关于申请ACCA会员的具体条件是什么,速来看看本文!
发布时间:2020-04-01
近期有一些小伙伴来咨询51题库考试学习网:ACCA会员申请条件是什么?满足哪些要求才能成为一个合格的ACCA会员,享有ACCA会员的薪酬待遇呢?接下来就跟随51题库考试学习网一起来看看具体内容吧。
ACCA会员的申请条件:
13科全部通过,完成在线职业操守课程的学习和测试,并且至少有3年相关工作经验(相关工作经验指的是你从事财务、会计、审计、税务或者金融任一方面的工作经验)的ACCA准会员即可申请成为会员。具体来说总共有三个条件:
(1)通过ACCA专业资格大纲13门课程的考试(其中9门根据学员的教育和专业背景可申请不同程度的免试);
(2)至少三年的相关工作经验;
3)完成在线职业操守训练课程的学习和测试。对在2007年1月1日之前注册的学员,完成在线职业操守训练课程不作为申请会员的必要条件,但ACCA鼓励学员完成这一课程。
如何申请成为会员?
(1)ACCA每年2月份和8月份会分别公布上一年12月份和本年6月份的考试成绩。每一个通过ACCA全部考试的学员随后会收到ACCA英国总部颁发的ACCA准会员证书,以确认学员成功通过所有考试。(一般收到时间是3月初和9月初);
(2)符合会员的必要条件”3E”的准会员可以填写《ACCA会员申请表》。《ACCA会员申请表》可以直接登陆ACCA网站下载。对于暂时未满足会员的必要条件的准会员,可以在条件满足的任何时间向ACCA递交ACCA会员申请表;
(3)ACCA总部将对会员申请材料进行审核,完全符合条件者将被批准成为ACCA会员,并会收到ACCA英国总部颁发的ACCA会员证书。一般这个过程需要两个月的时间;
(4)成为会员约五年后,经申请和资格审查,可以成为资深会员(FCCA)。
又到了与大家说再见的时候了,以上信息就是51题库考试学习网针对小伙伴们的问题做出的详细解答,相信小伙伴们看过之后也有了一定的了解了吧,如果大家还有什么疑问,欢迎大家前来咨询51题库考试学习网,我们会第一时间为大家答疑解惑。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) the strategy of the business regarding its treasury policies. (3 marks)
(Marks will be awarded in part (b) for the identification and discussion of relevant points and for the style. of the
report.)
(ii) Strategy of the business regarding its treasury policies
Treasury policies are reviewed regularly by the Board. It is group policy to account for all financial instruments as cash
flow hedges. As a result, changes in the fair values of financial instruments are deferred in reserves to the extent the
hedge is effective and released to profit or loss in the time periods in which the hedged item impacts profit or loss.
The Group contracts fixed rate currency swaps and issues floating to fixed rate interest rate swaps to meet the objective
of protecting borrowing costs. The cash flow effects of the interest rate swaps match the cash flows on the underlying
instruments so that there is no net cash flow effect from movements in market interest rates. If the interest rate swaps
had not been transacted there could have been an increase in the annual net interest payable to the Group. The strategy
of the group is to minimise the exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
Matthew Black is well aware that the achievement of the growth targets for the 2005 to 2007 period will depend on
successful implementation of the strategy, affecting all parts of the company’s activities.
(c) Explain the key issues affecting implementation and the changes necessary to achieve Universal’s ambitious
growth strategy. (15 marks)
(c) Matthew has set ambitious growth goals for the 2005–7 period in his quest to become ‘unquestioned leader’ in their region
and to roll out the model nationally. Clearly there are choices to be made in terms of implementing the strategy and much of
the success of the strategy will depend on the extent to which appropriate resources, structure and systems are in place to
facilitate growth. Many alternative models consider how strategy is implemented, but one of the most popular is the McKinsey
7S model in which the 7S’s are strategy, structure, systems (the so called ‘hard’ or tangible variables) and staff, style, skills
and shared values (the ‘soft’ or less tangible variables). The 7S model has a number of key assumptions built into it. Normally
we tend to think of strategy being the first variable in the strategic management process, with all other variables dependent
on the chosen strategy. However, Peters and Waterman argue that the assertion, for instance, that a firm’s structure follows
from its strategy ignores the fact that a particular structure may equally influence the strategy chosen. If we have a simple
functional structure, this may severely limit the ability of the firm to move or diversify into other areas of business. Equally
important is to understand the linkages between the variables, just as with the value chain, recognising if you change one of
the variables you then have to see the consequences for each of the other variables.
Our earlier analysis will have provided us with an understanding of the strategy being pursued by Universal. It is now looking
to offer its service to other parts of the country and become a national provider. In strategy terms, this is a process of growth
by way of market development, with the same service in different regions or markets. Universal’s experience is dominated by
operating in one region and the consequences of moving into new regions should not be underestimated. There are interesting
examples of companies having conspicuous success in their home territory but finding competition and customer relationships
very different outside their home market, even in the same country.
Matthew has already recognised the need to create a new structure to handle the growth strategy. This is ‘growth by
geographic expansion’ and while it may be the most simple growth strategy to control and co-ordinate, the creation of regional
centres managing the sales and installations in the region will add an additional level of administration and complexity.
This structural change will have significant implications for the systems employed by the company. Development of a national
operation will necessitate new methods of communication and reporting. Customer service levels depend on the management
information systems available. There is an opportunity for the new regions to benchmark themselves against the home region.
Efficient systems lie at the heart of Universal’s ability to offer a higher value added service to the customer. Standardised
processes have allowed a ‘no surprises’ policy to be successfully implemented. The extent to which the same business models
can be simply repeated in region after region will have to be tested. There is little mention of IT systems, but the pace of
expansion should be closely linked to the system’s ability to cope with increased demands.
Staff – reference has been made earlier to Universal being a people business, able to deliver a better quality of service to the
customer. The heavy reliance on self-employed staff means that a very active recruitment and training process will have to
be in place as Universal moves into different regions. New layers and levels of management will have implications for the
recruitment and development of both managers and staff reporting to them. The degrees of autonomy given to each of the
regions will materially affect the way they operate. Reward systems clearly link both staff and systems dimensions and there
is need to ensure that the right number and calibre of staff are recruited to expand the market coverage. Does Universal have
a staffing model that is easily ‘rolled’ out into other regions?
Equally important are any changes to the skill set needed by staff to operate nationally. Matthew feels that the model is
relatively lowly skilled with staff controlled through standardised systems. However, change is inevitable and the recruitment
and retention of staff in a labour intensive service will be key to success.
Universal is very much a family business dominated by the two founding brothers. Even with expansion being entirely within
their local region the rate of growth to a £6 million turnover business predicted to treble in size over the next three years, will
necessitate changes in the style. of management. Time management issues amongst the owner-managers have already begun
to emerge and a move from involvement with day-to-day management to a more strategic role is needed. Certainly growth to
date has been more emergent than planned, but vision and planning will be equally necessary as the firm operates nationally.
There are tensions for Matthew in making sure that his change in role and responsibilities does not result in him becoming
remote from his management and staff. Communication of the core values of the company will become even more necessary
and communication is key to managing the growth process.
The 7S’s is not the only model that will be useful in understanding the problems of implementing the growth strategy.
Greiner’s growth model has merit in drawing attention to the stages a growing business following an organic growth strategy
can expect to go through. Johnson and Scholes now refer to strategic implementation as ‘strategy in action’ made up of three
key activities, structuring an organisation to support successful performance. Universal’s move from a regional to a national
company will call for different structures and relationships. Enabling links the particular strengths and competences, built
round separate resource areas, to be combined to support the strategy – which in turn recognises and builds on identified
strengths. Finally, growth strategies will involve change and the management of the change process. They argue that change
will involve the need to change day-to-day routines and cultural aspects of the firm, together with overcoming resistance to
change.
All too often, a company grows at a rate which exceeds the capacity to implement the necessary change. This can expose
the firm to high levels of risk. Growth pressures can stimulate positive change and innovation, but in companies such as
Universal where considerable stress is placed on performance, targets and quality may be a casualty. Equally concerning is
if the rate of growth exceeds the capacity to invest in more people and technology. Growing the people and the systems isalmost a prerequisite to growing the business.
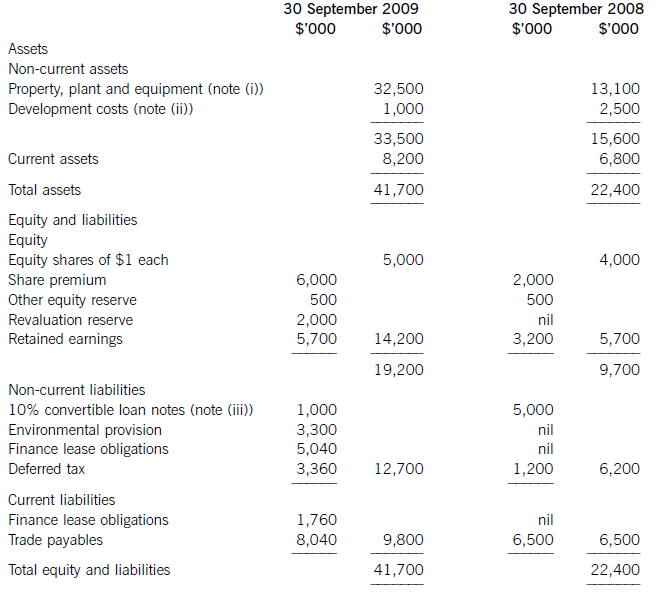
(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.
Summarised statements of financial position as at:
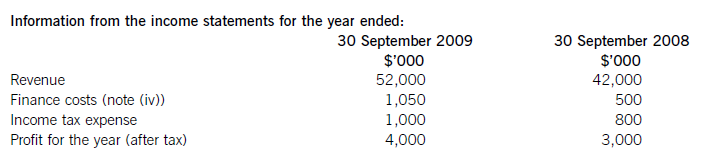
The following information is available:
(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansion programme for its non-current assets. The details of this programme are:
On 1 October 2008 Crosswire acquired a platinum mine at a cost of $5 million. A condition of mining the
platinum is a requirement to landscape the mining site at the end of its estimated life of ten years. The
present value of this cost at the date of the purchase was calculated at $3 million (in addition to the
purchase price of the mine of $5 million).
Also on 1 October 2008 Crosswire revalued its freehold land for the first time. The credit in the revaluation
reserve is the net amount of the revaluation after a transfer to deferred tax on the gain. The tax rate applicable to Crosswire for deferred tax is 20% per annum.
On 1 April 2009 Crosswire took out a finance lease for some new plant. The fair value of the plant was
$10 million. The lease agreement provided for an initial payment on 1 April 2009 of $2·4 million followed
by eight six-monthly payments of $1·2 million commencing 30 September 2009.
Plant disposed of during the year had a carrying amount of $500,000 and was sold for $1·2 million. The
remaining movement on the property, plant and equipment, after charging depreciation of $3 million, was
the cost of replacing plant.
(ii) From 1 October 2008 to 31 March 2009 a further $500,000 was spent completing the development
project at which date marketing and production started. The sales of the new product proved disappointing
and on 30 September 2009 the development costs were written down to $1 million via an impairment
charge.
(iii) During the year ended 30 September 2009, $4 million of the 10% convertible loan notes matured. The
loan note holders had the option of redemption at par in cash or to exchange them for equity shares on the
basis of 20 new shares for each $100 of loan notes. 75% of the loan-note holders chose the equity option.
Ignore any effect of this on the other equity reserve.
All the above items have been treated correctly according to International Financial Reporting Standards.
(iv) The finance costs are made up of:
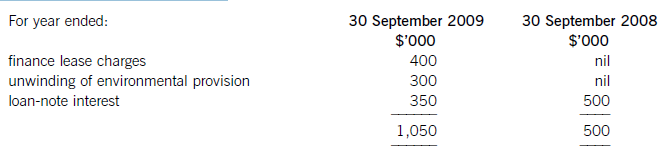
Required:
(i) Prepare a statement of the movements in the carrying amount of Crosswire’s non-current assets for the
year ended 30 September 2009; (9 marks)
(ii) Calculate the amounts that would appear under the headings of ‘cash flows from investing activities’
and ‘cash flows from financing activities’ in the statement of cash flows for Crosswire for the year ended
30 September 2009.
Note: Crosswire includes finance costs paid as a financing activity. (8 marks)
(b) A substantial shareholder has written to the directors of Crosswire expressing particular concern over the
deterioration of the company’s return on capital employed (ROCE)
Required:
Calculate Crosswire’s ROCE for the two years ended 30 September 2008 and 2009 and comment on the
apparent cause of its deterioration.
Note: ROCE should be taken as profit before interest on long-term borrowings and tax as a percentage of equity plus loan notes and finance lease obligations (at the year end). (8 marks)
(i)Thecashelementsoftheincreaseinproperty,plantandequipmentare$5millionforthemine(thecapitalisedenvironmentalprovisionisnotacashflow)and$2·4millionforthereplacementplantmakingatotalof$7·4million.(ii)Ofthe$4millionconvertibleloannotes(5,000–1,000)thatwereredeemedduringtheyear,75%($3million)ofthesewereexchangedforequitysharesonthebasisof20newsharesforeach$100inloannotes.Thiswouldcreate600,000(3,000/100x20)newsharesof$1eachandsharepremiumof$2·4million(3,000–600).As1million(5,000–4,000)newshareswereissuedintotal,400,000musthavebeenforcash.Theremainingincrease(aftertheeffectoftheconversion)inthesharepremiumof$1·6million(6,000–2,000b/f–2,400conversion)mustrelatetothecashissueofshares,thuscashproceedsfromtheissueofsharesis$2million(400nominalvalue+1,600premium).(iii)Theinitialleaseobligationis$10million(thefairvalueoftheplant).At30September2009totalleaseobligationsare$6·8million(5,040+1,760),thusrepaymentsintheyearwere$3·2million(10,000–6,800).(b)TakingthedefinitionofROCEfromthequestion:Fromtheaboveitcanbeclearlyseenthatthe2009operatingmarginhasimprovedbynearly1%point,despitethe$2millionimpairmentchargeonthewritedownofthedevelopmentproject.ThismeansthedeteriorationintheROCEisduetopoorerassetturnover.Thisimpliestherehasbeenadecreaseintheefficiencyintheuseofthecompany’sassetsthisyearcomparedtolastyear.Lookingatthemovementinthenon-currentassetsduringtheyearrevealssomemitigatingpoints:Thelandrevaluationhasincreasedthecarryingamountofproperty,plantandequipmentwithoutanyphysicalincreaseincapacity.Thisunfavourablydistortsthecurrentyear’sassetturnoverandROCEfigures.TheacquisitionoftheplatinummineappearstobeanewareaofoperationforCrosswirewhichmayhaveadifferent(perhapslower)ROCEtootherpreviousactivitiesoritmaybethatitwilltakesometimefortheminetocometofullproductioncapacity.Thesubstantialacquisitionoftheleasedplantwashalf-waythroughtheyearandcanonlyhavecontributedtotheyear’sresultsforsixmonthsatbest.Infutureperiodsafullyear’scontributioncanbeexpectedfromthisnewinvestmentinplantandthisshouldimprovebothassetturnoverandROCE.Insummary,thefallintheROCEmaybeduelargelytotheabovefactors(effectivelythereplacementandexpansionprogramme),ratherthantopooroperatingperformance,andinfutureperiodsthismaybereversed.ItshouldalsobenotedthathadtheROCEbeencalculatedontheaveragecapitalemployedduringtheyear(ratherthantheyearendcapitalemployed),whichisarguablymorecorrect,thenthedeteriorationintheROCEwouldnothavebeenaspronounced.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-29
- 2019-10-03
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-05-12
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-03-29
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-04-12
- 2020-03-29
- 2020-01-13
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-19