请问什么情况下安徽省考生ACCA国际会计师证书会被注销呢?
发布时间:2020-01-09
目前,有不少通过自己的努力已经考过ACCA考试进入证书申请阶段的同学出现了新的疑问:ACCA证书有有效年限吗?怎么样才能一直保持ACCA会员资格呢?有些什么规定会导致取消ACCA会员资格导致证书被吊销呢?接下来,51题库考试学习网一一解答大家心中的疑惑,避免在领证之路上出现一些不必要的意外。
首先,ACCA证书是不会过期的,拿到了ACCA证书就是终身有效的,但终身有效的前提是:只要成为ACCA会员以后每年维持ACCA年费的正常支付,就可以保持ACCA资格。
需要注意的是:但是在成为ACCA会员之前,ACCA考试的时候成绩是有有效期的。
ACCA有效期新规显示,ACCAF阶段不再设有时间限制,从P阶段通过第一门开始算有七年有效期,如果七年内没有全部通过,成绩将全部作废,意思是就是在七年之后你就需要重新考试你已经考过的科目了。
以下是关于ACCA P阶段有效期的官方原文:
ACCA学员有七年的时间通过专业阶段的考试(即P1、P2和P3,以及P4-P7中的任选两门)。如果学员不能在七年内通过所有专业阶段考试,超过七年的已通过专业阶段科目的成绩将作废,须重新考试。七年时限从学员通过第一门专业阶段考试之日算起。
当然你必须要遵守以下的一些规定,否则你的ACCA会员资格会被取消,导致你无法正常领取证书:
1.最首要的就是,在ACCA学员阶段需要注意的是千万不要在考试的时候出现作弊的情况,一旦发现就会被取消ACCA会员资格
2.违反职业道德将会被直接除名。何为违反职业道德呢?其实就是类似于做假账之类的情况发生,无论是什么情况,出于知情或者不知情的情况下,一旦被发现,自己的ACCA职业生涯就宣告结束~
3.要维持ACCA会员资格只需要按时缴纳年费即可。那么不按时缴纳年费呢?首先你的ACCA会员资格将会暂时被取消,您的ACCA账户也将被冻结。当然这个也是暂时的,你只要及时的申请补缴信息,成功缴费就可以恢复会员的身份了。如果不需要ACCA会员这个头衔可以通过不缴纳年费这个方法来实现。
ACCA会不会和国内会计证书一样需要继续教育来继续维持会员资格呢?
答案是否定的。和国内会计证书不一样,国内会计证首先是有时间年限的,是需要继续教育来维持证书年限的,而ACCA并没有开设继续教育等课程,学员需要维持会员资格只需要按时缴纳年费即可。但是ACCA后续有许多拓展课程,例如obu学士学位,UCL伦敦大学硕士学位等等,都是在ACCA学习过程中可以考的。
那如果不小心没有按时缴费造成了账户被冻结的情况应该怎么办呢?
很简单,写封邮件向官方解释一下情况,并表达想恢复ACCA会员资格的意愿,并通过官方回复的渠道补交年费和一定数额的罚金即可回复ACCA会员资格了。温馨提示一下,由于ACCA官方是在英国,所以办理的时限可能会很长,因此建各位考生还是按时缴纳会费,避免不必要的影响。
以上就是关于ACCA考试证书申请流程和后续注意事宜的相关内容,希望对大家有所帮助,最后再次恭喜成功通过ACCA全科考试的同学们,成功上岸~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Explain how the use of activity-based techniques may benefit Taliesin Ltd. (5 marks)
(c) The usefulness of activity-based techniques is accentuated in situations where overheads comprise a significant proportion of
product costs. Manufacturing overheads comprise 30·9% of turnover during the year ended 31 May 2005. Traditional
methods of allocating overheads to products might result in product cost information which is misleading and detrimental to
managerial decision-making. Calculations of product costs are more prone to error in situations where higher levels of
overhead exist. The consequences can prove disastrous as, for example, in the under-pricing or over-pricing of products.
Since Taliesin Ltd is going to confine its activities to its home country it must be prepared to face increased competition and
this increases the need for greater visibility and more accurate product cost information.
At present, Taliesin Ltd offers a range of products which is increasing in number and this may lead to the need for a more
detailed costing system. Traditional absorption systems might well be inadequate as the number of product variants increases.
One would expect that each new product developed is more complex than its predecessors. The company would probably
start with simple Vanilla, then a few basic flavours but as Taliesin Ltd has expanded one would expect it to take longer to
originate and test new products until they are ready to be introduced. It will probably take longer to mix the ingredients for a
run of each product.
These two, development and mixing ingredients, are examples of activities which arise when new products are considered.
If traditional absorption costing and budgeting are used based on machine-time in production then the effect of these activities
would be ignored.
In order to gain a full appreciation of the impact of new product introduction activity-based techniques should be used to
guide Taliesin Ltd into the easiest way to maintain its policy of growth. It may be a better decision to expand abroad or into
new markets at home with the existing products than pursue growth by introducing new products to a dwindling number of
customers.
We are not told of the composition of the customer base of Taliesin Ltd. However, one thing we do know is that the scope of
activity-based techniques extends beyond products and services. For example, the application of activity-based costing can
provide vital information that enables management to undertake customer profitability analysis, thereby further improving
management decision-making and operating performance.
(b) Using the information contained in Appendix 1.1, discuss the financial performance of HLP and MAS,
incorporating details of the following in your discussion:
(i) Overall client fees (total and per consultation)
(ii) Advisory protection scheme consultation ‘utilisation levels’ for both property and commercial clients
(iii) Cost/expense levels. (10 marks)
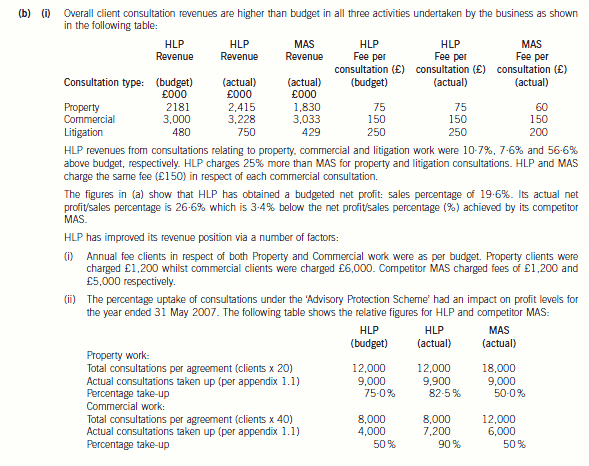
(ii) As far as annual agreements relating to property work are concerned, HLP had a take up rate of 82·5% whereas MAS
had a take up rate of only 50%. Therefore, HLP has ‘lost out’ to competitor MAS in relative financial terms as regards
the ‘take-up’ of consultations relating to property work. This is because both HLP and MAS received an annual fee from
each property client irrespective of the number of consultations given. MAS should therefore have had a better profit
margin from this area of business than HLP. However, the extent to which HLP has ‘lost out’ cannot be quantified since
we would need to know the variable costs per consultation and this detail is not available. What we do know is that
HLP earned actual revenue per effective consultation amounting to £90·90 whereas the budgeted revenue per
consultation amounted to £100. MAS earned £120 per effective consultation.
The same picture emerges from annual agreements relating to commercial work. HLP had a budgeted take up rate of
50%, however the actual take up rate during the period was 90%. MAS had an actual take up rate of 50%. The actual
revenue per effective consultation earned by HLP amounted to £167 whereas the budgeted revenue per consultation
amounted to £300. MAS earned £250 per effective consultation.
There could possibly be an upside to this situation for HLP in that it might be the case that the uptake of 90% of
consultations without further charge by clients holding annual agreements in respect of commercial work might be
indicative of a high level of customer satisfaction. It could on the other hand be indicative of a mindset which says ‘I
have already paid for these consultations therefore I am going to request them’.
(iii) Budgeted and actual salaries in HLP were £50,000 per annum, per advisor. Two additional advisors were employed
during the year in order to provide consultations in respect of commercial work. MAS paid a salary of £60,000 to each
advisor which is 20% higher than the salary of £50,000 paid to each advisor by HLP. Perhaps this is indicative that
the advisors employed by MAS are more experienced and/or better qualified than those employed by HLP.
HLP paid indemnity insurance of £250,000 which is £150,000 (150%) more than the amount of £100,000 paid by
MAS. This excess cost may well have arisen as a consequence of successful claims against HLP for negligence in
undertaking commercial work. It would be interesting to know whether HLP had been the subject of any successful
claims for negligent work during recent years as premiums invariably reflect the claims history of a business. Rather
worrying is the fact that HLP was subject to three such claims during the year ended 31 May 2007.
Significant subcontract costs were incurred by HLP during the year probably in an attempt to satisfy demand and retain
the goodwill of its clients. HLP incurred subcontract costs in respect of commercial properties which totalled £144,000.
These consultations earned revenue amounting to (320 x £150) = £48,000, hence a loss of £96,000 was incurred
in this area of the business.
HLP also paid £300,000 for 600 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned
revenue amounting to (600 x £250) = £150,000, hence a loss of £150,000 was incurred in this area of the business.
In contrast, MAS paid £7,000 for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of commercial work and an identical amount
for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned revenue amounting to
20 x (£150 + £200) =£7,000. Therefore, a loss of only £7,000 was incurred in respect of subcontract consultations
by MAS.
Other operating expenses were budgeted at 53·0% of sales revenue. The actual level incurred was 40·7% of sales
revenue. The fixed/variable split of such costs is not given but it may well be the case that the fall in this percentage is
due to good cost control by HLP. However, it might simply be the case that the original budget was flawed. Competitor
MAS would appear to have a slightly superior cost structure to that of HLP since its other operating expenses amounted
to 38·4% of sales revenue. Further information is required in order to draw firmer conclusions regarding cost control
within both businesses.
(ii) equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue; and (4 marks)
(ii) Equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue
Tutorial note: In the context of GVF, the principal issue to be addressed is whether or not the impairment loss previously
recognised should be reversed (by considering the determination of value in use). Marks will also be awarded for
consideration of depreciation, additions etc made specific to this equipment.
■ Agree cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses at the beginning of the year to prior year working
papers (and/or last year’s published financial statements).
■ Recalculate the current year depreciation charge based on the carrying amount (as reduced by the impairment
loss).
■ Calculate the carrying amount of the equipment as at 30 September 2005 without deduction of the impairment
loss.
Tutorial note: The equipment cannot be written back up to above this amount (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ Agree management’s schedule of future cash flows estimated to be attributable to the equipment for a period of up
to five years (unless a longer period can be justified) to approved budgets and forecasts.
■ Recalculate:
– on a sample basis, the make up of the cash flows included in the forecast;
– GVF’s weighted average cost of capital.
■ Review production records and sales orders for the year, as compared with the prior period, to confirm a ‘steady
increase’.
■ Compare sales volume at 30 September 2005 with the pre-‘scare’ level to assess how much of the previously
recognised impairment loss it would be prudent to write back (if any).
■ Scrutinize sales orders in the post balance sheet event period. Sales of such produce can be very volatile and
another ‘incident’ could have sales plummeting again – in which case the impairment loss should not be reversed.
(b) Assuming that the acquisition proceeds, what steps will Datum Paper Products need to take to build a shared
culture in the two companies? (10 marks)
(b) Developing a shared culture will be one of the key determinants of whether the anticipated benefits of the acquisition actually
materialise. Due diligence procedures before the merger should have established the key people issues. This will include
reviewing the two management styles and cultures. Clearly these are very different, looking at internal communication pre
and post acquisition, understanding the nature of reward systems in the firm to be acquired, assessing the nature of training
programmes in the firm both before and after the acquisition and attempting to gauge existing employee attitudes towards
Papier Presse and the likely reaction to the acquisition. Reviewing areas where there have been significant staff problems and
consequent negotiations will also be an important clue as to employee attitudes and morale. ‘Hard’ people issues including
pensions, management rewards, health insurance and redundancy terms will need to be realistically assessed and the
implications for both the price paid for the company and subsequent integration fully understood. All too often the compelling
strategic vision for the enlarged company ignores the people costs involved and the time needed to develop shared HR
systems.
Many models on culture and culture management could help to achieve a successful transition. Mintzberg’s cultural or
organisational configuration model, which would facilitate an understanding of the difference in structures and systems, could
be a useful starting point. DPP comes from a divisionalised company where the middle line managers are given considerable
autonomy in achieving agreed levels of performance. Papier Presse, with its dominance by family ownership and
management, could be argued to be entrepreneurial in character, where the owner/managers at the strategic apex of the
company operate a ‘hands-on’ approach and direct control of subordinates. Reconciling these different cultures and structures
will not be an easy task.
Lewin’s 3-step model of change can be used in helping a positive culture emerge from the combining of the two companies.
There is a need to unfreeze the current situation in which employees of both organisations are likely to be reluctant or resistant
to change. There needs to be a clear understanding of who does what in the new organisation – leadership and the role of
the French owners will be a critical factor in successfully changing the culture. Robbins emphasises the need for positive top
management role models in promoting and communicating the need for a change in culture. Policies to affect change on both
the hard and soft factors referred to above need to be in place to move the integration forward. A clear timescale and vision
for change will be a key part of the change process. Finally the systems will need to be in place to re-freeze or rather reinforce
the attitudes and behaviours necessary to achieve success in the merged organisation. Operating across national borderscreates real culture issues to be solved as shown in studies by Hofstede and Bartlett and Ghoshal.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-03-30
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-22
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-04-03
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-05-11
- 2020-05-12
- 2020-01-01
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-04-01
- 2021-04-23
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-05-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-15
- 2020-03-06
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-06
- 2020-04-12