如何帮助陕西省考生高效的学习ACCA考试?
发布时间:2020-01-10
2020年已经到来,第一次ACCAer们对考试已经了解了多少了呢?一点也不了解也不用担心,51题库考试学习网帮助大家收集到了一些关于考试的高效学习技巧,希望对备考的你有多帮助,现在且随51题库考试学习网,告诉你怎有哪些技巧吧:
复习的首要任务是巩固和加深对所学知识的理解和记忆。首先,要根据教材的知识体系确定好一个中心内容,把主要精力集中在教材的中心、重点和难点上,不真正搞懂,决不放松。其次,要及时巩固,防止遗忘。复习最好在遗忘之前,倘若在遗忘之后,效率就低了。复习还要经常,不能一曝十寒。
对于一个新人而言,刚刚学ACCA,肯定都在想:我是报班呢还是报班呢?报班的话该选择什么样的辅导班?其次,如果自学的话有没有希望?
首先,明确一点,无论是否报班学习,最终决定成败的还是自己。
其次ACCA学习是一个由浅入深、由简到难的过程。对于学习能力好的大神来说,选择自学也是没有问题的!但是这个过程会耗时耗力,难抓住重点,如果有高顿经验丰富的老师身经百战总结出来的重要知识点,将会如虎添翼!
最后自学备考ACCA的过程重在坚持,但是大多数人都会被周围的事情分散注意力而导致备考意志力不够坚定,最后的结果也很失败。而报高顿ACCA面授课,除了有专业讲师系统性的讲解,针对性的答疑,能遇到许多志同道合的小伙伴,互相鼓励,互相监督,更有负责的学管团队全程及时提醒沟通,帮你克服意志力薄弱的问题,早日全科通关。
学习acca是否有必要参加辅导班
根据每个人的基础来判别,有些基础比较好的考生,简单的科目完全自学,难点科目自己看看网课就可以顺利通过了;基础一般的同学大部分科目需要借助网课的帮助来通过考试;基础较差的同学可能就需要面授课老师来帮忙了。不管哪个级别的考生,基本上是不太可能不借助任何辅导通过的。
基础较差的考生参加ACCA辅导班跟着老师学习,会轻松很多,也会节省很多时间,自己自学不知道重点,遇到知识点要弄很久才弄明白,比较费劲。
所以考生们可以根据自己的情况来安排辅导的力度哦。
具体的备考步骤分为以下四步:
第一步是拿2-3套ACCA真题,自己扫一遍所有的题干,可以不看题目,然后用这几套真题总结一下出题的套路和重点的知识点。ACCA的考试中重要的知识点一定是每年都出的,用这几套完全可以总结出重要知识点。当然如果真的基础不错,可以拿一套真题先做一下,然后你就有动力去进行后续的复习了。
第二步是看书,不过是先根据课本的目录,给自己梳理出来一个框架图,然后结合第一步的总结,所有的重点都一目了然。
第三步就是看书了,ACCA的教材一般会分为16-18个章节,一个章节如果完全投入进去阅读,两个小时完全可以搞明白。更何况最开始还整理出来了重点,那么复习详略得当,这个时间是足够的。还要注意一下就是每个章节如果真题中有考到这个章节的知识点,BPP的教材是会给出提示的,务必保证每个章节在学习完做一道题,总结答题思路。
最后一步是真题,一具体就要做的真题数目决定。51题库考试学习网建议大家有时间就尽量多做题,虽然题海战术不算什么高端的战术,但它却是最有用的。用来检测知识点是否掌握,如果是重要知识点没掌握,务必要回去复习了。
总结必考题的答题套路,就想F7/P2的合并报表,一定有它必备的一些步骤一样,这些必考题一定有每年都要做的相同部分。
完全的考前模拟,看看考试的时候如何安排时间比较合理。
以上就是关于备考ACCA考试的相关经验分享,你Get到了吗?俗话说,好的开始是成功的一半,大家要积极地认真地备考ACCA考试哦,要相信你所付出的一定会得到结果的~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Assess the benefits of the separation of the roles of chief executive and chairman that Alliya Yongvanich
argued for and explain her belief that ‘accountability to shareholders’ is increased by the separation of these
roles. (12 marks)
(b) Separation of the roles of CEO and chairman
Benefits of separation of roles
The separation of the roles of chief executive and chairman was first provided for in the UK by the 1992 Cadbury provisions
although it has been included in all codes since. Most relevant to the case is the terms of the ICGN clause s.11 and OECD
VI (E) both of which provide for the separation of these roles. In the UK it is covered in the combined code section A2.
The separation of roles offers the benefit that it frees up the chief executive to fully concentrate on the management of the
organisation without the necessity to report to shareholders or otherwise become distracted from his or her executive
responsibilities. The arrangement provides a position (that of chairman) that is expected to represent shareholders’ interests
and that is the point of contact into the company for shareholders. Some codes also require the chairman to represent the
interests of other stakeholders such as employees.
Having two people rather than one at the head of a large organisation removes the risks of ‘unfettered powers’ being
concentrated in a single individual and this is an important safeguard for investors concerned with excessive secrecy or
lack of transparency and accountability. The case of Robert Maxwell is a good illustration of a single dominating
executive chairman operating unchallenged and, in so doing, acting illegally. Having the two roles separated reduces
the risk of a conflict of interest in a single person being responsible for company performance whilst also reporting on
that performance to markets. Finally, the chairman provides a conduit for the concerns of non-executive directors who,
in turn, provide an important external representation of external concerns on boards of directors.
Tutorial note: Reference to codes other than the UK is also acceptable. In all cases, detailed (clause number) knowledge
of code provisions is not required.
Accountability and separation of roles
In terms of the separation of roles assisting in the accountability to shareholders, four points can be made.
The chairman scrutinises the chief executive’s management performance on behalf of the shareholders and will be
involved in approving the design of the chief executive’s reward package. It is the responsibility of the chairman to hold
the chief executive to account on shareholders’ behalfs.
Shareholders have an identified person (chairman) to hold accountable for the performance of their investment. Whilst
day-to-day contact will normally be with the investor relations department (or its equivalent) they can ultimately hold
the chairman to account.
The presence of a separate chairman ensures that a system is in place to ensure NEDs have a person to report to outside the
executive structure. This encourages the freedom of expression of NEDs to the chairman and this, in turn, enables issues to
be raised and acted upon when necessary.
The chairman is legally accountable and, in most cases, an experienced person. He/she can be independent and more
dispassionate because he or she is not intimately involved with day-to-day management issues.
(a) List and explain FOUR methods of selecting a sample of items to test from a population in accordance with ISA 530 (Redrafted) Audit Sampling and Other Means of Testing. (4 marks)
(b) List and explain FOUR assertions from ISA 500 Audit Evidence that relate to the recording of classes of
transactions. (4 marks)
(c) In terms of audit reports, explain the term ‘modified’. (2 marks)
(a)SamplingmethodsMethodsofsamplinginaccordancewithISA530AuditSamplingandOtherMeansofTesting:Randomselection.Ensureseachiteminapopulationhasanequalchanceofselection,forexamplebyusingrandomnumbertables.Systematicselection.Inwhichanumberofsamplingunitsinthepopulationisdividedbythesamplesizetogiveasamplinginterval.Haphazardselection.Theauditorselectsthesamplewithoutfollowingastructuredtechnique–theauditorwouldavoidanyconsciousbiasorpredictability.Sequenceorblock.Involvesselectingablock(s)ofcontinguousitemsfromwithinapopulation.Tutorialnote:Othermethodsofsamplingareasfollows:MonetaryUnitSampling.Thisselectionmethodensuresthateachindividual$1inthepopulationhasanequalchanceofbeingselected.Judgementalsampling.Selectingitemsbasedontheskillandjudgementoftheauditor.(b)Assertions–classesoftransactionsOccurrence.Thetransactionsandeventsthathavebeenrecordedhaveactuallyoccurredandpertaintotheentity.Completeness.Alltransactionsandeventsthatshouldhavebeenrecordedhavebeenrecorded.Accuracy.Theamountsandotherdatarelatingtorecordedtransactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedappropriately.Cut-off.Transactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedinthecorrectaccountingperiod.Classification.Transactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedintheproperaccounts.(c)AuditreporttermModified.Anauditormodifiesanauditreportinanysituationwhereitisinappropriatetoprovideanunmodifiedreport.Forexample,theauditormayprovideadditionalinformationinanemphasisofmatter(whichdoesnotaffecttheauditor’sopinion)orqualifytheauditreportforlimitationofscopeordisagreement.
1 Rowlands & Medeleev (R&M), a major listed European civil engineering company, was successful in its bid to become
principal (lead) contractor to build the Giant Dam Project in an East Asian country. The board of R&M prided itself in
observing the highest standards of corporate governance. R&M’s client, the government of the East Asian country, had
taken into account several factors in appointing the principal contractor including each bidder’s track record in large
civil engineering projects, the value of the bid and a statement, required from each bidder, on how it would deal with
the ‘sensitive issues’ and publicity that might arise as a result of the project.
The Giant Dam Project was seen as vital to the East Asian country’s economic development as it would provide a
large amount of hydroelectric power. This was seen as a ‘clean energy’ driver of future economic growth. The
government was keen to point out that because hydroelectric power did not involve the burning of fossil fuels, the
power would be environmentally clean and would contribute to the East Asian country’s ability to meet its
internationally agreed carbon emission targets. This, in turn, would contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gases
in the environment. Critics, such as the environmental pressure group ‘Stop-the-dam’, however, argued that the
project was far too large and the cost to the local environment would be unacceptable. Stop-the-dam was highly
organised and, according to press reports in Europe, was capable of disrupting progress on the dam by measures such
as creating ‘human barriers’ to the site and hiding people in tunnels who would have to be physically removed before
proceeding. A spokesman for Stop-the-dam said it would definitely be attempting to resist the Giant Dam Project when
construction started.
The project was intended to dam one of the region’s largest rivers, thus creating a massive lake behind it. The lake
would, the critics claimed, not only displace an estimated 100,000 people from their homes, but would also flood
productive farmland and destroy several rare plant and animal habitats. A number of important archaeological sites
would also be lost. The largest community to be relocated was the indigenous First Nation people who had lived on
and farmed the land for an estimated thousand years. A spokesman for the First Nation community said that the ‘true
price’ of hydroelectric power was ‘misery and cruelty’. A press report said that whilst the First Nation would be unlikely
to disrupt the building of the dam, it was highly likely that they would protest and also attempt to mobilise opinion in
other parts of the world against the Giant Dam Project.
The board of R&M was fully aware of the controversy when it submitted its tender to build the dam. The finance
director, Sally Grignard, had insisted on putting an amount into the tender for the management of ‘local risks’. Sally
was also responsible for the financing of the project for R&M. Although the client was expected to release money in
several ‘interim payments’ as the various parts of the project were completed to strict time deadlines, she anticipated
a number of working capital challenges for R&M, especially near the beginning where a number of early stage costs
would need to be incurred. There would, she explained, also be financing issues in managing the cash flows to R&M’s
many subcontractors. Although the major banks financed the client through a lending syndicate, R&M’s usual bank
said it was wary of lending directly to R&M for the Giant Dam Project because of the potential negative publicity that
might result. Another bank said it would provide R&M with its early stage working capital needs on the understanding
that its involvement in financing R&M to undertake the Giant Dam Project was not disclosed. A press statement from
Stop-the-dam said that it would do all it could to discover R&M’s financial lenders and publicly expose them. Sally
told the R&M board that some debt financing would be essential until the first interim payments from the client
became available.
When it was announced that R&M had won the contract to build the Giant Dam Project, some of its institutional
shareholders contacted Richard Markovnikoff, the chairman. They wanted reassurance that the company had fully
taken the environmental issues and other risks into account. One fund manager asked if Mr Markovnikoff could
explain the sustainability implications of the project to assess whether R&M shares were still suitable for his
environmentally sensitive clients. Mr Markovnikoff said, through the company’s investor relations department, that he
intended to give a statement at the next annual general meeting (AGM) that he hoped would address these
environmental concerns. He would also, he said, make a statement on the importance of confidentiality in the
financing of the early stage working capital needs.
(a) Any large project such as the Giant Dam Project has a number of stakeholders.
Required:
(i) Define the terms ‘stakeholder’ and ‘stakeholder claim’, and identify from the case FOUR of R&M’s
external stakeholders as it carries out the Giant Dam Project; (6 marks)
(a) (i) Stakeholders
A stakeholder can be defined as any person or group that can affect or be affected by an entity. In this case, stakeholders
are those that can affect or be affected by the building of the Giant Dam Project. Stakeholding is thus bi-directional.
Stakeholders can be those (voluntarily or involuntarily) affected by the activities of an organisation or the stakeholder
may be seeking to influence the organisation in some way.
All stakeholding is characterised by the making of ‘claims’ upon an organisation. Put simply, stakeholders ‘want
something’ although in some cases, the ‘want’ may not be known by the stakeholder (such as future generations). It is
the task of management to decide on the strengths of each stakeholder’s claim in formulating strategy and in making
decisions. In most situations it is likely that some stakeholder claims will be privileged over others.
R&M’s external stakeholders include:
– The client (the government of the East Asian country)
– Stop-the-dam pressure group
– First Nation (the indigenous people group)
– The banks that will be financing R&M’s initial working capital
– Shareholders
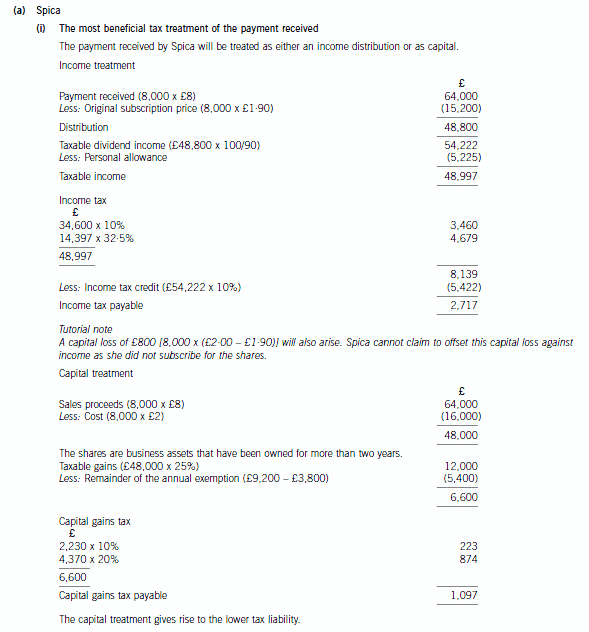
3 Spica, one of the director shareholders of Acrux Ltd, has been in dispute with the other shareholders over plans to
expand the company’s activities overseas. In order to resolve the position it has been agreed that Spica will sell her
shares back to the company. Once the purchase of her shares has taken place, the company intends to establish a
number of branches overseas and acquire a shareholding in a number of companies that are resident and trade in
overseas countries.
The following information has been obtained from client files and meetings with the parties involved.
Acrux Ltd:
– An unquoted UK resident company.
– Share capital consists of 50,000 ordinary shares issued at £1·90 per share in July 2000.
– None of the other shareholders has any connection with Spica.
The purchase of own shares:
– The company will purchase all of Spica’s shares for £8 per share.
– The transaction will take place by the end of 2008.
Spica:
– Purchased 8,000 shares in Acrux Ltd for £2 per share on 30 September 2003.
– Has no income in the tax year 2008/09.
– Has chargeable capital gains in the tax year 2008/09 of £3,800.
– Has houses in the UK and the country of Solaris and divides her time between them.
Investment in non-UK resident companies:
– Acrux Ltd will acquire between 15% and 20% of each of the non-UK resident companies.
– The companies will not be controlled foreign companies as the rates of tax in the overseas countries will be
between 23% and 42%.
– There may or may not be a double tax treaty between the UK and the overseas countries in which the companies
are resident. Where there is a treaty, it will be based on the OECD model treaty.
– None of the countries concerned levy withholding tax on dividends paid to UK companies.
– The directors of Acrux Ltd are concerned that the rate of tax suffered on the profits of the overseas companies
will be very high as they will be taxed in both the overseas country and in the UK.
Required:
(a) (i) Prepare detailed calculations to determine the most beneficial tax treatment of the payment Spica will
receive for her shares; (7 marks)
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-24
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-09-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-04-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-13
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-11-13
- 2020-02-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-26
- 2019-12-27
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-04-03
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-29