北京市考生注意:怎么才能避免ACCA考试失分?
发布时间:2020-01-10
51题库考试学习网结合了历年高分学霸们的心得体会后,得出了避免ACCA考试丢分7个小技巧,希望对备考的你有多帮助,现在51题库考试学习网就来告诉你怎样避免失分:
01填写信息,稳定情绪
试卷发下来后,立即忙于答题是不科学的,应先填写信息,写清姓名和准考证号等,这样做不仅是考试的要求,更是一剂稳定情绪的“良药”。等待自己的心情有所平静的时候,在慢慢地开始做题,尽快找到考试状态。
02总揽全卷,区别难易
打开试卷,看看哪些是基础题,哪些是中档题,哪些是难题或压轴题,按先易后难的原则,确定解题顺序,逐题进行解答。将低难度的题拿全分、中等难度的题不丢分、高难度的题尽可能多拿分。
力争做到“巧做低档题,题题全做对;稳做中档题,一分不浪费;尽力冲击高档题,做错也无悔。
03认真审题,灵活答题
审题要做到一不漏掉题,二不看错题,三要审准题,四要看全题目的条件和结论。
审题中还要灵活运用知识,发现和寻找简捷的解题方法。其实,所有的问题都是回归本质的知识点的。抓准知识要点即可,难题迎刃而解。
04过程清晰,稳中求快
一要书写清晰,速度略快;
二要一次成功;
三要提高答题速度;
四要科学使用草稿纸;
五要力求准确,防止欲速不达。
(当然这也是根据考生的能力而定的,总而言之准确率第一)
05心理状态,注意调节
考试中,要克服满不在乎的自负心理,要抛弃“胜败在此一举”的负重心理,要克服畏首畏尾的胆怯心理。面对难、中、易的试卷,调节好心理,积极应对。
(面对简单的题不骄傲放纵,以免马虎失分。面对十分困难的题不慌张焦急,将自己能解答的先上去,然后慢慢回忆背诵和复习的知识要点)
06尽量多做,分分必争
ACCA考试评分,多按步骤、按知识点给分、按要点给分毕竟ACCA考试费用不低。
通常来说,考试时间是不够的,因此,考生在答题时,就要会多少,答多少,哪怕是一条辅助线,一个符号,一小段文字,都可写上,没有把握也要敢于写,千万不要将不能完全做出或答案算不出的题放弃不做
07抓住“题眼”,构建“桥梁”
一般难题都有个关键点(称之为“题眼”),抓住了“题眼”,问题就易于解决了。
此外,还要利用相关的知识、规律、信息进行多方联系,构建“桥梁”,找出问题的内在联系,从而构思解题方案,准确、快捷地解决问题。
试纸飘墨香,金笔待启程。忍心为功名,墨汁污纸张。51题库考试学习网预祝参加3月ACCA考季的小伙伴取得好成绩哦~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Upwards; (3 marks)
(ii) Upwards communication is generally non-directive in nature and often takes two forms: personal problems or suggestions and/or technical feedback as part of the organisation’s control system.
(d) Additionally Router purchased 60% of the ordinary shares of a radio station, Playtime, a public limited company,
on 31 May 2007. The remaining 40% of the ordinary shares are owned by a competitor company who owns a
substantial number of warrants issued by Playtime which are currently exercisable. If these warrants are
exercised, they will result in Router only owning 35% of the voting shares of Playtime. (4 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
(d) IAS27 paragraph 14, ‘Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements’, states that warrants that have the potential to give
the holder voting power or reduce another party’s voting power over the financial and operating policies of the issuer should
be considered when existence of control is assessed. The warrants held by the competitor company, if exercised, would grant
that company control over Playtime. One party only can control Playtime and, therefore, the competitor company should
consolidate Playtime. In coming to this decision all the facts and circumstances that affect potential voting rights (except the
intention of management and the financial ability to exercise or convert) should be considered. It seems, however, that there
is a prima facie case for not consolidating Playtime but accounting for it under IAS28 or IAS39.
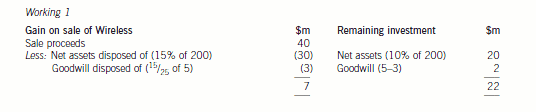
4 David Silvester is the founder and owner of a recently formed gift packaging company, Gift Designs Ltd. David has
spotted an opportunity for a new type of gift packaging. This uses a new process to make waterproof cardboard and
then shapes and cuts the card in such a way to produce a container or vase for holding cut flowers. The containers
can be stored flat and in bulk and then simply squeezed to create the flowerpot into which flowers and water are then
put. The potential market for the product is huge. In the UK hospitals alone there are 200,000 bunches of flowers
bought each year for patients. David’s innovative product does away with the need for hospitals to provide and store
glass vases. The paper vases are simple, safe and hygienic. He has also identified two other potential markets; firstly,
the market for fresh flowers supplied by florists and secondly, the corporate gift market where clients such as car
dealers present a new owner with an expensive bunch of flowers when the customer takes delivery of a new car. The
vase can be printed using a customer’s design and logo and creates an opportunity for real differentiation and impact
at sales conferences and other high profile PR events.
David anticipates a rapid growth in Gift Designs as its products become known and appreciated. The key question is
how quickly the company should grow and the types of funding needed to support its growth and development. The
initial financial demands of the business have been quite modest but David has estimated that the business needs
£500K to support its development over the next two years and is uncertain as to the types of funding best suited to
a new business as it looks to grow rapidly. He understands that business risk and financial risk is not the same thing
and is looking for advice on how he should organise the funding of the business. He is also aware of the need to avoid
reliance on friends and family for funding and to broaden the financial support for the business. Clearly the funding
required would also be affected by the activities David decides to carry out himself and those activities better provided
by external suppliers.
Required:
(a) Provide David with a short report on the key issues he should take into account when developing a strategy
for funding Gift Designs’ growth and development. (10 marks)
(a) To: David Silvester
From:
Funding strategy for Gift Designs Ltd
Clearly, you have identified a real business opportunity and face both business and financial risks in turning the opportunity
into reality. One possible model you can use is that of the product life cycle which as a one-product firm is effectively the life
cycle for the company. Linking business risk to financial risk is important – in the early stages of the business the business
risk is high and the high death rate amongst new start-ups is well publicised and, consequently, there is a need to go for low
financial risk. Funding the business is essentially deciding the balance between debt and equity finance, and equity offers the
low risk that you should be looking for. As the firm grows and develops so the balance between debt and equity will change.
A new business venture like this could in Boston Box terms be seen as a problem child with a non-existent market share but
high growth potential. The business risks are very high and consequently the financial risks taken should be very low and
avoid taking on large amounts of debt with a commitment to service the debt.
You need to take advantage of investors who are willing to accept the risks associated with a business start-up – venture
capitalists and business angels accept the risks associated with putting equity capital in but may expect a significant share
in the ownership of the business. This they will seek to realise once the business is successfully established. As the business
moves into growth and then maturity so the business risks will reduce and access to debt finance becomes feasible and cost
effective. In maturity the business should be able to generate significant retained earnings to finance further development.
Dividend policy will also be affected by the stage in the life cycle that the business has reached.
Yours,
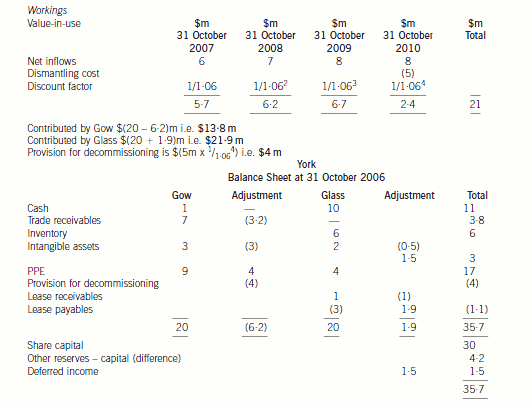
(b) Prepare the balance sheet of York at 31 October 2006, using International Financial Reporting Standards,
discussing the nature of the accounting treatments selected, the adjustments made and the values placed
on the items in the balance sheet. (20 marks)

Gow’s net assets
IAS36 ‘Impairment of Assets’, sets out the events that might indicate that an asset is impaired. These circumstances include
external events such as the decline in the market value of an asset and internal events such as a reduction in the cash flows
to be generated from an asset or cash generating unit. The loss of the only customer of a cash generating unit (power station)
would be an indication of the possible impairment of the cash generating unit. Therefore, the power station will have to be
impairment tested.
The recoverable amount will have to be determined and compared to the value given to the asset on the setting up of the
joint venture. The recoverable amount is the higher of the cash generating unit’s fair value less costs to sell, and its value-inuse.
The fair value less costs to sell will be $15 million which is the offer for the purchase of the power station ($16 million)
less the costs to sell ($1 million). The value-in-use is the discounted value of the future cash flows expected to arise from the
cash generating unit. The future dismantling costs should be provided for as it has been agreed with the government that it
will be dismantled. The cost should be included in the future cash flows for the purpose of calculating value-in-use and
provided for in the financial statements and the cost added to the property, plant and equipment ($4 million ($5m/1·064)).
The value-in-use based on a discount rate of 6 per cent is $21 million (working). Therefore, the recoverable amount is
$21 million which is higher than the carrying value of the cash generating unit ($20 million) and, therefore, the value of the
cash generating unit is not impaired when compared to the present carrying value of $20 million (value before impairment
test).
Additionally IAS39, ‘Financial Instruments: recognition and measurement’, says that an entity must assess at each balance
sheet date whether a financial asset is impaired. In this case the receivable of $7 million is likely to be impaired as Race is
going into administration. The present value of the estimated future cash flows will be calculated. Normally cash receipts from
trade receivables will not be discounted but because the amounts are not likely to be received for a year then the anticipated
cash payment is 80% of ($5 million × 1/1·06), i.e. $3·8 million. Thus a provision for the impairment of the trade receivables
of $3·2 million should be made. The intangible asset of $3 million would be valueless as the contract has been terminated.
Glass’s Net Assets
The leased property continues to be accounted for as property, plant and equipment and the carrying amount will not be
adjusted. However, the remaining useful life of the property will be revised to reflect the shorter term. Thus the property will
be depreciated at $2 million per annum over the next two years. The change to the depreciation period is applied prospectively
not retrospectively. The lease liability must be assessed under IAS39 in order to determine whether it constitutes a
de-recognition of a financial liability. As the change is a modification of the lease and not an extinguishment, the lease liability
would not be derecognised. The lease liability will be adjusted for the one off payment of $1 million and re-measured to the
present value of the revised future cash flows. That is $0·6 million/1·07 + $0·6 million/(1·07 × 1·07) i.e. $1·1 million. The
adjustment to the lease liability would normally be recognised in profit or loss but in this case it will affect the net capital
contributed by Glass.
The termination cost of the contract cannot be treated as an intangible asset. It is similar to redundancy costs paid to terminate
a contract of employment. It represents compensation for the loss of future income for the agency. Therefore it must be
removed from the balance sheet of York. The recognition criteria for an intangible asset require that there should be probable
future economic benefits flowing to York and the cost can be measured reliably. The latter criterion is met but the first criterion
is not. The cost of gaining future customers is not linked to this compensation.
IAS18 ‘Revenue’ contains a concept of a ‘multiple element’ arrangement. This is a contract which contains two or more
elements which are in substance separate and are separately identifiable. In other words, the two elements can operate
independently from each other. In this case, the contract with the overseas company has two distinct elements. There is a
contract not to supply gas to any other customer in the country and there is a contract to sell gas at fair value to the overseas
company. The contract has not been fulfilled as yet and therefore the payment of $1·5 million should not be taken to profit
or loss in its entirety at the first opportunity. The non supply of gas to customers in that country occurs over the four year
period of the contract and therefore the payment should be recognised over that period. Therefore the amount should be
shown as deferred income and not as a deduction from intangible assets. The revenue on the sale of gas will be recognised
as normal according to IAS18.
There may be an issue over the value of the net assets being contributed. The net assets contributed by Glass amount to
$21·9 million whereas those contributed by Gow only total $13·8 million after taking into account any adjustments required
by IFRS. The joint venturers have equal shareholding in York but no formal written agreements, thus problems may arise ifGlass feels that the contributions to the joint venture are unequal.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-28