江西省考生注意:怎么才能避免ACCA考试失分?
发布时间:2020-01-10
51题库考试学习网结合了历年高分学霸们的心得体会后,得出了避免ACCA考试丢分7个小技巧,希望对备考的你有多帮助,现在51题库考试学习网就来告诉你怎样避免失分:
01填写信息,稳定情绪
试卷发下来后,立即忙于答题是不科学的,应先填写信息,写清姓名和准考证号等,这样做不仅是考试的要求,更是一剂稳定情绪的“良药”。等待自己的心情有所平静的时候,在慢慢地开始做题,尽快找到考试状态。
02总揽全卷,区别难易
打开试卷,看看哪些是基础题,哪些是中档题,哪些是难题或压轴题,按先易后难的原则,确定解题顺序,逐题进行解答。将低难度的题拿全分、中等难度的题不丢分、高难度的题尽可能多拿分。
力争做到“巧做低档题,题题全做对;稳做中档题,一分不浪费;尽力冲击高档题,做错也无悔。
03认真审题,灵活答题
审题要做到一不漏掉题,二不看错题,三要审准题,四要看全题目的条件和结论。
审题中还要灵活运用知识,发现和寻找简捷的解题方法。其实,所有的问题都是回归本质的知识点的。抓准知识要点即可,难题迎刃而解。
04过程清晰,稳中求快
一要书写清晰,速度略快;
二要一次成功;
三要提高答题速度;
四要科学使用草稿纸;
五要力求准确,防止欲速不达。
(当然这也是根据考生的能力而定的,总而言之准确率第一)
05心理状态,注意调节
考试中,要克服满不在乎的自负心理,要抛弃“胜败在此一举”的负重心理,要克服畏首畏尾的胆怯心理。面对难、中、易的试卷,调节好心理,积极应对。
(面对简单的题不骄傲放纵,以免马虎失分。面对十分困难的题不慌张焦急,将自己能解答的先上去,然后慢慢回忆背诵和复习的知识要点)
06尽量多做,分分必争
ACCA考试评分,多按步骤、按知识点给分、按要点给分毕竟ACCA考试费用不低。
通常来说,考试时间是不够的,因此,考生在答题时,就要会多少,答多少,哪怕是一条辅助线,一个符号,一小段文字,都可写上,没有把握也要敢于写,千万不要将不能完全做出或答案算不出的题放弃不做
07抓住“题眼”,构建“桥梁”
一般难题都有个关键点(称之为“题眼”),抓住了“题眼”,问题就易于解决了。
此外,还要利用相关的知识、规律、信息进行多方联系,构建“桥梁”,找出问题的内在联系,从而构思解题方案,准确、快捷地解决问题。
试纸飘墨香,金笔待启程。忍心为功名,墨汁污纸张。51题库考试学习网预祝参加3月ACCA考季的小伙伴取得好成绩哦~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Critically discuss the adoption of activity-based management (ABM) in companies such as TOC. (6 marks)
(c) Activity-based management (ABM) is a method of identifying and evaluating activities that a business performs using
activity-based costing to carry out a value chain analysis or a re-engineering initiative to improve strategic and operational
decisions in an organisation. Activity-based costing establishes relationships between overhead costs and activities so that
overhead costs can be more precisely allocated to products, services, or customer segments. Activity-based management
focuses on managing activities to reduce costs and improve customer value.
Kaplan and Cooper (1998) divide ABM into operational ABM and strategic ABM:
Operational ABM is about ‘doing things right’, using ABC information to improve efficiency. Those activities which add value
to the product can be identified and improved. Activities that don’t add value are the ones that need to be reduced to cut costs
without reducing product value.
Strategic ABM is about ‘doing the right things’, using ABC information to decide which products to develop and which
activities to use. This can also be used for customer profitability analysis, identifying which customers are the most profitable
and focusing on them more.
A risk with ABM is that some activities have an implicit value, not necessarily reflected in a financial value added to any
product. For instance a particularly pleasant workplace can help attract and retain the best staff, but may not be identified as
adding value in operational ABM. A customer that represents a loss based on committed activities, but that opens up leads
in a new market, may be identified as a low value customer by a strategic ABM process.
ABM can give middle managers an understanding of costs to other teams to help them make decisions that benefit the whole
organisation, not just their activities’ bottom line.
(b) Discuss the key issues which the statement of cash flows highlights regarding the cash flow of the company.
(10 marks)
(b) Financial statement ratios can provide useful measures of liquidity but an analysis of the information in the cash flow
statement, particularly cash flow generated from operations, can provide specific insights into the liquidity of Warrburt. It is
important to look at the generation of cash and its efficient usage. An entity must generate cash from trading activity in order
to avoid the constant raising of funds from non-trading sources. The ‘quality of the profits’ is a measure of an entity’s ability
to do this. The statement of cash flow shows that the company has generated cash in the period despite sustaining a
significant loss ($92m cash flow but $21m loss). The problem is the fact that the entity will not be able to sustain this level
of cash generation if losses continue.
An important measure of cash flow is the comparison of the cash from operating activity to current liabilities. In the case of
Warrburt, this is $92m as compared to $155m. Thus the cash flow has not covered the current liabilities.
Operating cash flow ($92 million) determines the extent to which Warrburt has generated sufficient funds to repay loans,
maintain operating capability, pay dividends and make new investments without external financing. Operating cash flow
appears to be healthy, partially through the release of cash from working capital. This cash flow has been used to pay
contributions to the pension scheme, pay finance costs and income taxes. These uses of cash generated would be normal for
any entity. However, the release of working capital has also financed in part the investing activities of the entity which includes
the purchase of an associate and property, plant and equipment. The investing activities show a net cash outflow of
$43 million which has been financed partly out of working capital, partly from the sale of PPE and AFS financial assets and
partly out of cash generated from operations which include changes in working capital. It seems also that the issue of share
capital has been utilised to repay the long term borrowings and pay dividends. Also a significant amount of cash has been
raised through selling AFS investments. This may not continue in the future as it will depend on the liquidity of the market.
This action seems to indicate that the long term borrowings have effectively been ‘capitalised’. The main issue raised by the
cash flow statement is the use of working capital to partially finance investing activities. However, the working capital ratio
and liquidity ratios are still quite healthy but these ratios will deteriorate if the trend continues.
(ii) Explain THREE strategies that might be adopted in order to improve the future prospects of Diverse
Holdings Plc. (6 marks)
(ii) The forecast situation of Diverse Holdings Plc is not without its problems. KAL and OPL require the immediate attention
of management. The position of KAL is precarious to say the least. There is a choice of strategies for it:
(i) Outsource the manufacture of appliances
(ii) Set up a manufacturing operation overseas
(ii) Withdraw from the market.
Each alternative must be assessed. Whatever decision is taken it is unlikely to affect the other four subsidiaries.
PSL is also independent of the other subsidiaries. A strategic decision to widen its range of products and outlets must
surely help. Hence management should endeavour to find new markets for its products, which are separate and distinct
from those markets served by its appointed distributors.
21
In order to improve the prospects of OPL management need to adopt appropriate strategies since at the present time the
company appears to be in a high growth market but is unable to capture a reasonable market share. Perhaps the answer
lies in increased or more effective advertising of the endorsement of the product range by health and safety experts.
Management should endeavour to develop a strategy to integrate further its subsidiaries so that they can benefit from
each other and also derive as much synergy as possible from the acquisition of HTL.
It is of paramount importance that management ensure that sufficient funds are channelled into growing OFL and HTL,
which are both showing a rising trend in profitability. The group has depleted cash reserves which must to some extent
be attributable to the purchase of HTL. It is possible that the divestment of KAL would provide some much needed
funding.
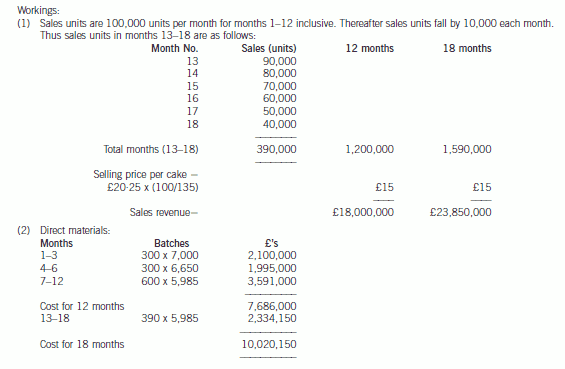
1 The Great Western Cake Company (GWCC) is a well-established manufacturer of specialist flour confectionery
products, including cakes. GWCC sells its products to national supermarket chains. The company’s success during
recent years is largely attributable to its ability to develop innovative products which appeal to the food selectors within
national supermarket chains.
The marketing department of Superstores plc, a national supermarket chain has asked GWCC to manufacture a cake
known as the ‘Mighty Ben’. Mighty Ben is a character who has recently appeared in a film which was broadcast
around the world. The cake is expected to have a minimum market life of one year although the marketing department
consider that this might extend to eighteen months.
The management accountant of GWCC has collated the following estimated information in respect of the Mighty Ben
cake:
(1) Superstores plc has decided on a launch price of £20·25 for the Mighty Ben cake and it is expected that this
price will be maintained for the duration of the product’s life. Superstores plc will apply a 35% mark-up on the
purchase price of each cake from GWCC.
(2) Sales of the Mighty Ben cake are expected to be 100,000 units per month during the first twelve months.
Thereafter sales of the Mighty Ben cake are expected to decrease by 10,000 units in each subsequent month.
(3) Due to the relatively short shelf-life of the Mighty Ben cake, management has decided to manufacture the cakes
on a ‘just-in-time’ basis for delivery in accordance with agreed schedules. The cakes will be manufactured in
batches of 1,000. Direct materials input into the baking process will cost £7,000 per batch for each of the first
three months’ production. The material cost of the next three months’ production is expected to be 95% of the
cost of the first three months’ production. All batches manufactured thereafter will cost 90% of the cost of the
second three months’ production.
(4) Packaging costs will amount to £0·75 per cake. The original costs of the artwork and design of the packaging
will amount to £24,000. Superstores plc will reimburse GWCC £8,000 in the event that the product is
withdrawn from sale after twelve months.
(5) The design of the Mighty Ben cake is such that it is required to be hand-finished. A 75% learning curve will
apply to the total labour time requirement until the end of month five. Thereafter a steady state will apply with
labour time required per batch stabilising at that of the final batch in month five. The labour requirement for the
first batch of Mighty Ben cakes to be manufactured is expected to be 6,000 hours at £10 per hour.
(6) A royalty of 5% of sales revenue (subject to a maximum royalty of £1·1 million) will be payable by GWCC to the
owners of the Mighty Ben copyright.
(7) Variable overheads are estimated at £3·50 per direct labour hour.
(8) The manufacture of the Mighty Ben cake will increase fixed overheads by £75,000 per month.
(9) In order to provide a production facility dedicated to the Mighty Ben cake, an investment of £1,900,000 will be
required and this will be fully depreciated over twelve months.
(10) The directors of GWCC require an average annual return of 35% on their investment over 12 months and
18 months.
(11) Ignore taxation and the present value of cash flows.
Note: Learning curve formula:
y = axb
where y = average cost per batch
a = the cost of the initial batch
x = the total number of batches
b = learning index (= –0·415 for 75% learning rate)
Required:
(a) Prepare detailed calculations to show whether the manufacture of Mighty Ben cakes will provide the required
rate of return for GWCC over periods of twelve months and eighteen months. (20 marks)


声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-04-24
- 2020-05-14
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-11
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-04-23
- 2019-04-10
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-06
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-04-01