速来看看ACCA会员的薪资福利,以及他们的职业发展状况吧!
发布时间:2020-04-01
关于ACCA,很多人都担心好不容易考下来却没有什么用,今天就跟随51题库考试学习网来看看ACCA会员的薪资福利,以及他们的职业发展状况吧。
ACCA会员福利、薪资待遇
据官方的调查显示,ACCA会员的年薪集中在10万至80万之间,部分会员的年薪更是达到了100万到150万,远高于市场上普通财务人员的收入,并超过研究生以及MBA毕业生的平均年收入。此外,ACCA会员们的加薪的空间也很大,已有数据显示,有63%的ACCA学员与准会员在工作一到二年获得加薪,其中,更有超过三分之二人数加薪幅度在6%以上。
ACCA会员发展状况
ACCA会员资格在国际上受到广泛认可,全球有超过7,500家“认可雇主企业”,其中更是有包括四大会计师事务所、联合利华、飞利浦、中国银行、阿里巴巴等等各行业的领军企业。因此大部分会员都在政府机构、大型跨国企业、著名会计师事务所、咨询公司以及证券金融企业担当着重要职务。那么,报考ACCA自然也会为我们在入职国内外大型企业时提供拥有无比巨大的发展机遇和竞争优势。
通过ACCA可以得到哪些提升
ACCA是特许公认会计师是当今社会上学员最多、学员规模发展最快的专业会计师资格。联合国通过了以ACCA课程大纲作为世界各地职业会计师考试课程设置的衡量基准,ACCA资格成了"国际财会界的通行证",并得到了欧盟及许多国家的立法许可。
ACCA以培养国际性的高级会计、财务管理专家著称,其高质量的课程设计,高标准的考试要求,不仅赢得了联合国和各大国际性组织的高度评价,更为众多跨国公司和专业机构所推崇。ACCA的课程设置使学员能全面掌握财务、审计、税务、管理及经营战略等方面的专业知识,其课程内容丰富,各课程之间联系紧密且其难度阶梯设置合理,使学员能在循序渐进的学习过程中,稳固基础知识的同时,不断提升自己的分析能力和战略思维,向企业高层和管理层的道路上迈进。可以说参加ACCA课程学习,不但可以让学员充分地掌握专业的会计技能,更能学到更多的高级财务管理知识,帮助他们更好地胜任高级财务管理者岗位。
ACCA的课程体系是根据市场对人才的需求点来设计和开发的,特别注重培养学员的分析能力和在复杂条件下的决策、判断能力,使得学员学成后能适应各种商业环境。通过对ACCA课程的学习使学员不仅拥有系统的专业理论知识,还能拥有相对成熟的实践操作能力,这也让众多企业对具有ACCA证书资格的求职者更加青睐。
好的,以上就是今天51题库考试学习网为大家分享的全部内容,大家是否清楚了呢?如想了解更多关于ACCA的内容,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Explain the matters that should be considered when planning the nature and scope of the examination of
Cusiter Co’s forecast balance sheet and income statement as prepared for the bank. (7 marks)
(b) Matters to be considered
Tutorial note: Candidates at this level must appreciate that the matters to be considered when planning the nature and
scope of the examination are not the same matters to be considered when deciding whether or not to accept an
engagement. The scenario clearly indicates that the assignment is being undertaken by the current auditor rendering any
‘pre-engagement’/‘professional etiquette’ considerations irrelevant to answering this question.
This PFI has been prepared to show an external user, the bank, the financial consequences of Cusiter’s plans to help the bank
in making an investment decision. If Cusiter is successful in its loan application the PFI provides a management tool against
which the results of investing in the plant and equipment can be measured.
The PFI is unpublished rather than published. That is, it is prepared at the specific request of a third party, the bank. It will
not be published to users of financial information in general.
The auditor’s report on the PFI will provide only negative assurance as to whether the assumptions provide a reasonable basis
for the PFI and an opinion whether the PFI is:
■ properly prepared on the basis of the assumptions; and
■ presented in accordance with the relevant financial reporting framework.
The nature of the engagement is an examination to obtain evidence concerning:
■ the reasonableness and consistency of assumptions made;
■ proper preparation (on the basis of stated assumptions); and
■ consistent presentation (with historical financial statements, using appropriate accounting principles).
Such an examination is likely to take the form. of inquiry, analytical procedures and corroboration.
The period of time covered by the prospective financial information is two years. The assumptions for 2008 are likely to be
more speculative than for 2007, particularly in relation to the impact on earnings, etc of the investment in new plant and
equipment.
The forecast for the year to 31 December 2007 includes an element of historical financial information (because only part of
this period is in the future) hence actual evidence should be available to verify the first three months of the forecast (possibly
more since another three-month period will expire at the end of the month).
Cusiter management’s previous experience in preparing PFI will be relevant. For example, in making accounting estimates
(e.g. for provisions, impairment losses, etc) or preparing cash flow forecasts (e.g. in support of the going concern assertion).
The basis of preparation of the forecast. For example, the extent to which it comprises:
■ proforma financial information (i.e. historical financial information adjusted for the effects of the planned loan and capital
expenditure transaction);
■ new information and assumptions about future performance (e.g. the operating capacity of the new equipment, sales
generated, etc).
The nature and scope of any standards/guidelines under which the PFI has been prepared is likely to assist the auditor in
discharging their responsibilities to report on it. Also, ISAE 3400 The Examination of Prospective Financial Information,
establishes standards and provides guidance on engagements to examine and report on PFI including examination
procedures.
The planned nature and scope of the examination is likely to take into account the time and fee budgets for the assignments
as adjusted for any ‘overlap’ with audit work. For example, the examination of the PFI is likely to draw on the auditor’s
knowledge of the business obtained in auditing the financial statements to 31 December 2006. Analytical procedures carried
out in respect of the PFI may provide evidence relevant to the 31 December 2007 audit.
Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the following
situations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:
(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject to a two
year vesting period. Local tax law allows a tax deduction at the exercise date of the intrinsic value of the options.
The intrinsic value of the ten million share options at 31 October 2004 was $16 million and at 31 October 2005
was $46 million. The increase in the share price in the year to 31 October 2005 could not be foreseen at
31 October 2004. The options were exercised at 31 October 2005. The directors are unsure how to account
for deferred taxation on this transaction for the years ended 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005.
(ii) Panel is leasing plant under a finance lease over a five year period. The asset was recorded at the present value
of the minimum lease payments of $12 million at the inception of the lease which was 1 November 2004. The
asset is depreciated on a straight line basis over the five years and has no residual value. The annual lease
payments are $3 million payable in arrears on 31 October and the effective interest rate is 8% per annum. The
directors have not leased an asset under a finance lease before and are unsure as to its treatment for deferred
taxation. The company can claim a tax deduction for the annual rental payment as the finance lease does not
qualify for tax relief.
(iii) A wholly owned overseas subsidiary, Pins, a limited liability company, sold goods costing $7 million to Panel on
1 September 2005, and these goods had not been sold by Panel before the year end. Panel had paid $9 million
for these goods. The directors do not understand how this transaction should be dealt with in the financial
statements of the subsidiary and the group for taxation purposes. Pins pays tax locally at 30%.
(iv) Nails, a limited liability company, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Panel, and is a cash generating unit in its own
right. The value of the property, plant and equipment of Nails at 31 October 2005 was $6 million and purchased
goodwill was $1 million before any impairment loss. The company had no other assets or liabilities. An
impairment loss of $1·8 million had occurred at 31 October 2005. The tax base of the property, plant and
equipment of Nails was $4 million as at 31 October 2005. The directors wish to know how the impairment loss
will affect the deferred tax provision for the year. Impairment losses are not an allowable expense for taxation
purposes.
Assume a tax rate of 30%.
Required:
(b) Discuss, with suitable computations, how the situations (i) to (iv) above will impact on the accounting for
deferred tax under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’ in the group financial statements of Panel. (16 marks)
(The situations in (i) to (iv) above carry equal marks)
(b) (i) The tax deduction is based on the option’s intrinsic value which is the difference between the market price and exercise
price of the share option. It is likely that a deferred tax asset will arise which represents the difference between the tax
base of the employee’s service received to date and the carrying amount which will effectively normally be zero.
The recognition of the deferred tax asset should be dealt with on the following basis:
(a) if the estimated or actual tax deduction is less than or equal to the cumulative recognised expense then the
associated tax benefits are recognised in the income statement
(b) if the estimated or actual tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recognised compensation expense then the excess
tax benefits are recognised directly in a separate component of equity.
As regards the tax effects of the share options, in the year to 31 October 2004, the tax effect of the remuneration expensewill be in excess of the tax benefit.
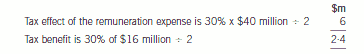
The company will have to estimate the amount of the tax benefit as it is based on the share price at 31 October 2005.
The information available at 31 October 2004 indicates a tax benefit based on an intrinsic value of $16 million.
As a result, the tax benefit of $2·4 million will be recognised within the deferred tax provision. At 31 October 2005,
the options have been exercised. Tax receivable will be 30% x $46 million i.e. $13·8 million. The deferred tax asset
of $2·4 million is no longer recognised as the tax benefit has crystallised at the date when the options were exercised.
For a tax benefit to be recognised in the year to 31 October 2004, the provisions of IAS12 should be complied with as
regards the recognition of a deferred tax asset.
(ii) Plant acquired under a finance lease will be recorded as property, plant and equipment and a corresponding liability for
the obligation to pay future rentals. Rents payable are apportioned between the finance charge and a reduction of the
outstanding obligation. A temporary difference will effectively arise between the value of the plant for accounting
purposes and the equivalent of the outstanding obligation as the annual rental payments qualify for tax relief. The tax
base of the asset is the amount deductible for tax in future which is zero. The tax base of the liability is the carrying
amount less any future tax deductible amounts which will give a tax base of zero. Thus the net temporary differencewill be:
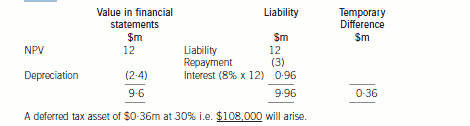
(iii) The subsidiary, Pins, has made a profit of $2 million on the transaction with Panel. These goods are held in inventory
at the year end and a consolidation adjustment of an equivalent amount will be made against profit and inventory. Pins
will have provided for the tax on this profit as part of its current tax liability. This tax will need to be eliminated at the
group level and this will be done by recognising a deferred tax asset of $2 million x 30%, i.e. $600,000. Thus any
consolidation adjustments that have the effect of deferring or accelerating tax when viewed from a group perspective will
be accounted for as part of the deferred tax provision. Group profit will be different to the sum of the profits of the
individual group companies. Tax is normally payable on the profits of the individual companies. Thus there is a need
to account for this temporary difference. IAS12 does not specifically address the issue of which tax rate should be used
calculate the deferred tax provision. IAS12 does generally say that regard should be had to the expected recovery or
settlement of the tax. This would be generally consistent with using the rate applicable to the transferee company (Panel)
rather than the transferor (Pins).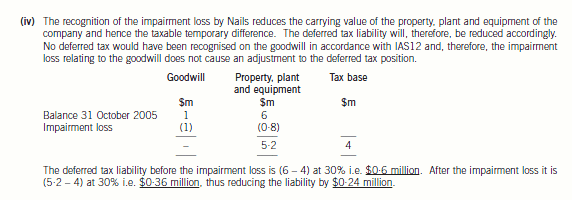
(ii) Explain, with reasons, the relief available in respect of the fall in value of the shares in All Over plc,
identify the years in which it can be claimed and state the time limit for submitting the claim.
(3 marks)

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-05-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-04-17
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09