及时测试导致不熟悉机考流程的情况)
3.考生在考试开始前15分钟经过监考老师批准方可进入考场。逾时不得再进入考场。
4. 考生在到达考场并进行签到后,如因特殊原因需要离场,请主动联系监考人员,不得擅自离开,经过监考老师允许之后才可以离开。
5. 最好不要携带贵重物品前往考场,丢失了后果自负的。
注意:ACCA机考必须带那些东西
首先是自行在官网上打印的准考证其次就是身份证再是可以携带不带有记忆存储功能的计算器。(如考生有携带手机、包包等私人物品,请将其放至监考老师指定区域。)
进入考场后的规则
1.考生进入考场后必须把考试相关书籍材料等放到指定位置,并将手机等通讯设备关闭。考生只允许携带考试规定携带的东西进入考场,例如本人身份证、笔、单功能计算器进入考场,一经发现,按作弊处理。
2.考试开始前,监考人员会宣读考场纪律;考生需要在电脑上输入个人信息,监考人员会核对考生的身份;身份核对后,电脑上会显示出3页考试操作指南,考生仔细阅读,阅读完毕之后,举手向监控人员请示,得到监考人员的允许后才可点击考试科目,开始考试。
3.考试开始时,题目会直接在屏幕上显示,请直接在电脑上输入答案。不能点开电脑里的其他软件
4.考试结束后,需要打印2份考试成绩通知单,自己保留一份,机考中心保留一份。
5.机考中心会在考试结束后上传考试成绩,72小时内成绩会上传到考生的MYACCA成绩记录中。
6.考试费用一旦交付,如因考生自身原因缺考,作弃权处理,不须考虑退款事宜。因此建议各位考生要谨慎报名,毕竟考试费用也是一笔不小的费用。
7.ACCA机考中心保留因不可抗力因素(如网络问题,停电等)调整机考时间或取消考试的权力。出现了以上情况,及时向监考人员反映,他们会为你解决问题。
迟到及提早交卷规定:
在开考后1小时内到达的迟到考生可以入场,但不能补偿考试时间。简单的来说就是即便是晚到1小时,你的考试时间也不会往后延时1小时,交卷铃声响起你同样得交卷。而开考1小时以后到达的考生就算做放弃此次考试,不能入场。
这些考场规则有没有帮助到各位ACCAer们呀?相信大家看了之后或多或少对ACCA考场规则都有了一定的了解,51题库考试学习网提醒大家,认真阅读考场规则,如果和上面所述的规则有一定的出入,各地的相关考场规则以各地的为准,最后51题库考试学习网预祝大家考试顺利上岸~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) A summary of the information needed to satisfy our obligations under the money laundering legislation and
any action that should be taken before agreeing to become tax advisers to the Saturn Ltd group. (5 marks)
(b) Before agreeing to become tax advisers to the Saturn Ltd group
Information needed:
– Proof of incorporation and primary business address and registered office.
– The structure, directors and shareholders of the company.
– The identities of those persons instructing the firm on behalf of the company and those persons that are authorised to
do so.
Action to take:
– Consider whether becoming tax advisers to the Saturn Ltd group would create any threats to compliance with the
fundamental principles of professional ethics, for example integrity and professional competence. Where such threats
exist, we should not accept the appointment unless the threats can be reduced to an acceptable level via the
implementation of safeguards.
– Contact the existing tax adviser in order to ensure that there has been no action by the Saturn Ltd group that would, on
ethical grounds, preclude us from accepting appointment.
Moonstar Co is a property development company which is planning to undertake a $200 million commercial property development. Moonstar Co has had some difficulties over the last few years, with some developments not generating the expected returns and the company has at times struggled to pay its finance costs. As a result Moonstar Co’s credit rating has been lowered, affecting the terms it can obtain for bank finance. Although Moonstar Co is listed on its local stock exchange, 75% of the share capital is held by members of the family who founded the company. The family members who are shareholders do not wish to subscribe for a rights issue and are unwilling to dilute their control over the company by authorising a new issue of equity shares. Moonstar Co’s board is therefore considering other methods of financing the development, which the directors believe will generate higher returns than other recent investments, as the country where Moonstar Co is based appears to be emerging from recession.
Securitisation proposals
One of the non-executive directors of Moonstar Co has proposed that it should raise funds by means of a securitisation process, transferring the rights to the rental income from the commercial property development to a special purpose vehicle. Her proposals assume that the leases will generate an income of 11% per annum to Moonstar Co over a ten-year period. She proposes that Moonstar Co should use 90% of the value of the investment for a collateralised loan obligation which should be structured as follows:
– 60% of the collateral value to support a tranche of A-rated floating rate loan notes offering investors LIBOR plus 150 basis points
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of B-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 12%
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of C-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 13%
– 10% of the collateral value to support a tranche as subordinated certificates, with the return being the excess of receipts over payments from the securitisation process
The non-executive director believes that there will be sufficient demand for all tranches of the loan notes from investors. Investors will expect that the income stream from the development to be low risk, as they will expect the property market to improve with the recession coming to an end and enough potential lessees to be attracted by the new development.
The non-executive director predicts that there would be annual costs of $200,000 in administering the loan. She acknowledges that there would be interest rate risks associated with the proposal, and proposes a fixed for variable interest rate swap on the A-rated floating rate notes, exchanging LIBOR for 9·5%.
However the finance director believes that the prediction of the income from the development that the non-executive director has made is over-optimistic. He believes that it is most likely that the total value of the rental income will be 5% lower than the non-executive director has forecast. He believes that there is some risk that the returns could be so low as to jeopardise the income for the C-rated fixed rate loan note holders.
Islamic finance
Moonstar Co’s chief executive has wondered whether Sukuk finance would be a better way of funding the development than the securitisation.
Moonstar Co’s chairman has pointed out that a major bank in the country where Moonstar Co is located has begun to offer a range of Islamic financial products. The chairman has suggested that a Mudaraba contract would be the most appropriate method of providing the funds required for the investment.
Required:
(a) Calculate the amounts in $ which each of the tranches can expect to receive from the securitisation arrangement proposed by the non-executive director and discuss how the variability in rental income affects the returns from the securitisation. (11 marks)
(b) Discuss the benefits and risks for Moonstar Co associated with the securitisation arrangement that the non-executive director has proposed. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Discuss the suitability of Sukuk finance to fund the investment, including an assessment of its appeal to potential investors. (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss whether a Mudaraba contract would be an appropriate method of financing the investment and discuss why the bank may have concerns about providing finance by this method. (4 marks)
(a) An annual cash flow account compares the estimated cash flows receivable from the property against the liabilities within the securitisation process. The swap introduces leverage into the arrangement.
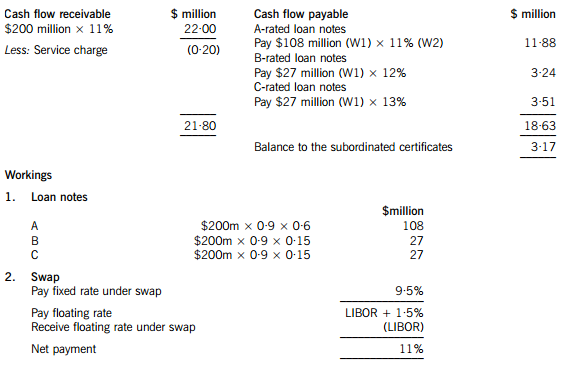
The holders of the certificates are expected to receive $3·17million on $18 million, giving them a return of 17·6%. If the cash flows are 5% lower than the non-executive director has predicted, annual revenue received will fall to $20·90 million, reducing the balance available for the subordinated certificates to $2·07 million, giving a return of 11·5% on the subordinated certificates, which is below the returns offered on the B and C-rated loan notes. The point at which the holders of the certificates will receive nothing and below which the holders of the C-rated loan notes will not receive their full income will be an annual income of $18·83 million (a return of 9·4%), which is 14·4% less than the income that the non-executive director has forecast.
(b) Benefits
The finance costs of the securitisation may be lower than the finance costs of ordinary loan capital. The cash flows from the commercial property development may be regarded as lower risk than Moonstar Co’s other revenue streams. This will impact upon the rates that Moonstar Co is able to offer borrowers.
The securitisation matches the assets of the future cash flows to the liabilities to loan note holders. The non-executive director is assuming a steady stream of lease income over the next 10 years, with the development probably being close to being fully occupied over that period.
The securitisation means that Moonstar Co is no longer concerned with the risk that the level of earnings from the properties will be insufficient to pay the finance costs. Risks have effectively been transferred to the loan note holders.
Risks
Not all of the tranches may appeal to investors. The risk-return relationship on the subordinated certificates does not look very appealing, with the return quite likely to be below what is received on the C-rated loan notes. Even the C-rated loan note holders may question the relationship between the risk and return if there is continued uncertainty in the property sector.
If Moonstar Co seeks funding from other sources for other developments, transferring out a lower risk income stream means that the residual risks associated with the rest of Moonstar Co’s portfolio will be higher. This may affect the availability and terms of other borrowing.
It appears that the size of the securitisation should be large enough for the costs to be bearable. However Moonstar Co may face unforeseen costs, possibly unexpected management or legal expenses.
(c) (i) Sukuk finance could be appropriate for the securitisation of the leasing portfolio. An asset-backed Sukuk would be the same kind of arrangement as the securitisation, where assets are transferred to a special purpose vehicle and the returns and repayments are directly financed by the income from the assets. The Sukuk holders would bear the risks and returns of the relationship.
The other type of Sukuk would be more like a sale and leaseback of the development. Here the Sukuk holders would be guaranteed a rental, so it would seem less appropriate for Moonstar Co if there is significant uncertainty about the returns from the development.
The main issue with the asset-backed Sukuk finance is whether it would be as appealing as certainly the A-tranche of the securitisation arrangement which the non-executive director has proposed. The safer income that the securitisation offers A-tranche investors may be more appealing to investors than a marginally better return from the Sukuk. There will also be costs involved in establishing and gaining approval for the Sukuk, although these costs may be less than for the securitisation arrangement described above.
(ii) A Mudaraba contract would involve the bank providing capital for Moonstar Co to invest in the development. Moonstar Co would manage the investment which the capital funded. Profits from the investment would be shared with the bank, but losses would be solely borne by the bank. A Mudaraba contract is essentially an equity partnership, so Moonstar Co might not face the threat to its credit rating which it would if it obtained ordinary loan finance for the development. A Mudaraba contract would also represent a diversification of sources of finance. It would not require the commitment to pay interest that loan finance would involve.
Moonstar Co would maintain control over the running of the project. A Mudaraba contract would offer a method of obtaining equity funding without the dilution of control which an issue of shares to external shareholders would bring. This is likely to make it appealing to Moonstar Co’s directors, given their desire to maintain a dominant influence over the business.
The bank would be concerned about the uncertainties regarding the rental income from the development. Although the lack of involvement by the bank might appeal to Moonstar Co's directors, the bank might not find it so attractive. The bank might be concerned about information asymmetry – that Moonstar Co’s management might be reluctant to supply the bank with the information it needs to judge how well its investment is performing.
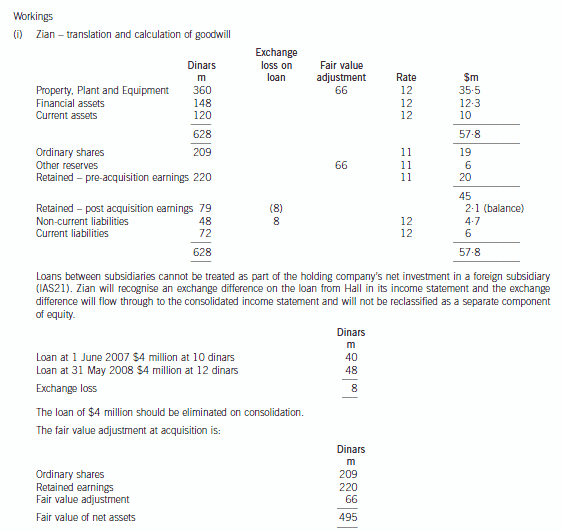
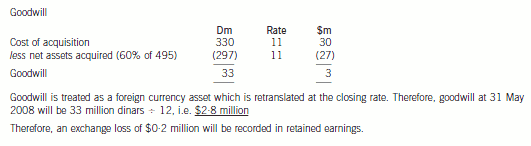
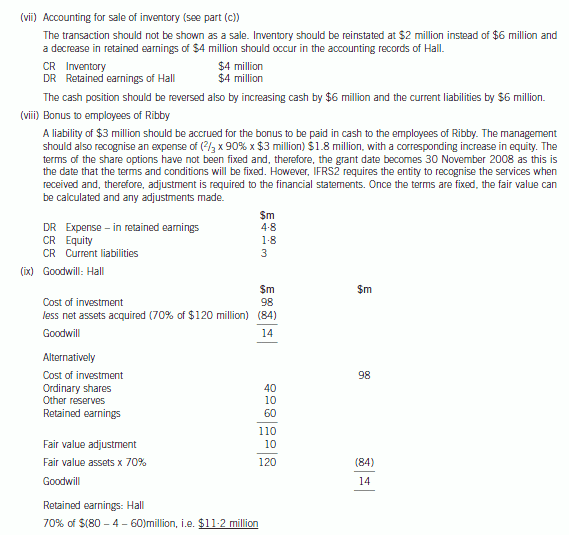
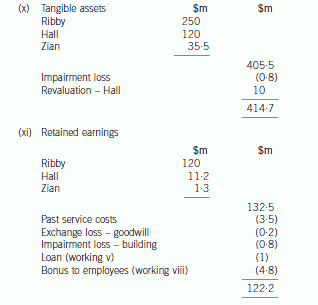
(b) Prepare a consolidated statement of financial position of the Ribby Group at 31 May 2008 in accordance
with International Financial Reporting Standards. (35 marks)




(b) How might the marketing mix vary between the three channels Helen is considering using? (8 marks)
(b) The analysis of each of the market entry strategies has begun the process of identifying how the marketing mix of product,
price, place and promotion will vary significantly between the three outlets.
Product – here the nature of the product in terms of recipes and product range can be varied reasonably easily to meet the
demands of the outlet.
Price – again this will vary in significance between the three outlets with the greatest pressure coming from the supermarkets
and catering wholesalers. Margins may come under pressure with the supermarkets looking for a contribution to sales
promotions.
Promotion – here the issue of brand development is a crucial factor. Using her own brand, Helen can develop the product
range and extend the outlets she sells through.

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-12
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-11
- 2020-04-01
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-03-21
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-30
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-05-14
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-21
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-05
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-01-03